
Which of the following pairs of structures represent facial and meridional isomers respectively?
A.
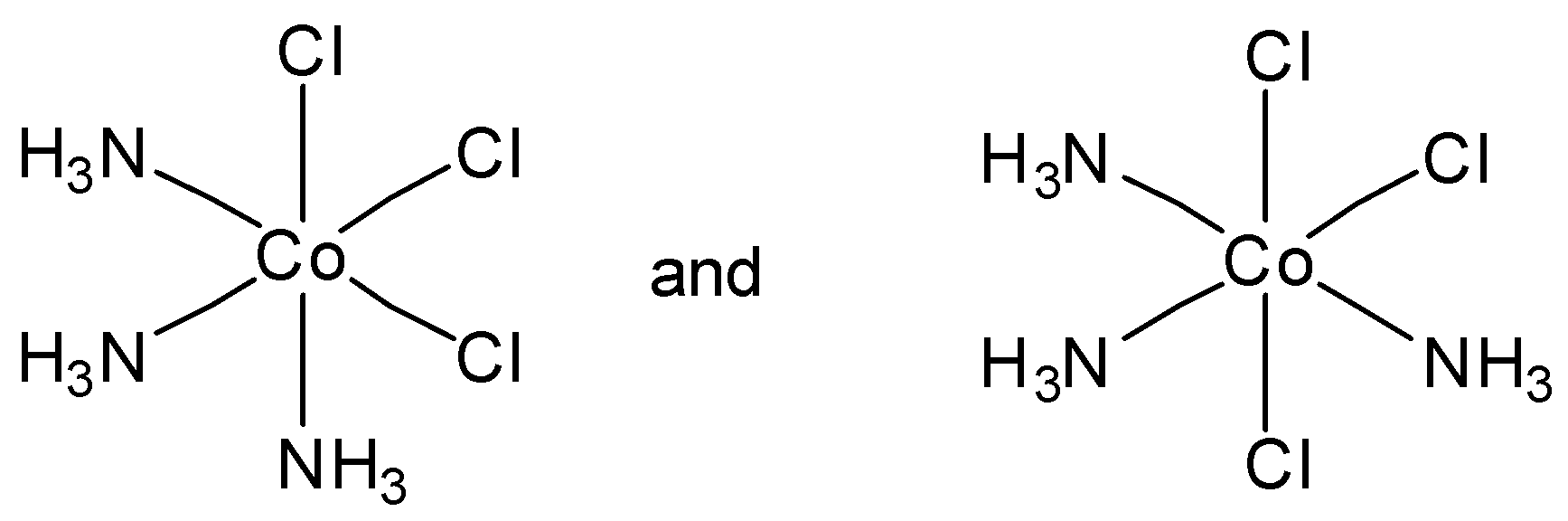
B.
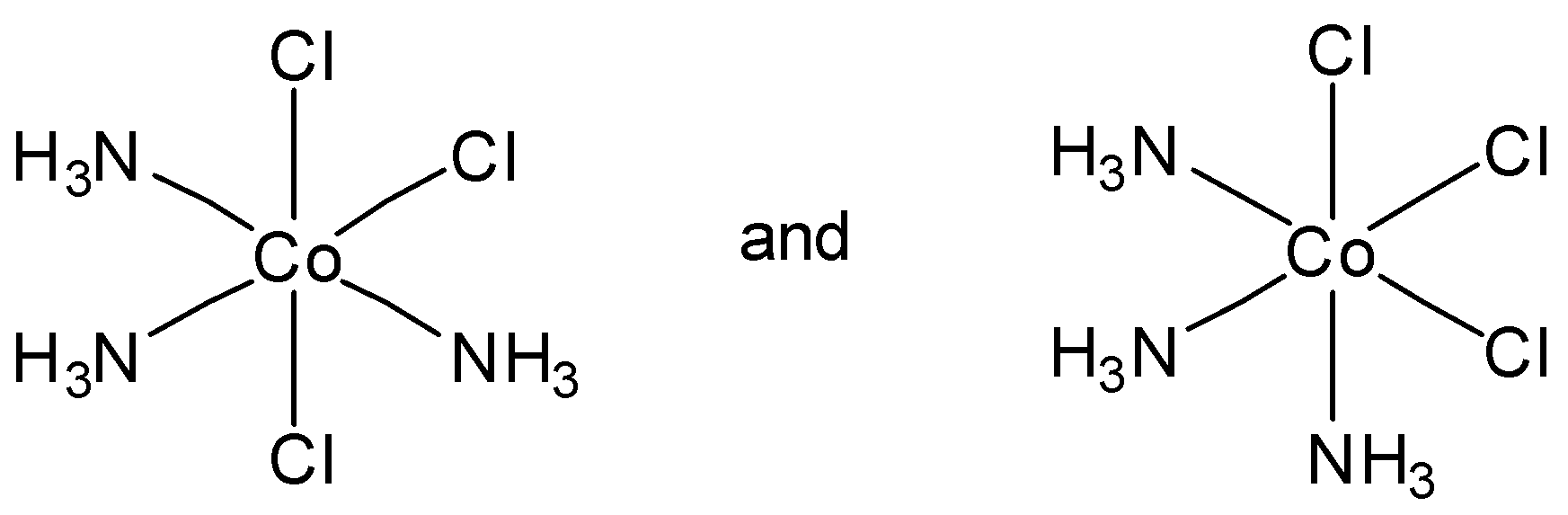
C.
