
Which of the following is optically active?
(A) n- propanal
(B) 2- chlorobutane
(C) n – butanal
(D) 3 - pentanol
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We call a compound to be optically active when it has non-superimposable mirror images and can rotate a plane polarized light either in clockwise or anticlockwise direction. It must also contain a chiral carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
-We know that to show optical activity a compound must have a carbon with four different groups attached to it and they also must form non-superimposable mirror images, this means they cannot be stacked on top of each other. Two isomers are formed which differ in their reaction to plane polarized light. One rotates it to the right and is known as dextrorotatory while the other turns it towards right left and is called levorotatory.
-To find out which among this has a chiral carbon, let us have a look at their structures.
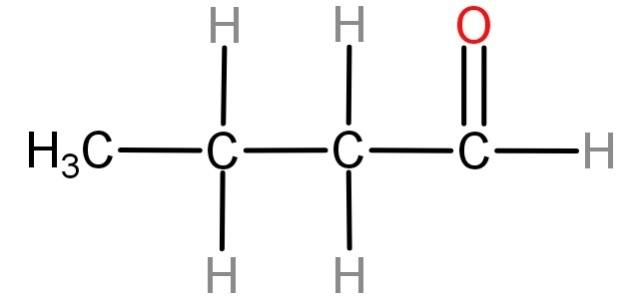
For (A) n-propanal ($C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$): Neither of the carbon atoms of this compound has all 4 valencies occupied by different groups. Hence this compound cannot be optically active.
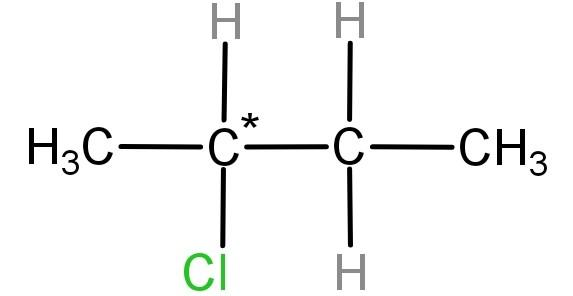
For (B) 2- chlorobutane ($C{H_3} - CH(Cl) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$): In this compound the carbon atom marked as * is the carbon which has all 4 groups different, which makes it a chiral carbon. Hence this compound is an optically active compound.
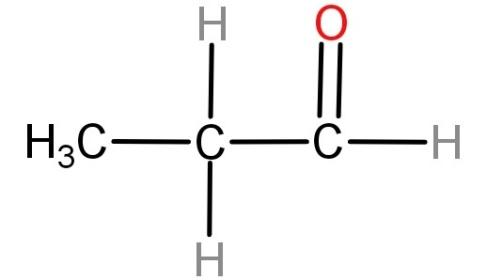
For (C) n- butanal (${H_3}C - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CHO$): Neither of the carbon atoms of this compound has all 4 valencies occupied by different groups. Hence this compound cannot be optically active.
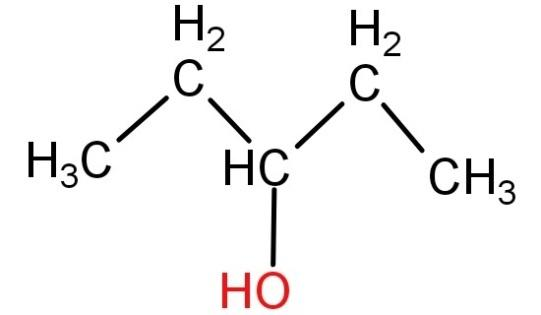
For (D) 3- pentanol (${H_3}C - C{H_2} - CH(OH) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$): Neither of the carbon atoms of this compound has all 4 valencies occupied by different groups. Hence this compound cannot be optically active.
-Since, 2-chlorobutane has a chiral carbon it has the chance to be optically active.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The formation of racemic mixtures is more likely in a laboratory reaction than in a chemical process occurring naturally in the body. If a compound can exist in more than one form, only one of the optical isomers is usually effective.
Note: 2-chlorobutane is an essential intermediate in various organic reactions. Since the halogen group is an effective leaving group which makes this compound useful in both elimination and substitution reactions. The compound is also a reactant for coupling reactions through a Grignard reagent. For example:
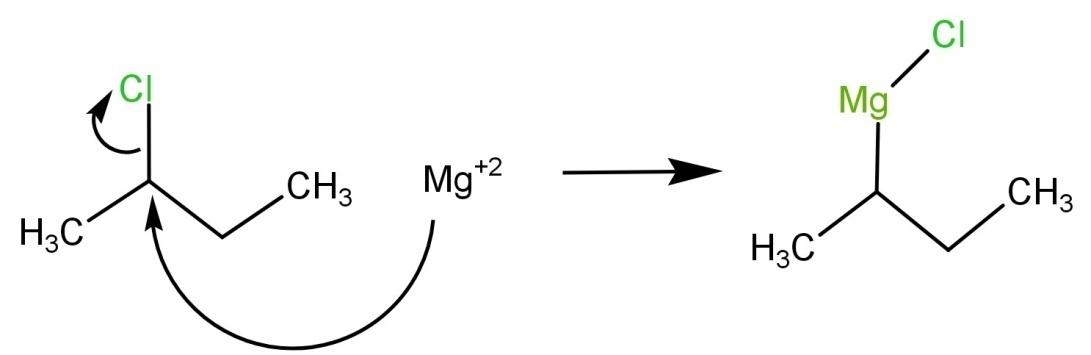
Complete step by step answer:
-We know that to show optical activity a compound must have a carbon with four different groups attached to it and they also must form non-superimposable mirror images, this means they cannot be stacked on top of each other. Two isomers are formed which differ in their reaction to plane polarized light. One rotates it to the right and is known as dextrorotatory while the other turns it towards right left and is called levorotatory.
-To find out which among this has a chiral carbon, let us have a look at their structures.
For (A) n-propanal ($C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$): Neither of the carbon atoms of this compound has all 4 valencies occupied by different groups. Hence this compound cannot be optically active.

For (B) 2- chlorobutane ($C{H_3} - CH(Cl) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$): In this compound the carbon atom marked as * is the carbon which has all 4 groups different, which makes it a chiral carbon. Hence this compound is an optically active compound.

For (C) n- butanal (${H_3}C - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - CHO$): Neither of the carbon atoms of this compound has all 4 valencies occupied by different groups. Hence this compound cannot be optically active.

For (D) 3- pentanol (${H_3}C - C{H_2} - CH(OH) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$): Neither of the carbon atoms of this compound has all 4 valencies occupied by different groups. Hence this compound cannot be optically active.

-Since, 2-chlorobutane has a chiral carbon it has the chance to be optically active.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The formation of racemic mixtures is more likely in a laboratory reaction than in a chemical process occurring naturally in the body. If a compound can exist in more than one form, only one of the optical isomers is usually effective.
Note: 2-chlorobutane is an essential intermediate in various organic reactions. Since the halogen group is an effective leaving group which makes this compound useful in both elimination and substitution reactions. The compound is also a reactant for coupling reactions through a Grignard reagent. For example:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




