
Which of the following products is not formed in the above reaction?
(A) \[{\rm{BrC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Br}}\]
(B) \[{\rm{ClC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Cl}}\]\[\]
(C) \[{\rm{BrC}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{Cl}}\]
(D) All are formed
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that the alkenes are very reactive towards electrophilic substitution reaction. The reactivity is due to its \[{\rm{\pi }}\]electrons present in it. All the halides are electronegative in nature and can act as a nucleophile.
Complete answer
The ethene molecule contains double bond one is sigma (\[{\rm{\sigma }}\])bonding and other is pi (\[{\rm{\pi }}\]) bonding. The bonding electrons are not much stable due to side wise overlapping. Therefore, the pi electrons are responsible for the reactivity of ethene compounds toward electrophilic substitution.
When the ethene attacks on bromine, the atom’s shared pair electrons repel with ethene pi electrons and then one bromine atom splits into bromide ion and one is bromonium ion. This bromonium ion is very electron deficient, the pi electrons on each carbon of ethene are polarized by positive charge on bromine and hence cyclization occurs with the ethene compound.
Now, the free bromide ion acts as nucleophile due to negative charge, attacks on this cyclized product and forms \[1,2 - \]dibromoethane.
As we can see that there is also sodium chloride which in aqueous medium give chloride ion. The chloride ion acts as nucleophile due to negative charge and attacks on also cyclized product and form product as \[{\rm{1 - bromo - 2 - chloroethane}}\].
The mechanism is shown as below-
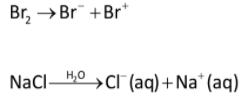
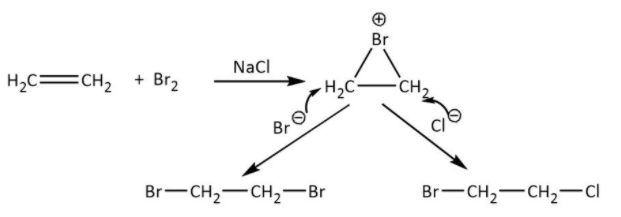
So, the only option we are left with is option (B).
Note:
There are two types of state of electrons
(a) Ground state- in which electrons are paired up.
(b) The excited state -in which electrons are in triplet state.
The ethene electrons when reacted with bromonium ions are excited to triplet state then the cyclization occurs.
Complete answer
The ethene molecule contains double bond one is sigma (\[{\rm{\sigma }}\])bonding and other is pi (\[{\rm{\pi }}\]) bonding. The bonding electrons are not much stable due to side wise overlapping. Therefore, the pi electrons are responsible for the reactivity of ethene compounds toward electrophilic substitution.
When the ethene attacks on bromine, the atom’s shared pair electrons repel with ethene pi electrons and then one bromine atom splits into bromide ion and one is bromonium ion. This bromonium ion is very electron deficient, the pi electrons on each carbon of ethene are polarized by positive charge on bromine and hence cyclization occurs with the ethene compound.
Now, the free bromide ion acts as nucleophile due to negative charge, attacks on this cyclized product and forms \[1,2 - \]dibromoethane.
As we can see that there is also sodium chloride which in aqueous medium give chloride ion. The chloride ion acts as nucleophile due to negative charge and attacks on also cyclized product and form product as \[{\rm{1 - bromo - 2 - chloroethane}}\].
The mechanism is shown as below-
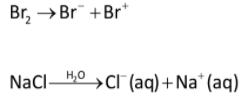

So, the only option we are left with is option (B).
Note:
There are two types of state of electrons
(a) Ground state- in which electrons are paired up.
(b) The excited state -in which electrons are in triplet state.
The ethene electrons when reacted with bromonium ions are excited to triplet state then the cyclization occurs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