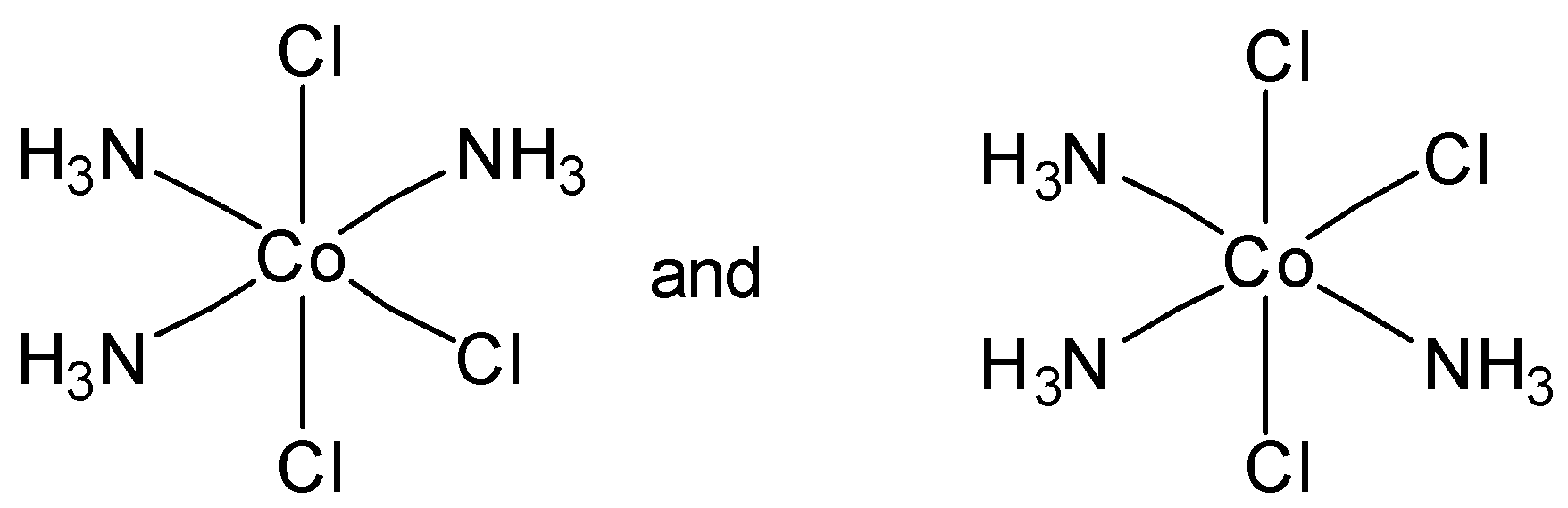
D.
