
Which of the following pairs of coils has zero couplings constant?
A.
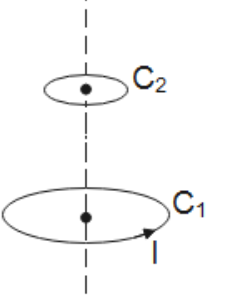
B.
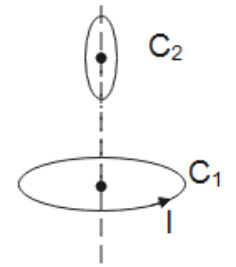
C.
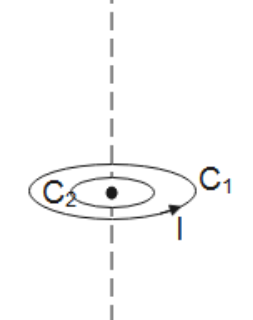
D. All of these



Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Coupling constant is zero if coils are not flux-linked. The direction of the magnetic field due to a current-carrying loop can be found using the right-hand thumb rule. If the direction of the magnetic field produced due to coil ${{C}_{1}}$ is normal to the area vector of loop ${{C}_{2}}$ then the coils are not flux-linked.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The ratio of magnetic flux produced by the current in one coil that links with the other coil is called the coefficient of coupling or coupling between the two coils. It is denoted by k.
The coupling constant is zero if coils are not flux-linked.
“Magnetic flux is the rate of flow of the magnetic field through a given area.” In other words, it is the number of lines of magnetic force passing through a given area.
Magnetic flux through a surface is defined as a dot product of the magnetic field and surface area vector.
${{\phi }_{B}}=\mathbf{B}.\mathbf{A}=BA\cos \theta $
The area vector is defined as the vector of a plane surface. Its magnitude is similar to the area of the plane and direction is normal to that plane.
SO, we can note here that if the area vector of loop ${{C}_{2}}$ is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field produced by the loop ${{C}_{1}}$ ( which is given by the right-hand thumb rule), then, the magnetic flux through loop ${{C}_{2}}$ will be zero which means the coil is not flux-linked.
This is the same case as option B in which loop ${{C}_{1}}$ and loop ${{C}_{2}}$ are perpendicular to each other.
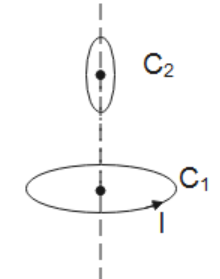
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: Magnetic flux is the rate of flow of the magnetic field through a given area. A varying magnetic field induces a current in the loop. The coupling constant is zero if coils are not flux-linked.
The area vector is defined as the vector of a plane surface. Note that its direction is not along the plane of the area rather perpendicular to it.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The ratio of magnetic flux produced by the current in one coil that links with the other coil is called the coefficient of coupling or coupling between the two coils. It is denoted by k.
The coupling constant is zero if coils are not flux-linked.
“Magnetic flux is the rate of flow of the magnetic field through a given area.” In other words, it is the number of lines of magnetic force passing through a given area.
Magnetic flux through a surface is defined as a dot product of the magnetic field and surface area vector.
${{\phi }_{B}}=\mathbf{B}.\mathbf{A}=BA\cos \theta $
The area vector is defined as the vector of a plane surface. Its magnitude is similar to the area of the plane and direction is normal to that plane.
SO, we can note here that if the area vector of loop ${{C}_{2}}$ is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field produced by the loop ${{C}_{1}}$ ( which is given by the right-hand thumb rule), then, the magnetic flux through loop ${{C}_{2}}$ will be zero which means the coil is not flux-linked.
This is the same case as option B in which loop ${{C}_{1}}$ and loop ${{C}_{2}}$ are perpendicular to each other.

Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: Magnetic flux is the rate of flow of the magnetic field through a given area. A varying magnetic field induces a current in the loop. The coupling constant is zero if coils are not flux-linked.
The area vector is defined as the vector of a plane surface. Note that its direction is not along the plane of the area rather perpendicular to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




