
Which of the following is the correct answer?
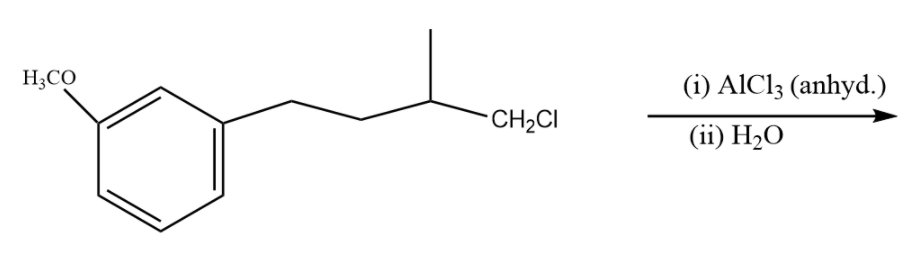
A.
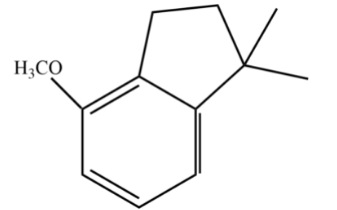
B.
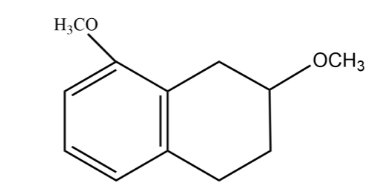
C.
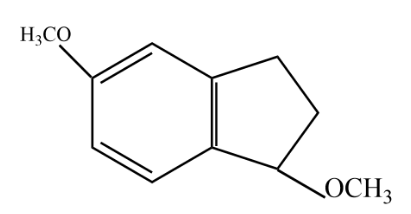
D.
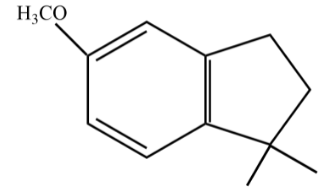