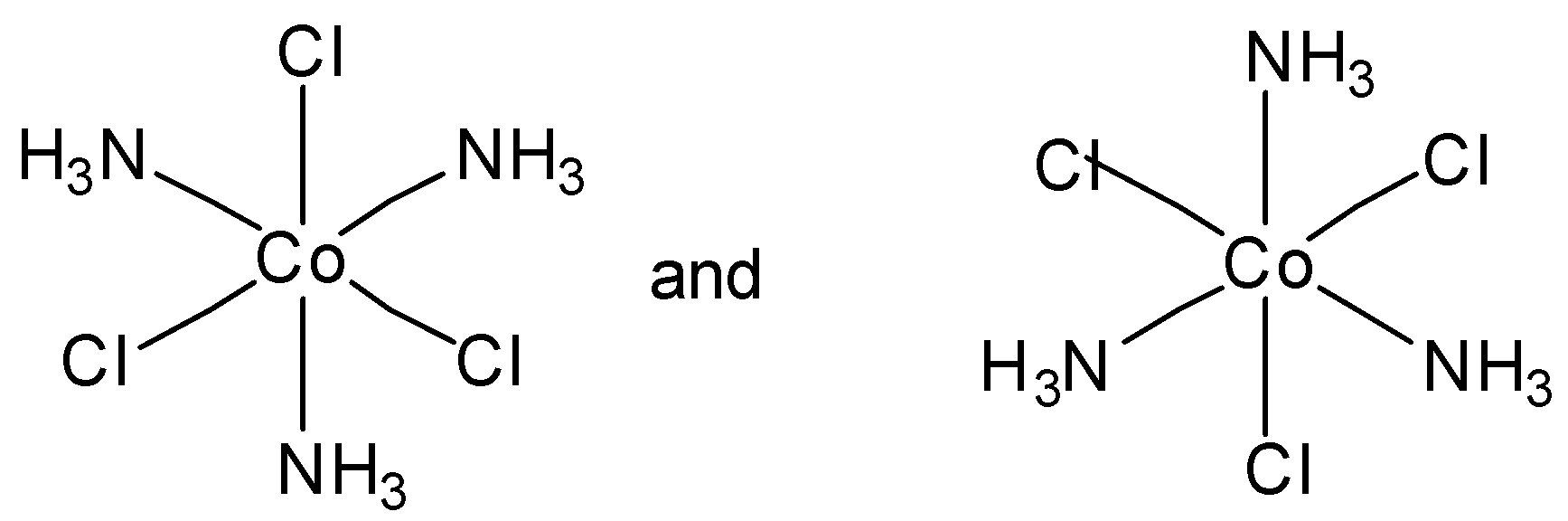
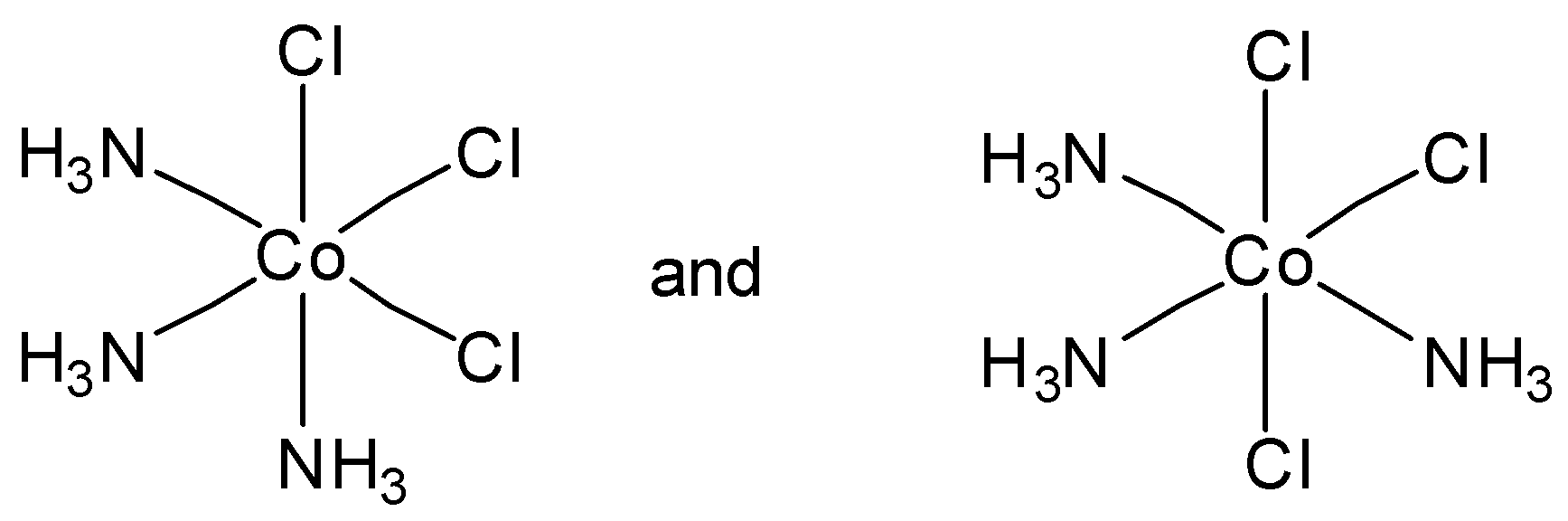
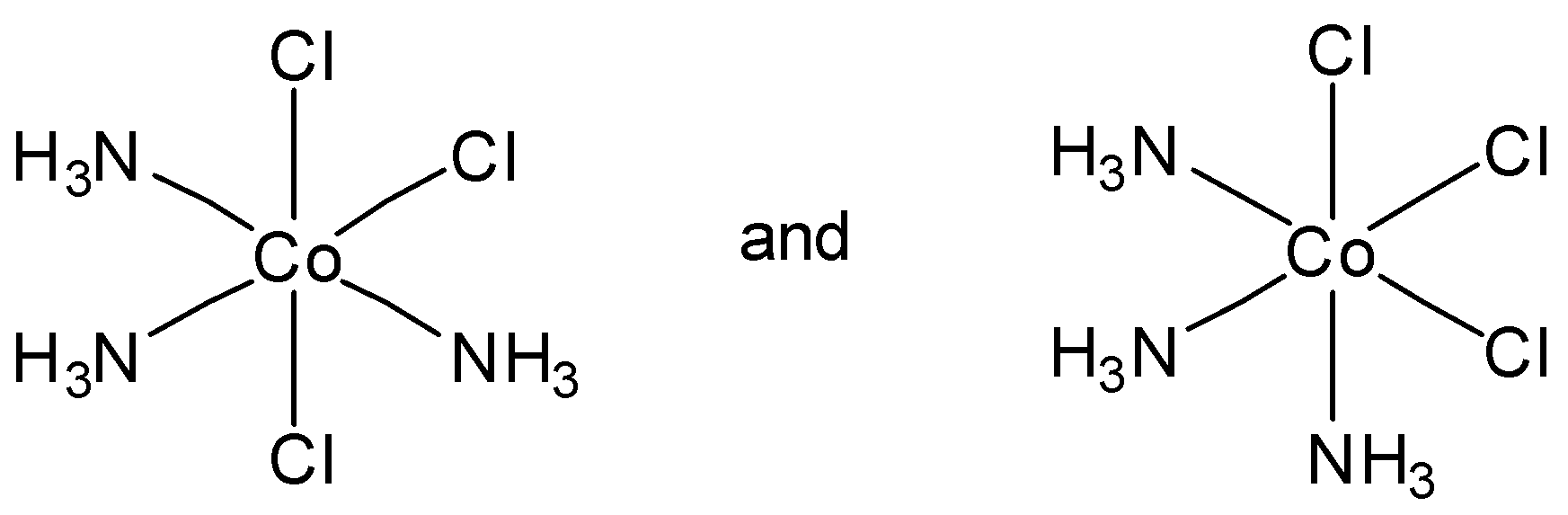
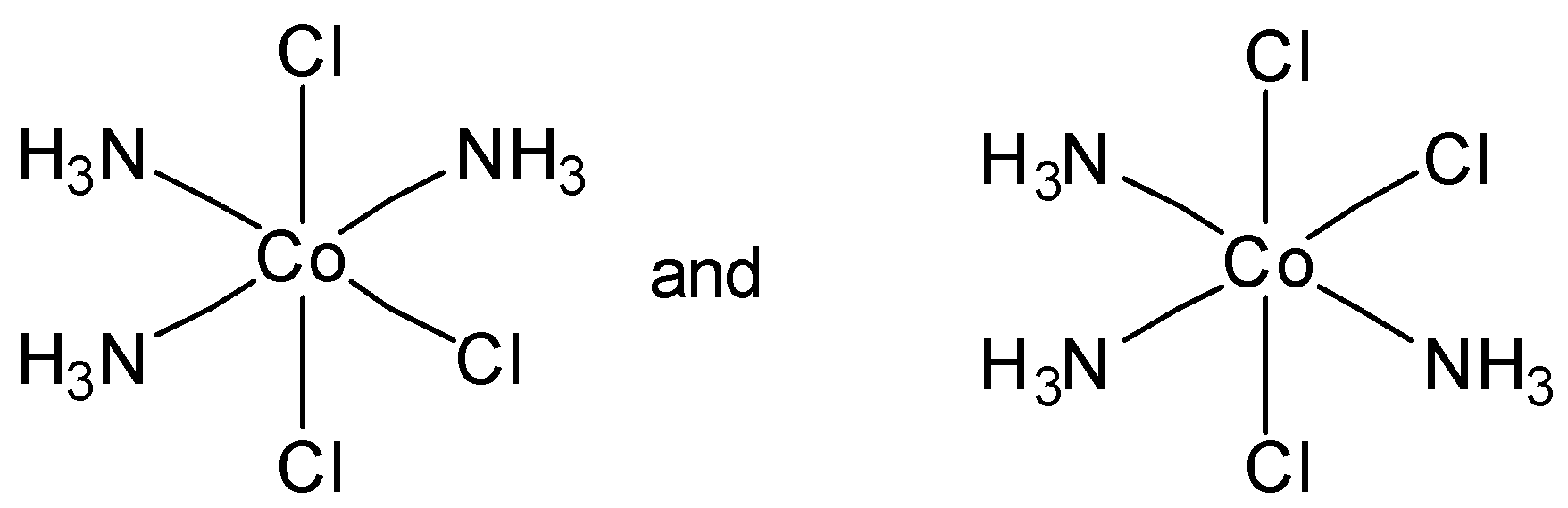
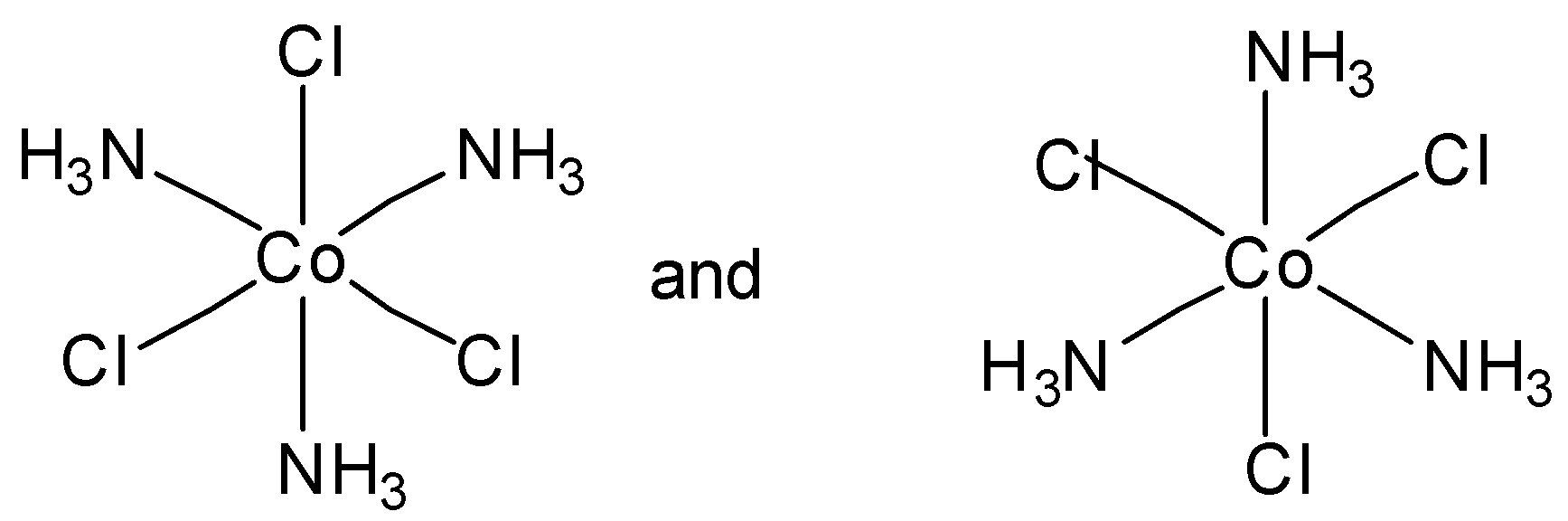
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Definition: Coordination compounds are an important class of inorganic compounds. They are stable compounds that retain their identity in solid as well as liquid state. They find numerous applications in all the fields. In short it is a complex that contains metal and ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
The properties of such compounds are totally different from the individual constituents. In these compounds there is a central metal atom or ion and it is surrounded by ligands. These can be neutral, cationic or anionic. These donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal ion. They attach to the metal atom by co-ordinate bond or dative bond.
