
Which of the following statements is not true about sucrose?
A) On hydrolysis, it produces glucose and fructose.
B) The glycosidic linkage is present between $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ of $\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ -glucose and $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ of $\text{ }\beta \text{-}$ - fructose.
C) It is also named as invert sugar.
D) It is a non-reducing sugar.
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Sucrose is a disaccharide of glucose and fructose. On hydrolysis, the glycosidic linkage ruptures to generate the optical isomers of glucose and fructose. $\text{ }\begin{matrix}
{{\text{C}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{11}}} & \text{+} & {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} & \xrightarrow{\text{HCl}} & {{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} & \text{+} & {{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} \\
\text{(Sucrose)} & {} & {} & {} & \text{(D-Glucose)} & {} & \text{(D-Fructose)} \\
\end{matrix}$
-On hydrolysis, the specific rotation of the sucrose is changed from Dextro to laevo. The sucrose does not have the free aldehyde or carboxylic group to undergo the reduction.
Complete step by step answer:
-Sucrose is a common disaccharide and it is widely distributed in the plants particularly sugar cane and sugar beet. Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of two monosaccharides glucose and fructose. It is a $\text{ 1:1 }$ mixture of glucose and fructose. The glucose and fructose are joined together by the glycosidic bond.
-The glucose and fructose are linked by the acetal oxygen bridge $\text{ }-\text{O}-\text{ }$ . This bride links the carbon at 1 position of the $\text{ }\alpha \text{ }$glucose to the carbon of the 2 positions of the $\text{ }\beta \text{ }$fructose.
-On hydrolysis, the sucrose breaks down in to give the dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory
fructose.
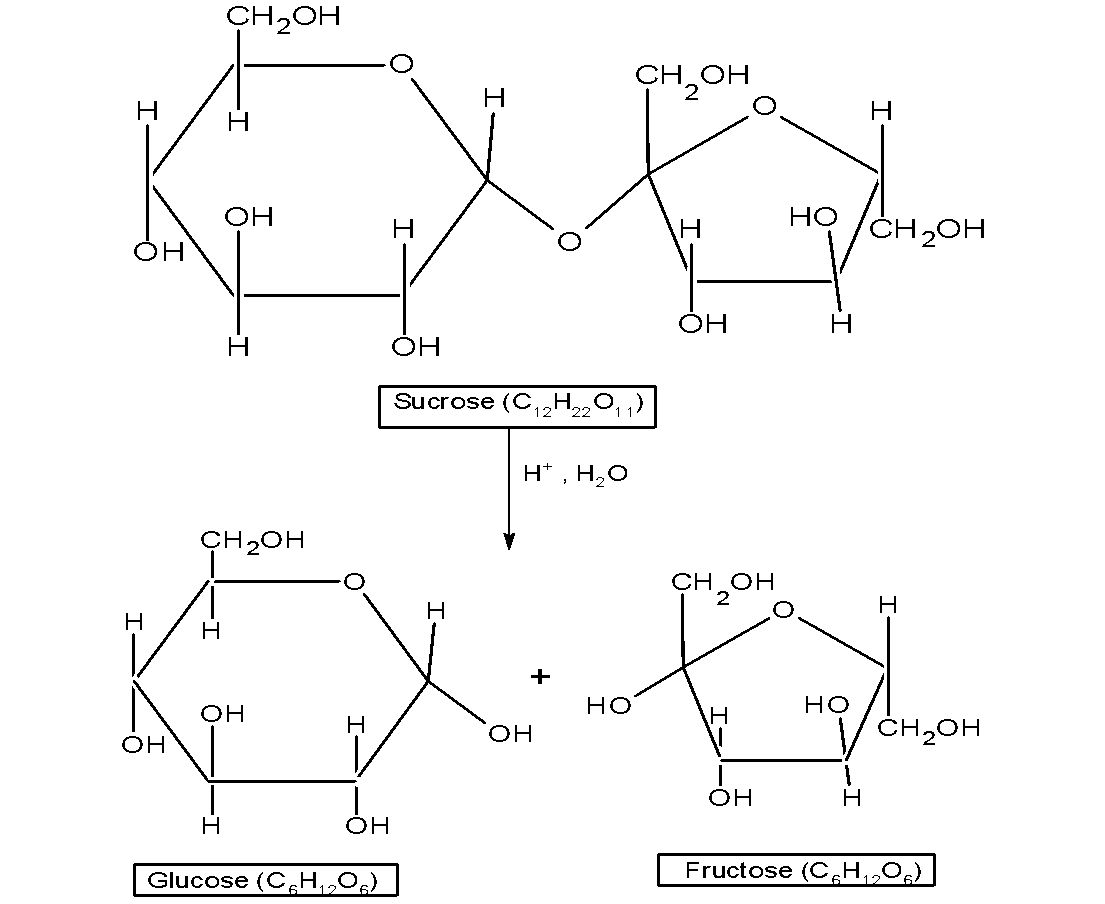
-The dextrorotation of the glucose is $\text{ }+52.5{}^\circ \text{ }$ and the laevorotation of the fructose is by $\text{ -90}\text{.4}{}^\circ \text{ }$. That is the optical isomer of the glucose and fructose changes after the hydrolysis reaction.
