
Which of the following is an example of chelating ligand?
A. $NO_{2}^{-}$
B. Chloro
C. Bromo
D. en
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: A ligand will be called a chelating ligand if it can have two or more than two points of attachment to the central metal atom of a coordination compound. Find out which of the ligands in the options have two centres and from each of the centres, a lone pair of electrons can be donated to form a coordinate bond with the central metal atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s learn about chelating ligands first.
- Chelating ligands are those which use its donor atoms (more than one) to form a coordinated Bond with the central metal atom to give a ring-like structure. This ring is called the chelate ring and the ligand is called the chelating ligand.
- The process of forming metal chelate by attachment of multidentate ligands i.e. ligands with more than one donor atom, with the central metal atom, in which ligand acts as a chelating agent is known as chelation.
- The stability of chelate is dependent on the size of the chelating ring. The stability of the coordination complex increases with the increase in chelation.
Coming back to the question, we will now check each option and find out which one of them is a chelating ligand.
Option A) $NO_{2}^{-}$ is a ligand which contains two or more different donor atoms present in it and it is the example of an ambidentate ligand. An ambidentate ligand can donate lone pairs of electrons by more than one donor but only one at a time. Only one atom can link with the central metal atom so this option is incorrect as it cannot form chelating ligand.
Option B) and C) are also incorrect as Chloro and Bromo are monodentate ligands which means that it can only donate one electron pair to the central metal atom or ion. So, it cannot form chelating ligands.
Now for option (D) en i.e ethylenediamine ligand is a bidentate ligand which means it has more than one donor atom to form a coordinate bond with a central metal atom and each of these donors can donate electrons simultaneously to form a ring-like structure.
The chemical formula of ethylenediamine $N{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}$.
As we can see from the formula that there are two amine groups in the compound and these two amine groups have lone pairs of electrons in their respective nitrogens. Thus, each of them can donate the lone pair of electrons and act as a chelating agent.
The structure of ethylenediamine is given below.
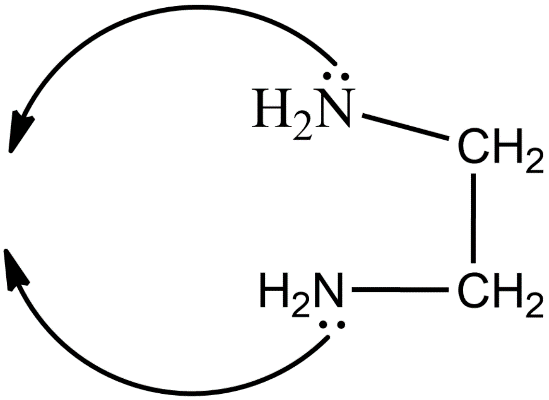
The coordination compound having this ligand is tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride. The structure of this compound is given below.
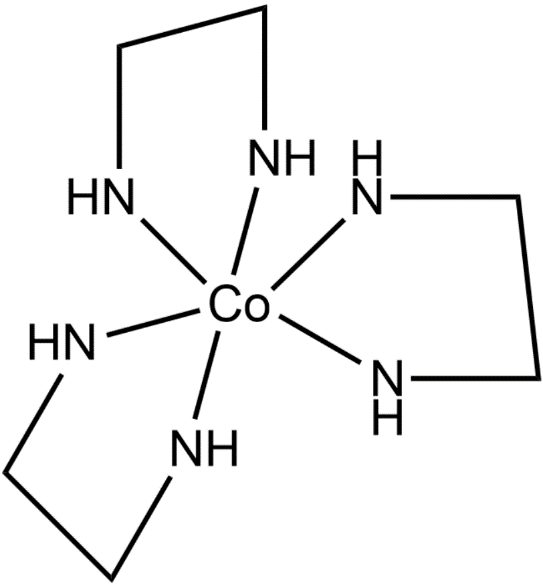
Hence, the option (D) is the correct one.
Note: Some people might think that since the ambidentate ligand $NO_{2}^{-}$ has two donor sites and thus it can act as a chelating ligand. But, the main criteria for the chelating ligand is that both the donor atoms should be able to donate electrons simultaneously i.e. together. But in the case of ambidentate ligands, only one of them can donate electrons at a time. Thus, they can't form chelating compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s learn about chelating ligands first.
- Chelating ligands are those which use its donor atoms (more than one) to form a coordinated Bond with the central metal atom to give a ring-like structure. This ring is called the chelate ring and the ligand is called the chelating ligand.
- The process of forming metal chelate by attachment of multidentate ligands i.e. ligands with more than one donor atom, with the central metal atom, in which ligand acts as a chelating agent is known as chelation.
- The stability of chelate is dependent on the size of the chelating ring. The stability of the coordination complex increases with the increase in chelation.
Coming back to the question, we will now check each option and find out which one of them is a chelating ligand.
Option A) $NO_{2}^{-}$ is a ligand which contains two or more different donor atoms present in it and it is the example of an ambidentate ligand. An ambidentate ligand can donate lone pairs of electrons by more than one donor but only one at a time. Only one atom can link with the central metal atom so this option is incorrect as it cannot form chelating ligand.
Option B) and C) are also incorrect as Chloro and Bromo are monodentate ligands which means that it can only donate one electron pair to the central metal atom or ion. So, it cannot form chelating ligands.
Now for option (D) en i.e ethylenediamine ligand is a bidentate ligand which means it has more than one donor atom to form a coordinate bond with a central metal atom and each of these donors can donate electrons simultaneously to form a ring-like structure.
The chemical formula of ethylenediamine $N{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}$.
As we can see from the formula that there are two amine groups in the compound and these two amine groups have lone pairs of electrons in their respective nitrogens. Thus, each of them can donate the lone pair of electrons and act as a chelating agent.
The structure of ethylenediamine is given below.

The coordination compound having this ligand is tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride. The structure of this compound is given below.

Hence, the option (D) is the correct one.
Note: Some people might think that since the ambidentate ligand $NO_{2}^{-}$ has two donor sites and thus it can act as a chelating ligand. But, the main criteria for the chelating ligand is that both the donor atoms should be able to donate electrons simultaneously i.e. together. But in the case of ambidentate ligands, only one of them can donate electrons at a time. Thus, they can't form chelating compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