For instance, in the above given example, chlorine is an anionic ligand (it carries a charge of $ - 1$ ) whereas ammonia is a neutral ligand.
The number of ligands directly attached to the central metal ion is called the co-ordination number of the metal atom or ion. This number varies for each metal ion or atom. Generally it ranges from two to nine.
In the co-ordination sphere, ligands occupy the space around the metal atom giving rise to different geometries of the complex. The common geometries of complexes are octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar, trigonal bipyramidal, square pyramidal.
Complexes with co-ordination number $6$ generally have an octahedral type of geometry. The above given example also has octahedral geometry. In this geometry four ligands are in the plane at four corners forming a square and one ligand is above the plane and the other is below the plane.
Now isomerism is also present in co-ordination compounds. Structures having the same molecular formula but differ in chemical and physical structures on account of having different structures are called isomers.
Octahedral complexes having two different sets of ligands shows two types of isomers-facial and meridional isomers. When three similar ligands are present on the same face of an octahedron it gives rise to facial (fac) isomer. The diagram below shows a facial isomer where a and b are the two sets of three similar ligands.
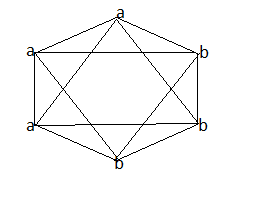
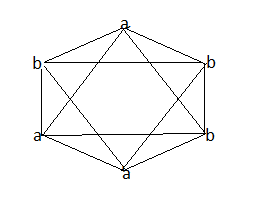
When a set of three similar ligands is arranged on an octahedron with one pair trans(on meridian of octahedron) , the isomer is called a meridional isomer.
So in the above example we can see that in option A, the first diagram depicts a facial isomer and meridional complex respectively.
In option B, the first option is meridional and second option is facial isomer. So this is not the correct answer.
In option C, both are meridional complexes. And in option D, none of the structure is facial or meridional. So option C and option D are incorrect.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: In facial isomer three similar ligands are on the same face and in meridional isomer the ligands are not able to form a face while they are present trans to each other on the opposite sides of the plane. Apart from these there are other types of isomers possible in case of complexes like geometrical isomers, optical isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
The properties of such compounds are totally different from the individual constituents. In these compounds there is a central metal atom or ion and it is surrounded by ligands. These can be neutral, cationic or anionic. These donate lone pairs of electrons to the central metal ion. They attach to the metal atom by co-ordinate bond or dative bond.
For instance, in the above given example, chlorine is an anionic ligand (it carries a charge of $ - 1$ ) whereas ammonia is a neutral ligand.
The number of ligands directly attached to the central metal ion is called the co-ordination number of the metal atom or ion. This number varies for each metal ion or atom. Generally it ranges from two to nine.
In the co-ordination sphere, ligands occupy the space around the metal atom giving rise to different geometries of the complex. The common geometries of complexes are octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar, trigonal bipyramidal, square pyramidal.
Complexes with co-ordination number $6$ generally have an octahedral type of geometry. The above given example also has octahedral geometry. In this geometry four ligands are in the plane at four corners forming a square and one ligand is above the plane and the other is below the plane.
Now isomerism is also present in co-ordination compounds. Structures having the same molecular formula but differ in chemical and physical structures on account of having different structures are called isomers.
Octahedral complexes having two different sets of ligands shows two types of isomers-facial and meridional isomers. When three similar ligands are present on the same face of an octahedron it gives rise to facial (fac) isomer. The diagram below shows a facial isomer where a and b are the two sets of three similar ligands.

When a set of three similar ligands is arranged on an octahedron with one pair trans(on meridian of octahedron) , the isomer is called a meridional isomer.

So in the above example we can see that in option A, the first diagram depicts a facial isomer and meridional complex respectively.
In option B, the first option is meridional and second option is facial isomer. So this is not the correct answer.
In option C, both are meridional complexes. And in option D, none of the structure is facial or meridional. So option C and option D are incorrect.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: In facial isomer three similar ligands are on the same face and in meridional isomer the ligands are not able to form a face while they are present trans to each other on the opposite sides of the plane. Apart from these there are other types of isomers possible in case of complexes like geometrical isomers, optical isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