-In hydrolysis, the sign of the sucrose changes from Dextro to the leavo thus the reaction is an inversion reaction and the mixture (glucose and fructose) is called the invert sugar.
-The saccharide which does not reduce the Fehling’s solution or tollen’s reagent is called the non –reducing sugars. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because the reducing groups (i.e. free $\,-\text{CHO }$ or $\text{ }-\text{CO}-\text{ }$ of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation.
-Thus, the glycosidic linkage is present between $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ of $\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ -glucose and $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ of $\text{ }\beta \text{-}$ - fructose is an incorrect statement.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar and is not readily oxidized as reducing sugar. Therefore, it is much more useful for preserving foods such as jams and jellies. A reducing sugar like glucose would oxidize and spoil the food.
{{\text{C}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{11}}} & \text{+} & {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O} & \xrightarrow{\text{HCl}} & {{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} & \text{+} & {{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{12}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}} \\
\text{(Sucrose)} & {} & {} & {} & \text{(D-Glucose)} & {} & \text{(D-Fructose)} \\
\end{matrix}$
-On hydrolysis, the specific rotation of the sucrose is changed from Dextro to laevo. The sucrose does not have the free aldehyde or carboxylic group to undergo the reduction.
Complete step by step answer:
-Sucrose is a common disaccharide and it is widely distributed in the plants particularly sugar cane and sugar beet. Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of two monosaccharides glucose and fructose. It is a $\text{ 1:1 }$ mixture of glucose and fructose. The glucose and fructose are joined together by the glycosidic bond.
-The glucose and fructose are linked by the acetal oxygen bridge $\text{ }-\text{O}-\text{ }$ . This bride links the carbon at 1 position of the $\text{ }\alpha \text{ }$glucose to the carbon of the 2 positions of the $\text{ }\beta \text{ }$fructose.
-On hydrolysis, the sucrose breaks down in to give the dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory
fructose.

-The dextrorotation of the glucose is $\text{ }+52.5{}^\circ \text{ }$ and the laevorotation of the fructose is by $\text{ -90}\text{.4}{}^\circ \text{ }$. That is the optical isomer of the glucose and fructose changes after the hydrolysis reaction.
-In hydrolysis, the sign of the sucrose changes from Dextro to the leavo thus the reaction is an inversion reaction and the mixture (glucose and fructose) is called the invert sugar.
-The saccharide which does not reduce the Fehling’s solution or tollen’s reagent is called the non –reducing sugars. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because the reducing groups (i.e. free $\,-\text{CHO }$ or $\text{ }-\text{CO}-\text{ }$ of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation.
-Thus, the glycosidic linkage is present between $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ of $\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ -glucose and $\text{ }{{\text{C}}_{\text{1}}}\text{ }$ of $\text{ }\beta \text{-}$ - fructose is an incorrect statement.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar and is not readily oxidized as reducing sugar. Therefore, it is much more useful for preserving foods such as jams and jellies. A reducing sugar like glucose would oxidize and spoil the food.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




