
Which of the following is aromatic in nature?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. None of these




Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Compounds that contain one or more isolated or fused benzene rings are called aromatic compounds.
When the bonding orbital/electron is not restricted to only two atoms but is spread over more than two atoms then, such orbitals/electrons are called delocalized and this phenomenon is known as delocalization.
Complete step by step solution:
Hückel's rule estimates whether a compound will have aromatic properties or not. Criteria for simple aromatics are:
The molecule must have ${ 4(n+2)\Pi { e }^{ - } }$ in the delocalized p-orbital cloud.
The molecule must be able to be planar and are cyclic.
Each atom making up the cyclic compound must be able to participate in delocalizing the electrons by having a p-orbital or an unshared pair of electrons.
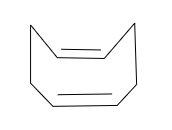
It is a cyclic compound and it has conjugate but Huckel’s rule ${ 4(n+2)\Pi { e }^{ - } }$ rule is not followed. Also, this structure is not a plan. Hence, it is non-aromatic in nature.
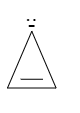
As there is an extra lone pair of electrons present so the total number of electrons comes out to be ${ 4\Pi { e }^{ - } }$. It is also cyclic. Hence, it is anti-aromatic in nature.
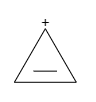
It is cyclic and planer. Also, due to the presence of ${ 4(n+2)\Pi { e }^{ - } }$, it follows Huckel’s rule and therefore, it is aromatic in nature.
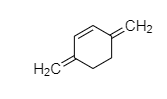
It is cyclic but it is not planer and it has ${ 4\Pi { e }^{ - } }$ in conjugation but not in the ring. Hence, it is non-aromatic in nature.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option B. As it is cyclic and planar but it does not follow Huckel’s rule, so it is antiaromatic, not aromatic in nature.
When the bonding orbital/electron is not restricted to only two atoms but is spread over more than two atoms then, such orbitals/electrons are called delocalized and this phenomenon is known as delocalization.
Complete step by step solution:
Hückel's rule estimates whether a compound will have aromatic properties or not. Criteria for simple aromatics are:
The molecule must have ${ 4(n+2)\Pi { e }^{ - } }$ in the delocalized p-orbital cloud.
The molecule must be able to be planar and are cyclic.
Each atom making up the cyclic compound must be able to participate in delocalizing the electrons by having a p-orbital or an unshared pair of electrons.
It is a cyclic compound and it has conjugate but Huckel’s rule ${ 4(n+2)\Pi { e }^{ - } }$ rule is not followed. Also, this structure is not a plan. Hence, it is non-aromatic in nature.
As there is an extra lone pair of electrons present so the total number of electrons comes out to be ${ 4\Pi { e }^{ - } }$. It is also cyclic. Hence, it is anti-aromatic in nature.
It is cyclic and planer. Also, due to the presence of ${ 4(n+2)\Pi { e }^{ - } }$, it follows Huckel’s rule and therefore, it is aromatic in nature.
It is cyclic but it is not planer and it has ${ 4\Pi { e }^{ - } }$ in conjugation but not in the ring. Hence, it is non-aromatic in nature.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option B. As it is cyclic and planar but it does not follow Huckel’s rule, so it is antiaromatic, not aromatic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




