
Which of the following is the most correct electron displacement for a nucleophilic reaction to take place?
A)
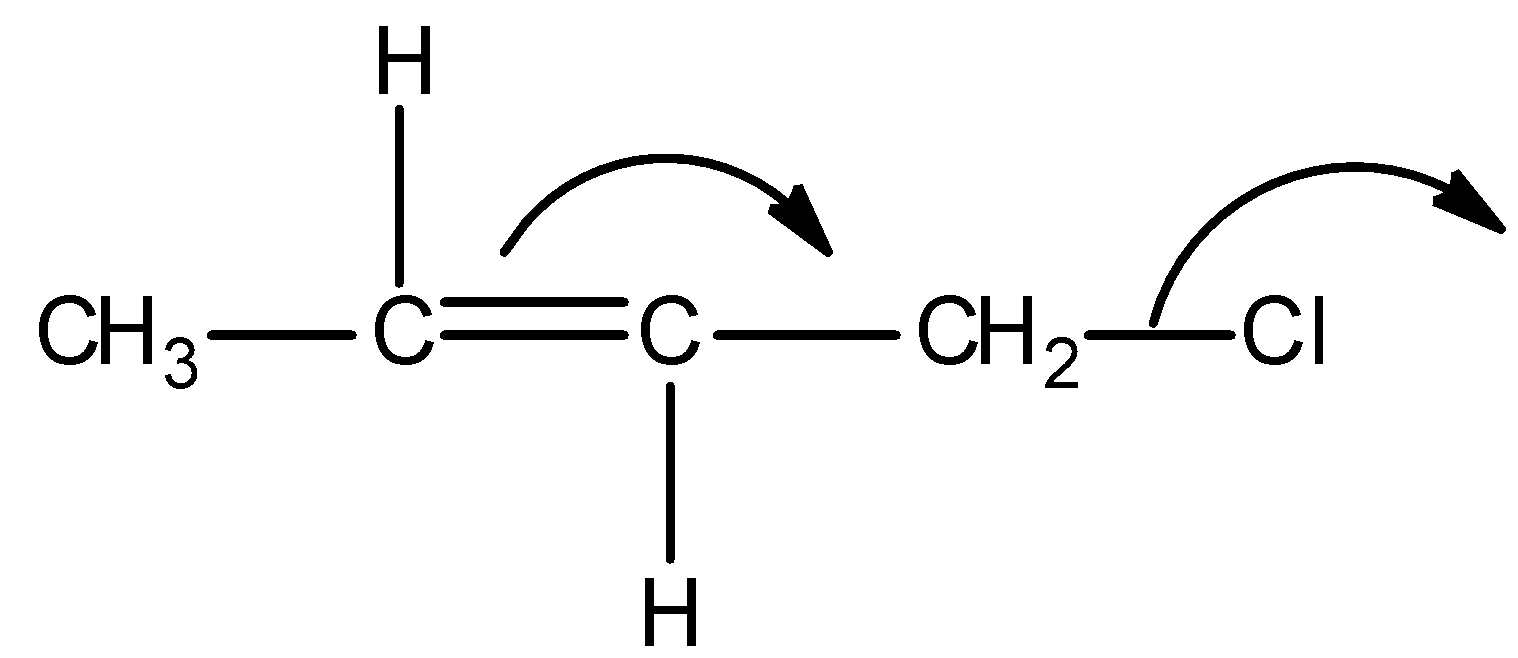
B)
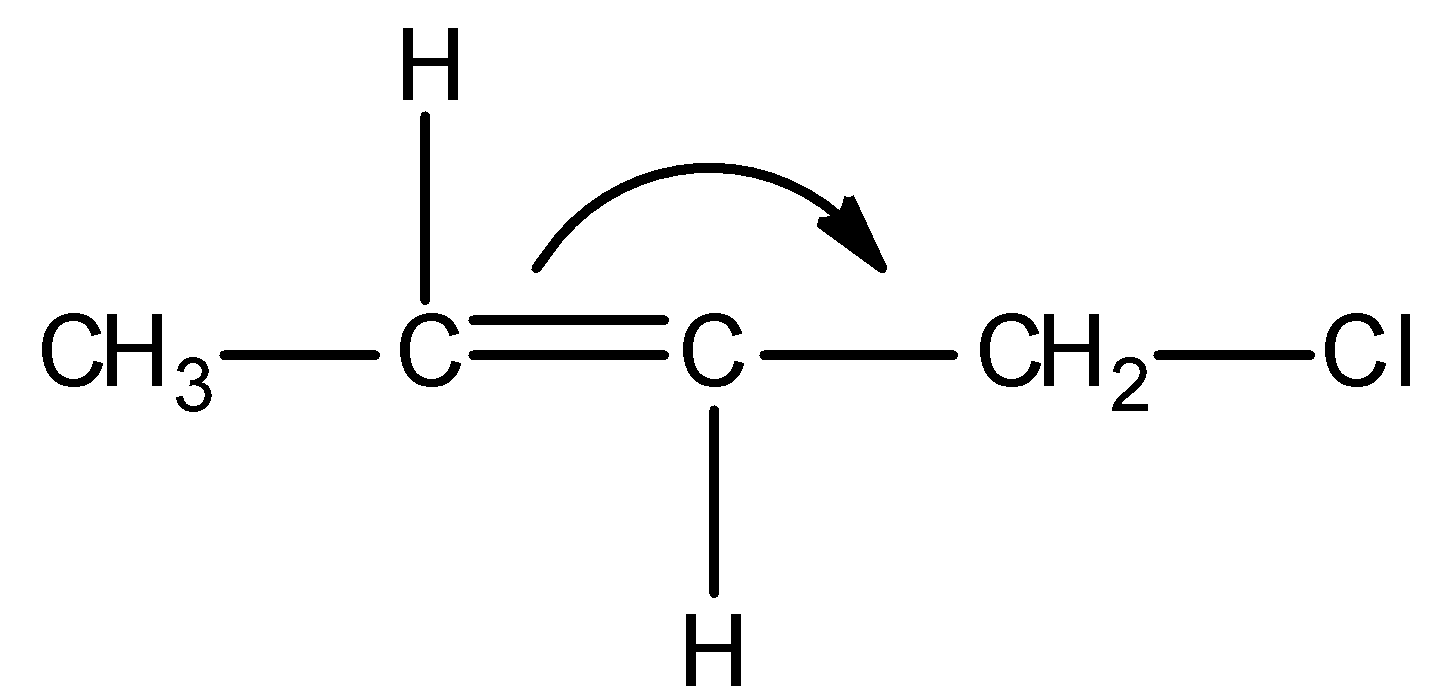
C)
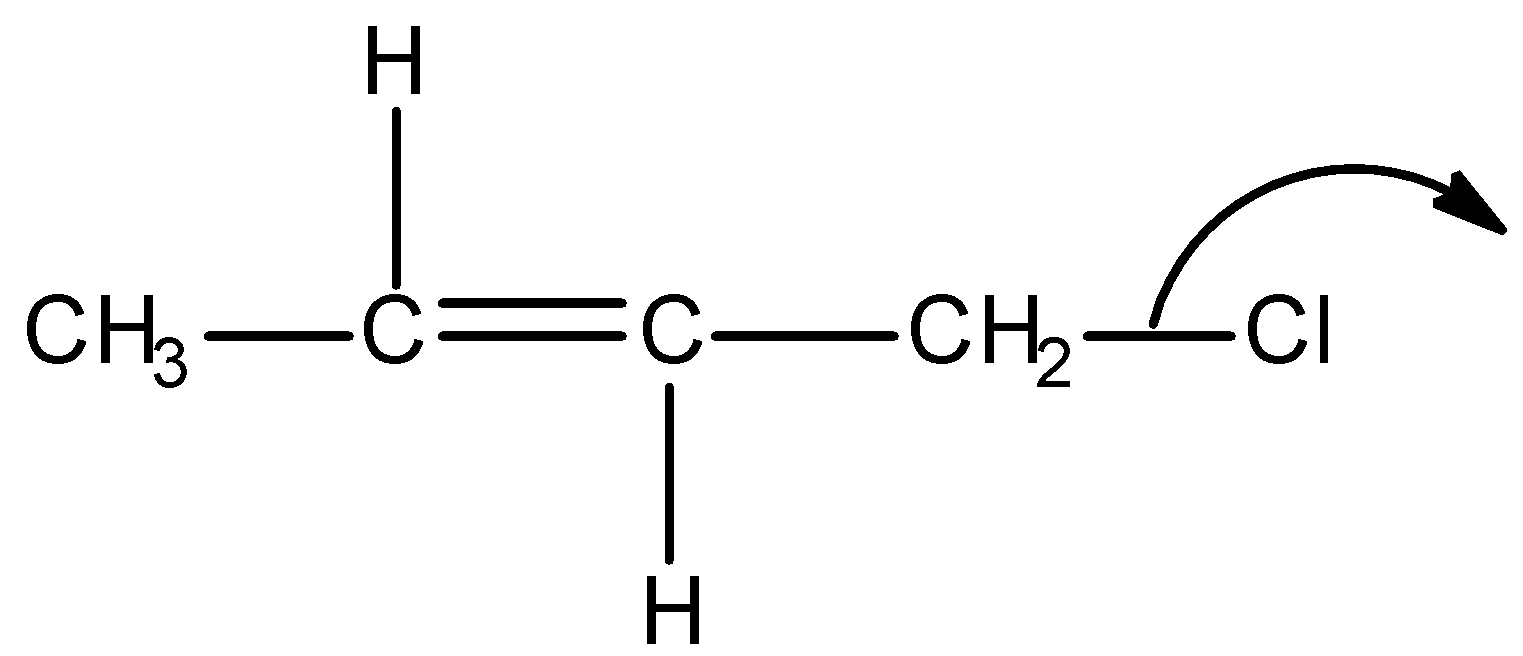