Answer
517.2k+ views
Hint: Friedel crafts alkylation reaction is an electrophilic aromatic reaction in which a carbocation attacks an aromatic ring with the end result that one of the aromatic protons is replaced by an alkyl group.
Complete answer:
If we prefer, we can regard these reactions as involving an attack by an aromatic ring on a carbocation. This latter approach is used in the textbook, but the former approach is probably common. When more than one alkyl group is introduced into an aromatic ring during the course of a Friedel crafts alkylation reaction, polyalkylation is said to have occurred.
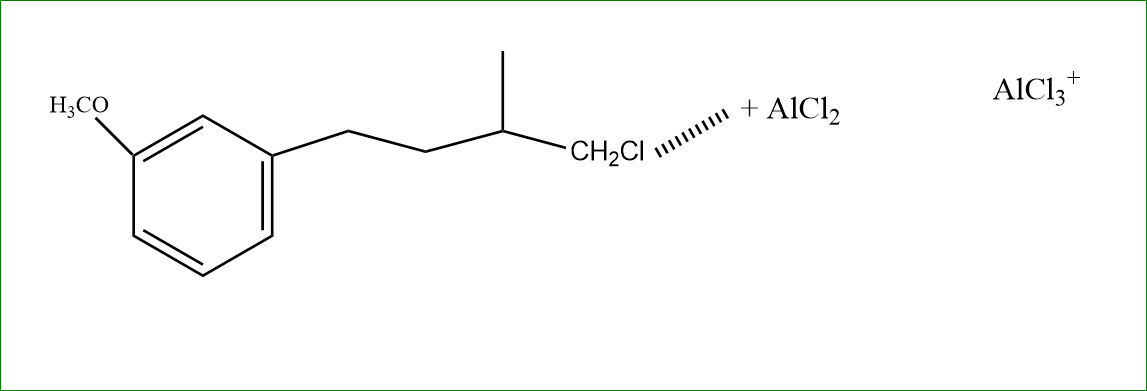
Step 1: The Cl reacts with $AlCl_2$, which makes the $CHC_l2$ bond weak.
Now in step 2: There is a formation of carbocation.
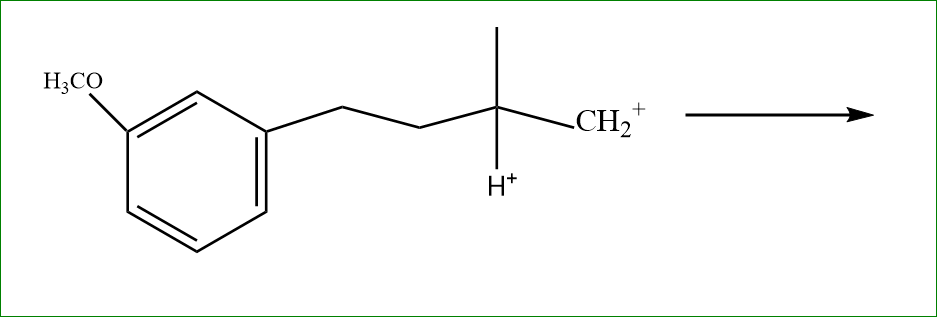
We know that more stable carbocation is tertiary, So the carbocation moves to tertiary carbon with eliminating the hydrogen bond.
Step 3: If there are more than 3, they try to form rings if possible. Hence the tertiary carbocation vacancy is filled by extracting electrons from the nearest Pi bond.
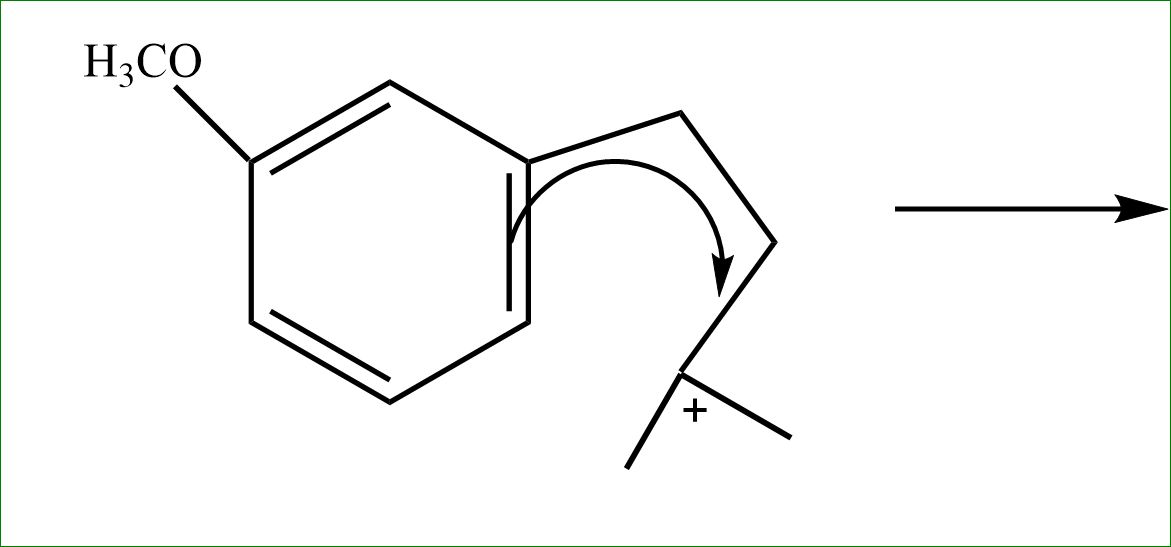
Step 4: the adjacent hydrogen is released further, to satisfy the valency and the bond is formed on the penta ring cycle side. Here intramolecular alkylation occurs.
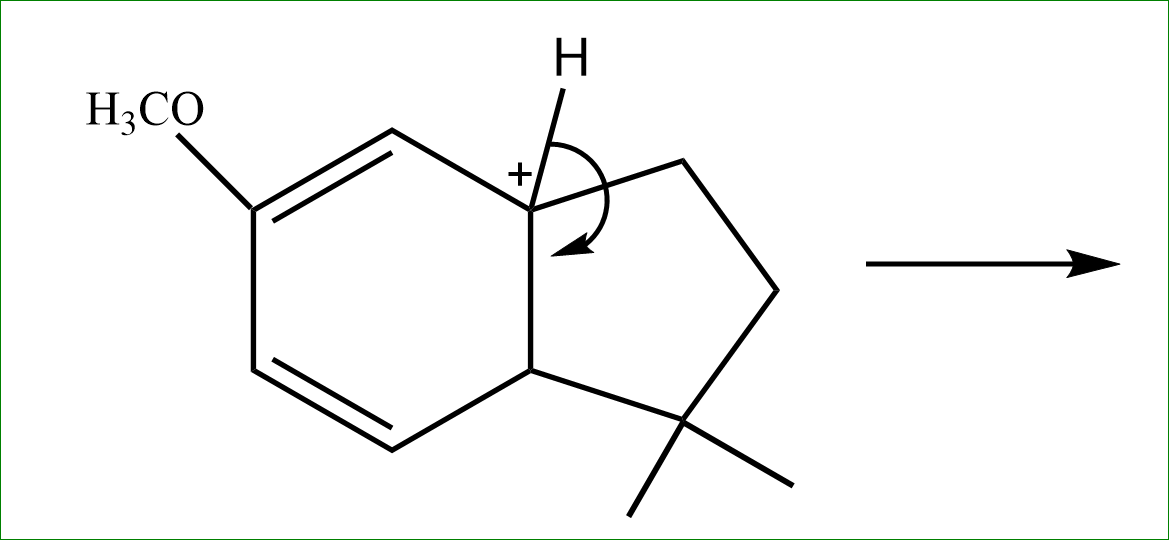
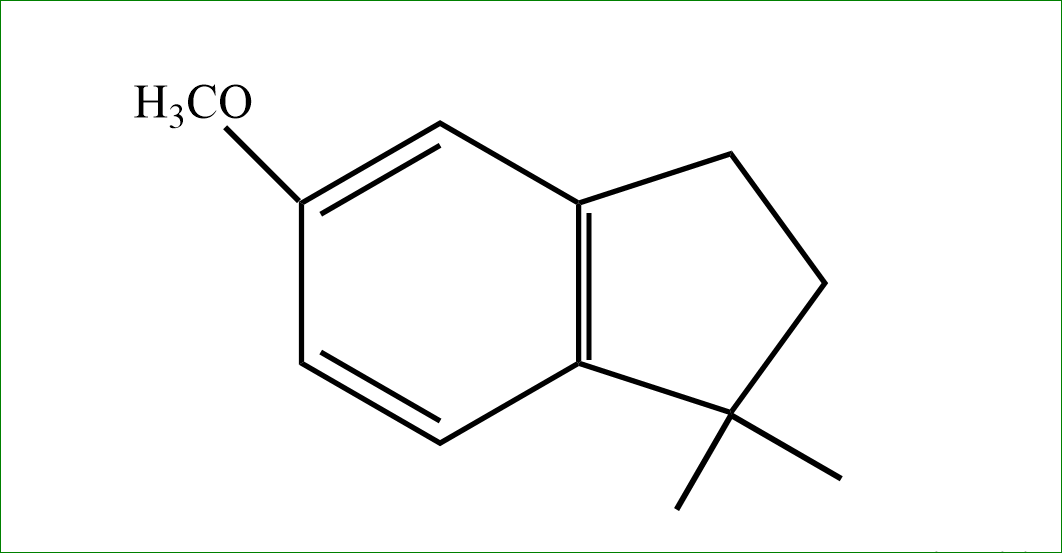
So, the answer is option (D).
Note:
The reaction of an aromatic substrate with an acid chloride in the presence of an aluminium chloride catalyst is used to introduce an acyl group into the aromatic ring through an electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism.
Complete answer:
If we prefer, we can regard these reactions as involving an attack by an aromatic ring on a carbocation. This latter approach is used in the textbook, but the former approach is probably common. When more than one alkyl group is introduced into an aromatic ring during the course of a Friedel crafts alkylation reaction, polyalkylation is said to have occurred.
Step 1: The Cl reacts with $AlCl_2$, which makes the $CHC_l2$ bond weak.

Now in step 2: There is a formation of carbocation.

We know that more stable carbocation is tertiary, So the carbocation moves to tertiary carbon with eliminating the hydrogen bond.
Step 3: If there are more than 3, they try to form rings if possible. Hence the tertiary carbocation vacancy is filled by extracting electrons from the nearest Pi bond.

Step 4: the adjacent hydrogen is released further, to satisfy the valency and the bond is formed on the penta ring cycle side. Here intramolecular alkylation occurs.

So, the answer is option (D).

Note:
The reaction of an aromatic substrate with an acid chloride in the presence of an aluminium chloride catalyst is used to introduce an acyl group into the aromatic ring through an electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




