
Which of the following reactions will not give either a major product?
A) $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+A{{g}_{2}}O(dry)\to $
B) ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}CCl+C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}\to $
C)
D)


Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: The ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbocation, is the most reactive carbocation for the elimination reaction.
- The tertiary alkyl halides forms the tertiary carbocation during .
Complete step by step answer:
So in the question, it is asked which of the following options given will not give the major product as ether.
We should have to compare the reactions that happens for each options and we should know the product that forms to predict the major product.So lets see the different reaction-
- Option (A), $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+A{{g}_{2}}O(dry)\to $
Here an alkyl halide,specifically saying a ${{1}^{\circ }}$alkyl halide is reacting with the silver oxide ,here the product formed will be an ether and the ether is the major product formed here.
So the reaction is ,
$2C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+A{{g}_{2}}O(dry)\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OC{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}\left( Major\,product \right)+2AgCl$
So this is not the option.
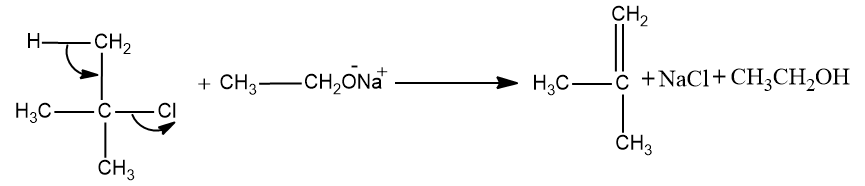
- Option (B), ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}CCl+C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}\to $
In this case,here the reactants are tertiary Alkyl chain and sodium alkoxide.
Here the ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbon chain forms the ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbocation which cannot undergo the Williamson ether synthesis.
Since Williamson’s ether synthesis is a ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ reaction .So ${{3}^{\circ }}$carbocation are the least reactive carbocations towards the ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ reaction.And it will undergo elimination reaction (${{E}_{1}}$ reaction) and the product formed will be alkene.
So this may be the correct option.
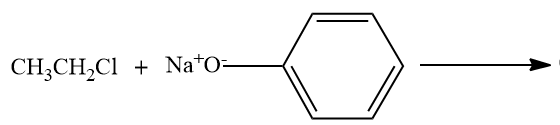
- Option C,
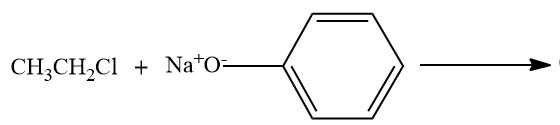
Here, the alkyl chloride ie ethyl chloride is reacting with the sodium phenoxide ion, and this chemical reaction forms the aryl-alkyl ether.Here the product formed is phenetole or called as Ethyl phenyl ether.
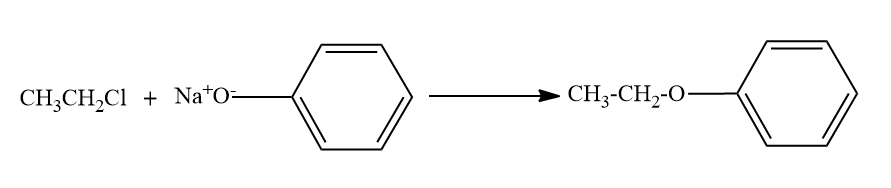
So here also ether is the major product formed.
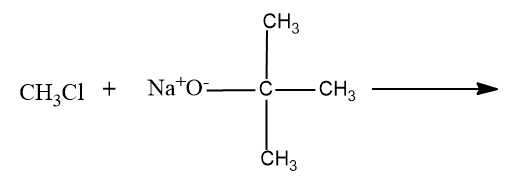
- Option (D),
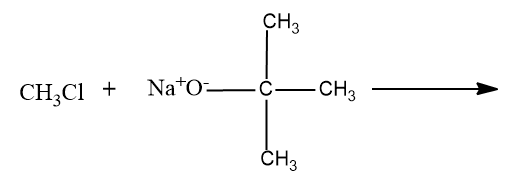
Here a primary carbocation will be formed during the chemical reaction and it undergoes the ether formation through Williamson’s ether synthesis.
So the product formed will be,
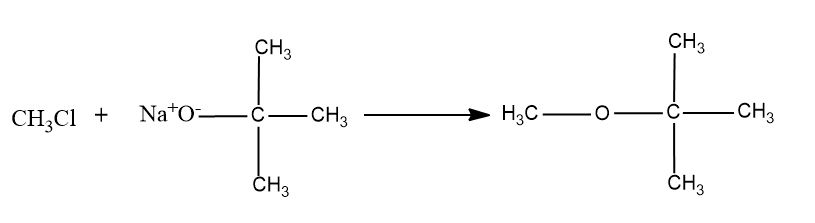
So this option is not the correct option.
From the above reactions we could conclude that the correct option is option (B), which gives alkene as the major product.
Note: We should know that for the ether formation through Williamson’s ether synthesis, the reactivity of the carbocation formed during the chemical reaction will be, ${{1}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{2}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{3}^{\circ }}$
- And the Williamson’s ether synthesis is a ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ reaction, hence the stability of the carbocations will be as given above.