D)
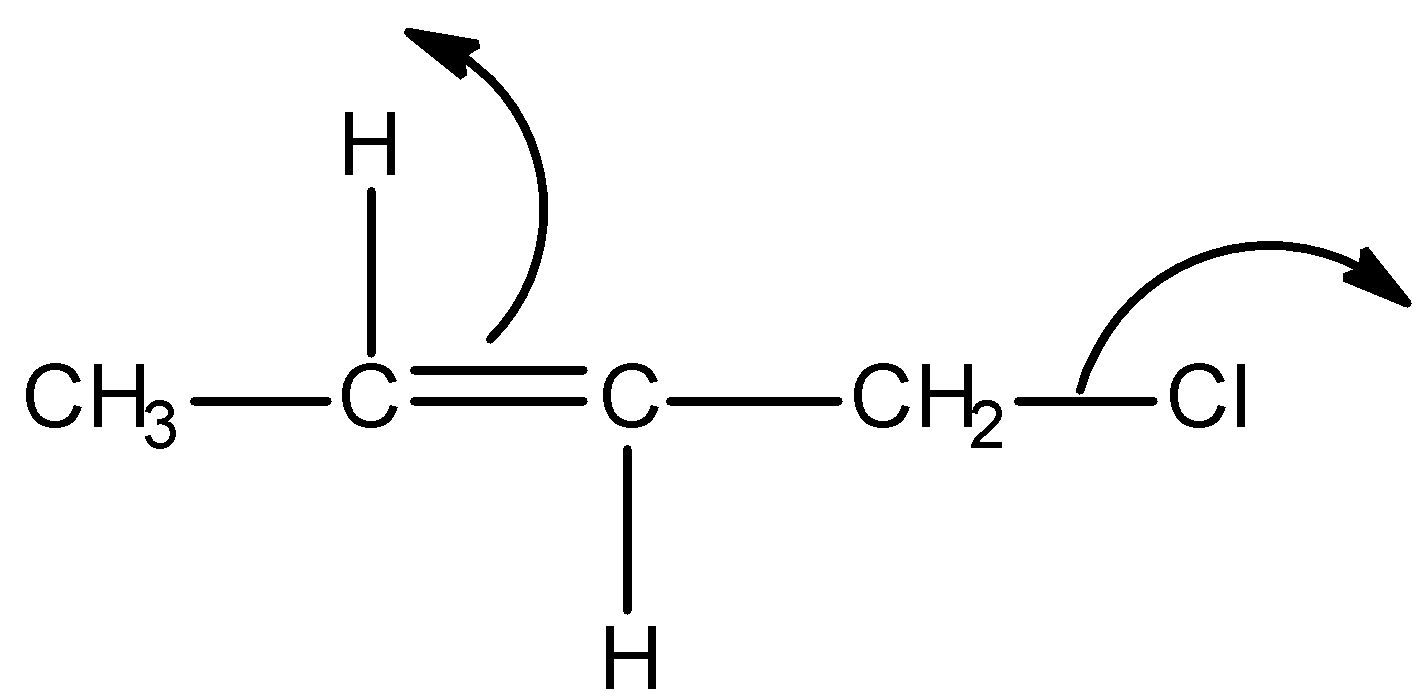




Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Refer to the mechanism of reverse hyperconjugation. Reverse hyperconjugation is most commonly observed in the case of $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$. In this phenomenon, there is movement of electron density from the filled $\pi - $ or p-orbital to the neighbouring empty ${\sigma ^*} - orbital$.
