
Which of the following is referred to as Baeyer’s reagent?
(A) Alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$
(B) Acidic ${{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
(C) Alkaline $N{{a}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
(D) $Mn{{O}_{2}}$
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Baeyer’s reagent is a strong oxidizing reagent which helps identify the presence of double or triple bonds in a hydrocarbon that is used to identify the unsaturation in organic compounds.
Complete answer:
Let us dive straight into the physical and chemical properties of Baeyer’s reagent and analyse its possible uses.
- An alkaline solution of cold potassium permanganate is known as Bayer’s reagent, which is a powerful oxidant.
- It dissolves in water to give purple colour.
- On evaporation it leaves prismatic purplish-black glistening crystals.
- $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is used in organic qualitative analysis to test for the presence of unsaturation. Reaction with double or triple bonds (-C=C- or $-C\equiv C-$ ) causes the colour to fade from purplish-pink to brown.
- Here is the example of reaction of alkene which is an unsaturated compound and it will react with alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ to give corresponding vicinal-diols. Hence, we can conclude that here the double bond between carbon atoms will break and both of the valencies of carbon atoms will be occupied by hydroxyl groups.
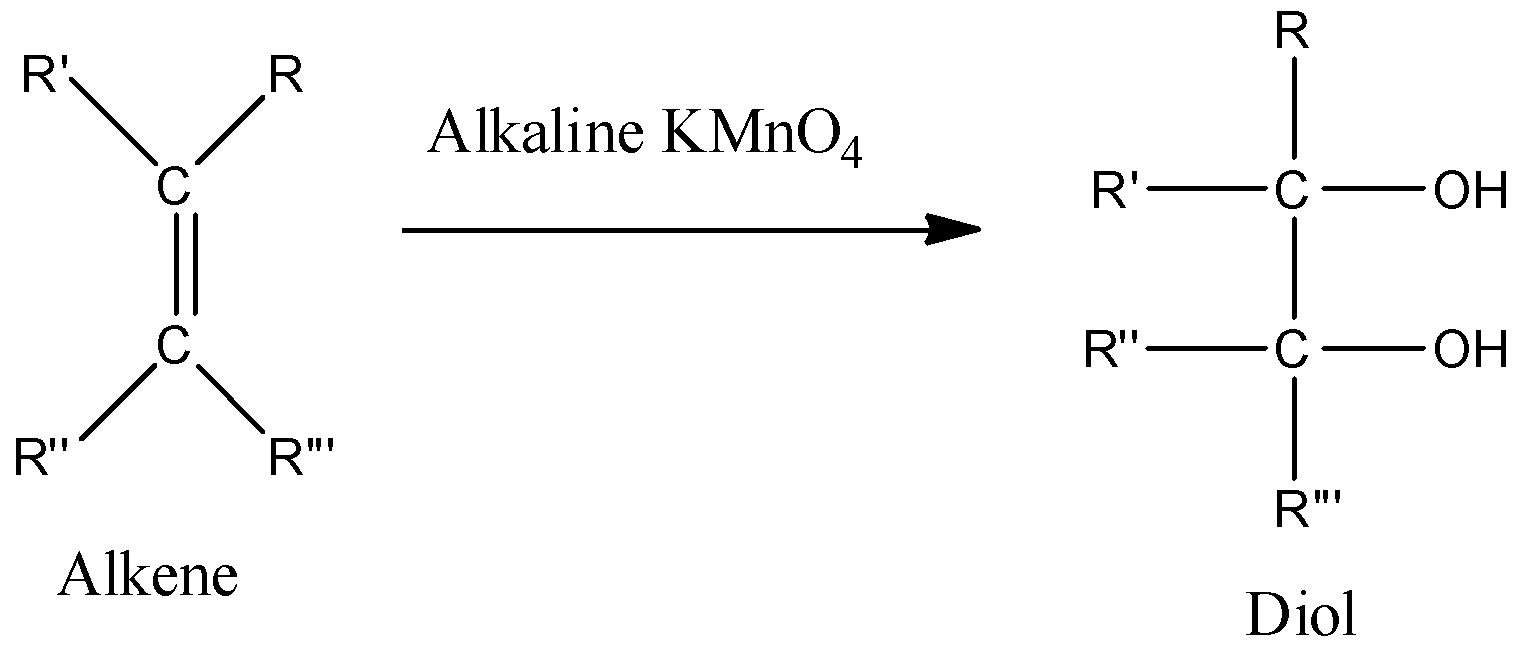
- Baeyer's reagent is also used as a reagent in many organic conversions. However, it uses manganate ions which are somewhat toxic to the environment, so it is not a part of the green chemistry approach.
Thus, we can safely conclude that the required answer to the given question is quite clearly (A).
Note: Remember that Bayer’s reagent cannot oxidise the double bonds of aromatic rings because those double bonds are conjugated with each other and hence they are very stable. Also note that the neutral or acidic solution of $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is not considered as Bayer’s reagent as they have different reactivity.
Complete answer:
Let us dive straight into the physical and chemical properties of Baeyer’s reagent and analyse its possible uses.
- An alkaline solution of cold potassium permanganate is known as Bayer’s reagent, which is a powerful oxidant.
- It dissolves in water to give purple colour.
- On evaporation it leaves prismatic purplish-black glistening crystals.
- $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is used in organic qualitative analysis to test for the presence of unsaturation. Reaction with double or triple bonds (-C=C- or $-C\equiv C-$ ) causes the colour to fade from purplish-pink to brown.
- Here is the example of reaction of alkene which is an unsaturated compound and it will react with alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ to give corresponding vicinal-diols. Hence, we can conclude that here the double bond between carbon atoms will break and both of the valencies of carbon atoms will be occupied by hydroxyl groups.

- Baeyer's reagent is also used as a reagent in many organic conversions. However, it uses manganate ions which are somewhat toxic to the environment, so it is not a part of the green chemistry approach.
Thus, we can safely conclude that the required answer to the given question is quite clearly (A).
Note: Remember that Bayer’s reagent cannot oxidise the double bonds of aromatic rings because those double bonds are conjugated with each other and hence they are very stable. Also note that the neutral or acidic solution of $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is not considered as Bayer’s reagent as they have different reactivity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




