
Which of the following represents the magnetic field due to a straight conductor of uniform cross section of radius ‘a’ and carrying a steady current?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Use ampere’s law to obtain magnetic fields inside and outside the straight conductor. The variation of magnetic field with respect to its distance from the axis of conductor can be analysed from the expression.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume that the steady current flowing through the straight conductor is ‘I’. Then, according to ampere’s circuital law magnetic field density along an imaginary circular path around the conductor at perpendicular distance ‘r’ from the axis of the straight conductor is
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2\pi r}$
This relation is valid only for circles of radius $r\ge a$.
To derive relation for $r\le a$ we assume that the uniform current density in the conductor is $J$. Then,
$J=\dfrac{I}{\pi {{a}^{2}}}$
Since, J is constant, the current flowing through a circular cross-section of radius ‘r’ is
$I=J\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Where $a$ is the radius of the cross section. Then, according to ampere’s circuital law magnetic field density inside the conductor along an imaginary circular path around the conductor at perpendicular distance ‘r’ from the axis of the straight conductor is
$B=\dfrac{\mu I}{2\pi r}=\dfrac{\mu J\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2\pi r}=\dfrac{\mu Jr}{2}$
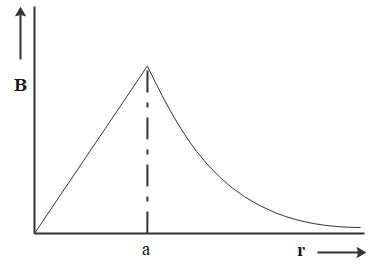
From the above equation, we can note that the magnetic field inside the conductor is directly proportional to its distance from the axis. We also observed that for a radius of imaginary circular path greater than the radius of cross-section of conductor, the magnetic field intensity is inversely proportional. This corresponds to option A.
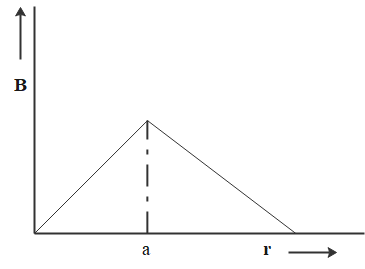
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Magnetic field intensity due to a current carrying conductor is linearly proportional to its distance from its axis inside the conductor. But for distances lying outside the conductor, the magnetic field density is inversely proportional to the same.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume that the steady current flowing through the straight conductor is ‘I’. Then, according to ampere’s circuital law magnetic field density along an imaginary circular path around the conductor at perpendicular distance ‘r’ from the axis of the straight conductor is
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2\pi r}$
This relation is valid only for circles of radius $r\ge a$.
To derive relation for $r\le a$ we assume that the uniform current density in the conductor is $J$. Then,
$J=\dfrac{I}{\pi {{a}^{2}}}$
Since, J is constant, the current flowing through a circular cross-section of radius ‘r’ is
$I=J\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Where $a$ is the radius of the cross section. Then, according to ampere’s circuital law magnetic field density inside the conductor along an imaginary circular path around the conductor at perpendicular distance ‘r’ from the axis of the straight conductor is
$B=\dfrac{\mu I}{2\pi r}=\dfrac{\mu J\pi {{r}^{2}}}{2\pi r}=\dfrac{\mu Jr}{2}$
From the above equation, we can note that the magnetic field inside the conductor is directly proportional to its distance from the axis. We also observed that for a radius of imaginary circular path greater than the radius of cross-section of conductor, the magnetic field intensity is inversely proportional. This corresponds to option A.

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Magnetic field intensity due to a current carrying conductor is linearly proportional to its distance from its axis inside the conductor. But for distances lying outside the conductor, the magnetic field density is inversely proportional to the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