Complete answer:
Firstly, observe that we are given a particular type of system in all the options and it is as shown below:
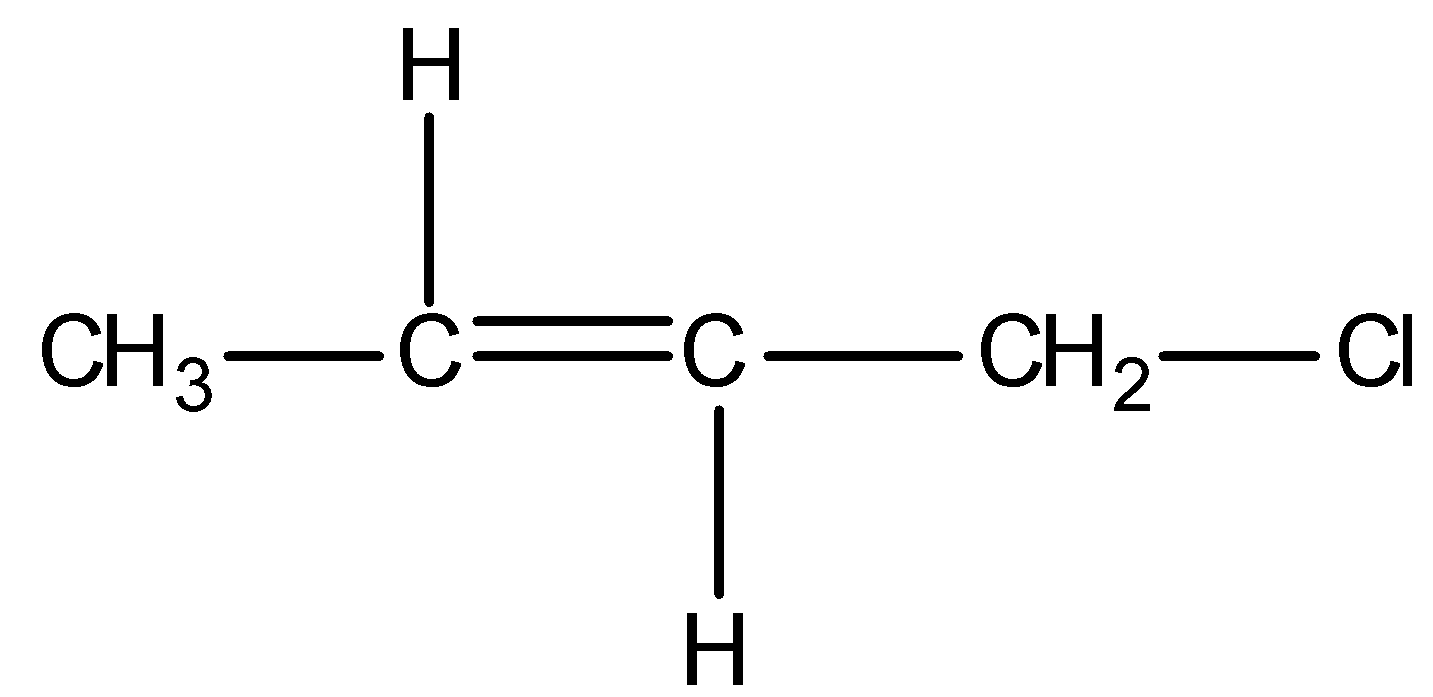
This above structure belongs to the class of $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$. Reverse hyperconjugation phenomenon is observed in $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$, where the ${\sigma ^*} - orbital$ is located on the carbon-halogen bond. In reverse hyperconjugation, there is movement of electron density from the filled $\pi - $ or p-orbital to the neighbouring ${\sigma ^*}$-orbital. Therefore, in case of $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$, there is delocalization of electron density from the double bond (i.e., filled $\pi - orbital$ electron density) towards the electrophilic carbon (i.e., neighbouring ${\sigma ^*}$-orbital). The electrophilic carbon or carbocation is generated when a halogen group leaves with its shared pair of electrons. Simply, we can say that delocalization of electrons occurs towards the halogen group through the hyperconjugative mechanism in $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$.
