
Which of the following is a tetrabasic acid?
(A) Hypophosphorous acid
(B) Metaphosphoric acid
(C) Pyrophosphoric acid
(D) Orthophosphoric acid
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: Bronsted-Lowry theory, which is also termed as proton theory of acids and bases, states that the compound which can transfer a proton to another compound is termed as acid and those that accept the protons are bases. The proton is the nuclear particle which contains positive charge and is represented by the symbol $ {H^ + } $ because it makes the nucleus of a hydrogen atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Monobasic acids are those acids which enhance only one hydrogen ion $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in the water. Example: acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid. Dibasic acids are those acids which enhance two hydrogen ions $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in water. Example: Oxalic acid, sulphuric acid, carbonic acid. Tribasic acid are those acids which enhance three hydrogen ions $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in water. Example: phosphorus acid and phosphoric acid.
Tetrabasic acids are those acids which enhance four hydrogen ions $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in water.
In Hypophosphorous acid which is $ {H_3}P{O_2} $ .
Structure of $ {H_3}P{O_2} $ :
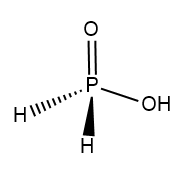
In Metaphosphoric acid whose formula is $ HP{O_3} $ .
Structure of $ HP{O_3} $ :
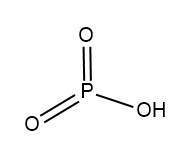
In pyrophosphoric acid whose formula is $ {H_4}{P_2}{O_7} $ .
Structure of $ {H_4}{P_2}{O_7} $ :
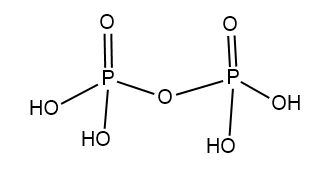
In Orthophosphoric acid whose formula is $ {H_3}P{O_4} $ .
Structure of $ {H_3}P{O_4} $ :
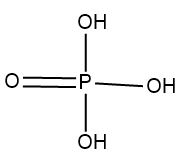
Thus, option $ \left( C \right) $ is the right answer.
Note:
The number of hydronium ions formed by one molecule of the acid in the aqueous solution is termed as the basicity of an acid. A monobasic acid has one hydrogen atom to donate in the acid-base reaction. Thus, the monobasic molecule has merely one replaceable hydrogen atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Monobasic acids are those acids which enhance only one hydrogen ion $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in the water. Example: acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid. Dibasic acids are those acids which enhance two hydrogen ions $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in water. Example: Oxalic acid, sulphuric acid, carbonic acid. Tribasic acid are those acids which enhance three hydrogen ions $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in water. Example: phosphorus acid and phosphoric acid.
Tetrabasic acids are those acids which enhance four hydrogen ions $ \left( {{H^ + }} \right) $ per molecule in water.
In Hypophosphorous acid which is $ {H_3}P{O_2} $ .
Structure of $ {H_3}P{O_2} $ :

In Metaphosphoric acid whose formula is $ HP{O_3} $ .
Structure of $ HP{O_3} $ :

In pyrophosphoric acid whose formula is $ {H_4}{P_2}{O_7} $ .
Structure of $ {H_4}{P_2}{O_7} $ :

In Orthophosphoric acid whose formula is $ {H_3}P{O_4} $ .
Structure of $ {H_3}P{O_4} $ :

Thus, option $ \left( C \right) $ is the right answer.
Note:
The number of hydronium ions formed by one molecule of the acid in the aqueous solution is termed as the basicity of an acid. A monobasic acid has one hydrogen atom to donate in the acid-base reaction. Thus, the monobasic molecule has merely one replaceable hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




