
Which of the following reagents may be used to distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid?
A. Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$
B. Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$
C. Tollen’s reagent
D. Schiff’s reagent
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ forms complex with aldehyde functional group but not with a carboxylic functional group. The aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ forms sodium salt of aldehyde and carboxylic functional groups. Tollen’s reagent is used to detect the presence of the carbonyl group. Schiff’s reagent is used to distinguish the aldehyde and ketone.
Complete answer:
The structure of phenol and benzoic acid is as follows:
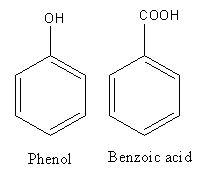
The phenol and benzoic acid have aldehyde and carboxylic functional groups respectively.
Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ reacts with phenol to give a violet colour complex. The reaction of neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ with phenol is as follows:
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}\, + \,6\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{OH}}\, \to \,\,{\mathop {\left[ {{\text{Fe}} - {{\left( {{\text{O - }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3-}}\limits_{{\text{violet}}\,{\text{colour}}}} + \,{\text{3}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}} + \,{\text{3}}\,{\text{HCl}}$
Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ does not react with carboxylic acids. So, they form a buff coloured solution with neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$. Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (A) is correct.
Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ reacts with phenol and benzoic acid both and forms sodium salt of both. The formation of salt is shown as follows:
${\text{aq}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{NaOH}}\, + \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{OH}}\, \to \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + } + \,\,{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
${\text{aq}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{NaOH}}\, + \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{COOH}}\, \to \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + } + \,\,{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ does not distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (B) is incorrect.
Tollen’s reagent is used to determine the presence of the carbonyl group in chemical compounds. Tollen’s reagent does not distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (C) is incorrect.
Schiff’s reagent is used to differentiate the aldehyde and ketone. Schiff’s reagent is used to detect the presence of formaldehyde. The formaldehyde gives magenta colour with Schiff’s reagent. Schiff’s reagent does not distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (D) is incorrect.
Therefore, option (A) Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ is correct.
Note: Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ reacts similarly with carboxylic and aldehyde functional groups. The chemical compound having a ketone functional group gives the oxime and hydroxylamine with Tollen’s reagent whereas the chemical compound having an aldehyde functional group gives the silver mirror. Ketone does not react with Schiff’s reagent.
Complete answer:
The structure of phenol and benzoic acid is as follows:

The phenol and benzoic acid have aldehyde and carboxylic functional groups respectively.
Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ reacts with phenol to give a violet colour complex. The reaction of neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ with phenol is as follows:
${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}\, + \,6\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{OH}}\, \to \,\,{\mathop {\left[ {{\text{Fe}} - {{\left( {{\text{O - }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}}} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3-}}\limits_{{\text{violet}}\,{\text{colour}}}} + \,{\text{3}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}} + \,{\text{3}}\,{\text{HCl}}$
Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ does not react with carboxylic acids. So, they form a buff coloured solution with neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$. Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (A) is correct.
Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ reacts with phenol and benzoic acid both and forms sodium salt of both. The formation of salt is shown as follows:
${\text{aq}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{NaOH}}\, + \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{OH}}\, \to \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + } + \,\,{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
${\text{aq}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{NaOH}}\, + \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{COOH}}\, \to \,\,{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{H}}{ _{\text{5}}} - {\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + } + \,\,{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ does not distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (B) is incorrect.
Tollen’s reagent is used to determine the presence of the carbonyl group in chemical compounds. Tollen’s reagent does not distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (C) is incorrect.
Schiff’s reagent is used to differentiate the aldehyde and ketone. Schiff’s reagent is used to detect the presence of formaldehyde. The formaldehyde gives magenta colour with Schiff’s reagent. Schiff’s reagent does not distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid, so option (D) is incorrect.
Therefore, option (A) Neutral ${\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ is correct.
Note: Aqueous ${\text{NaOH}}$ reacts similarly with carboxylic and aldehyde functional groups. The chemical compound having a ketone functional group gives the oxime and hydroxylamine with Tollen’s reagent whereas the chemical compound having an aldehyde functional group gives the silver mirror. Ketone does not react with Schiff’s reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