We can express the reverse hyperconjugation mechanism in the given $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkene}}$ as:
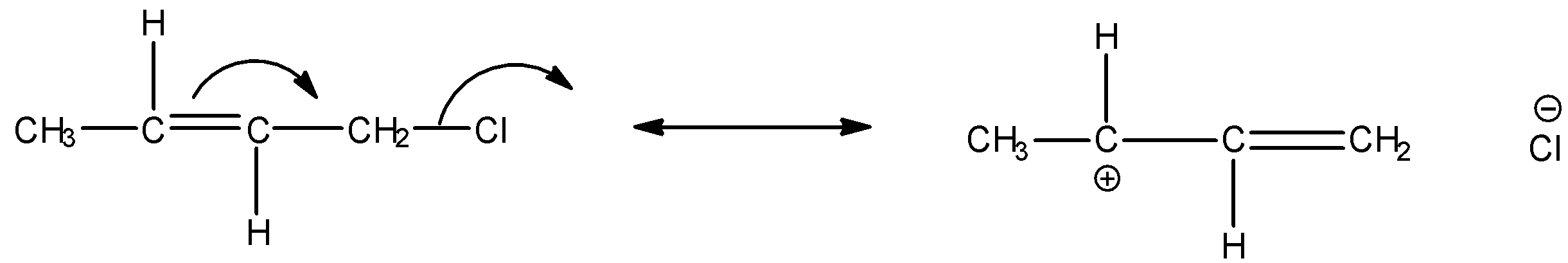
Thus among the given options, only in option A, reverse hyperconjugation mechanism is directed.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
Reverse hyperconjugation phenomenon is also known as negative hyperconjugation. This is attributed to the fact that in negative hyperconjugation, the electron density flows in the opposite direction (from filled p-orbital to empty ${\sigma ^*} - orbital$) than it does in the more common hyperconjugation phenomenon (from $\sigma - orbital$ to empty $\pi - orbital$). Negative hyperconjugation stabilizes the molecule or transition state. It causes the elongation of the $\sigma - bond$ by adding electron density to its anti-bonding orbital.
Complete answer:
Firstly, observe that we are given a particular type of system in all the options and it is as shown below:

This above structure belongs to the class of $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$. Reverse hyperconjugation phenomenon is observed in $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$, where the ${\sigma ^*} - orbital$ is located on the carbon-halogen bond. In reverse hyperconjugation, there is movement of electron density from the filled $\pi - $ or p-orbital to the neighbouring ${\sigma ^*}$-orbital. Therefore, in case of $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$, there is delocalization of electron density from the double bond (i.e., filled $\pi - orbital$ electron density) towards the electrophilic carbon (i.e., neighbouring ${\sigma ^*}$-orbital). The electrophilic carbon or carbocation is generated when a halogen group leaves with its shared pair of electrons. Simply, we can say that delocalization of electrons occurs towards the halogen group through the hyperconjugative mechanism in $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkenes}}$.
We can express the reverse hyperconjugation mechanism in the given $\alpha - {\text{Halo alkene}}$ as:

Thus among the given options, only in option A, reverse hyperconjugation mechanism is directed.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
Reverse hyperconjugation phenomenon is also known as negative hyperconjugation. This is attributed to the fact that in negative hyperconjugation, the electron density flows in the opposite direction (from filled p-orbital to empty ${\sigma ^*} - orbital$) than it does in the more common hyperconjugation phenomenon (from $\sigma - orbital$ to empty $\pi - orbital$). Negative hyperconjugation stabilizes the molecule or transition state. It causes the elongation of the $\sigma - bond$ by adding electron density to its anti-bonding orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