- And the elimination reaction here ,the ${{E}_{1}}$ reaction is similar to ${{S}_{N}}^{1}$ reaction and have a reactivity order of carbocations as, ${{3}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{2}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{1}^{\circ }}$ and product formed here will be an alkene.
- The tertiary alkyl halides forms the tertiary carbocation during .
Complete step by step answer:
So in the question, it is asked which of the following options given will not give the major product as ether.
We should have to compare the reactions that happens for each options and we should know the product that forms to predict the major product.So lets see the different reaction-
- Option (A), $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+A{{g}_{2}}O(dry)\to $
Here an alkyl halide,specifically saying a ${{1}^{\circ }}$alkyl halide is reacting with the silver oxide ,here the product formed will be an ether and the ether is the major product formed here.
So the reaction is ,
$2C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl+A{{g}_{2}}O(dry)\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OC{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}\left( Major\,product \right)+2AgCl$
So this is not the option.
- Option (B), ${{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}}CCl+C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}\to $
In this case,here the reactants are tertiary Alkyl chain and sodium alkoxide.
Here the ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbon chain forms the ${{3}^{\circ }}$ carbocation which cannot undergo the Williamson ether synthesis.
Since Williamson’s ether synthesis is a ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ reaction .So ${{3}^{\circ }}$carbocation are the least reactive carbocations towards the ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ reaction.And it will undergo elimination reaction (${{E}_{1}}$ reaction) and the product formed will be alkene.

So this may be the correct option.
- Option C,

Here, the alkyl chloride ie ethyl chloride is reacting with the sodium phenoxide ion, and this chemical reaction forms the aryl-alkyl ether.Here the product formed is phenetole or called as Ethyl phenyl ether.

So here also ether is the major product formed.
- Option (D),

Here a primary carbocation will be formed during the chemical reaction and it undergoes the ether formation through Williamson’s ether synthesis.
So the product formed will be,

So this option is not the correct option.
From the above reactions we could conclude that the correct option is option (B), which gives alkene as the major product.
Note: We should know that for the ether formation through Williamson’s ether synthesis, the reactivity of the carbocation formed during the chemical reaction will be, ${{1}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{2}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{3}^{\circ }}$
- And the Williamson’s ether synthesis is a ${{S}_{N}}^{2}$ reaction, hence the stability of the carbocations will be as given above.
- And the elimination reaction here ,the ${{E}_{1}}$ reaction is similar to ${{S}_{N}}^{1}$ reaction and have a reactivity order of carbocations as, ${{3}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{2}^{\circ }}\,>\,{{1}^{\circ }}$ and product formed here will be an alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




