
Which of the following is an example of a direct band gap intrinsic semiconductor?
A. Silicon
B. Germanium
C. Gallium Arsenide
D. None of these
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint:For solving this question, we need to understand the concept of direct band gap. Normally, all semiconductors are classified according to their band gaps into two types: direct band gap and indirect band gap. We will discuss the direct band gap and then see which one of the given options falls under the category of direct band gap.
Complete answer:
Let us first define direct band gap intrinsic semiconductors. The materials for which maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band lie for the same value of k are called the direct band gap materials. This satisfies the condition of energy and momentum conservation. For example, GaAs, InP and CdS.
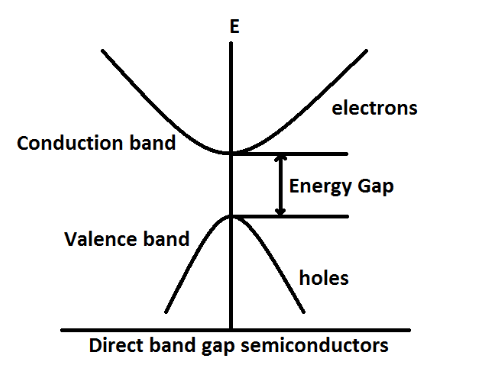
From the figure, we can clearly see that the maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band lie for the same vector which is called the k-vector.
Indirect band gap materials are defined as the materials for which maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band do not occur at the same value of k. For example, Si and Ge.
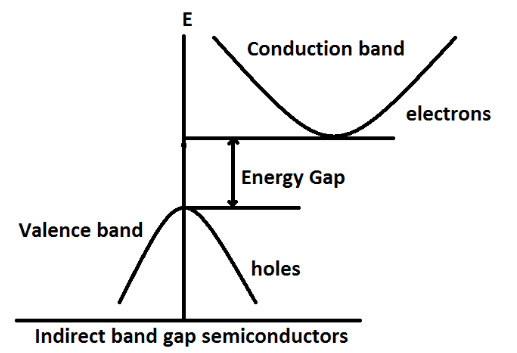
From the figure, we can clearly see that maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band do not lie for same vector which is called the k-vector.As we have seen, Gallium Arsenide GaAs is a direct band gap semiconductor and other two options Silicon Si and Germanium Ge are an indirect gap semiconductor.
Thus, option C is the right answer.
Note:The difference between direct gap and indirect gap semiconductors is very important. It helps in deciding which semiconductors can be used in devices requiring light output. For instance, generally semiconductor light emitters and lasers must be made of materials capable of direct band to band transactions or of indirect materials with vertical transactions between defect states.
Complete answer:
Let us first define direct band gap intrinsic semiconductors. The materials for which maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band lie for the same value of k are called the direct band gap materials. This satisfies the condition of energy and momentum conservation. For example, GaAs, InP and CdS.

From the figure, we can clearly see that the maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band lie for the same vector which is called the k-vector.
Indirect band gap materials are defined as the materials for which maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band do not occur at the same value of k. For example, Si and Ge.

From the figure, we can clearly see that maximum of valence band and minimum of conduction band do not lie for same vector which is called the k-vector.As we have seen, Gallium Arsenide GaAs is a direct band gap semiconductor and other two options Silicon Si and Germanium Ge are an indirect gap semiconductor.
Thus, option C is the right answer.
Note:The difference between direct gap and indirect gap semiconductors is very important. It helps in deciding which semiconductors can be used in devices requiring light output. For instance, generally semiconductor light emitters and lasers must be made of materials capable of direct band to band transactions or of indirect materials with vertical transactions between defect states.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




