
Which of the following is a polar molecule?
A. \[{{H}_{2}}\]
B. \[C{{O}_{2}}\]
C. \[{{H}_{2}}O\]
D. \[NaCl\]
E. \[C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}\]
Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: Transfer of electrons from one atom to another implies polar molecule. Equal share of electrons between two atoms implies a nonpolar molecule. So, first draw the electron distribution of the molecule that is the path of formation of the bond, then you can easily identify polar and nonpolar molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
A polar molecule is a molecule where there is transfer of electrons from less electronegative to more electronegative atom. In other words, we can say that there is a considerable electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.
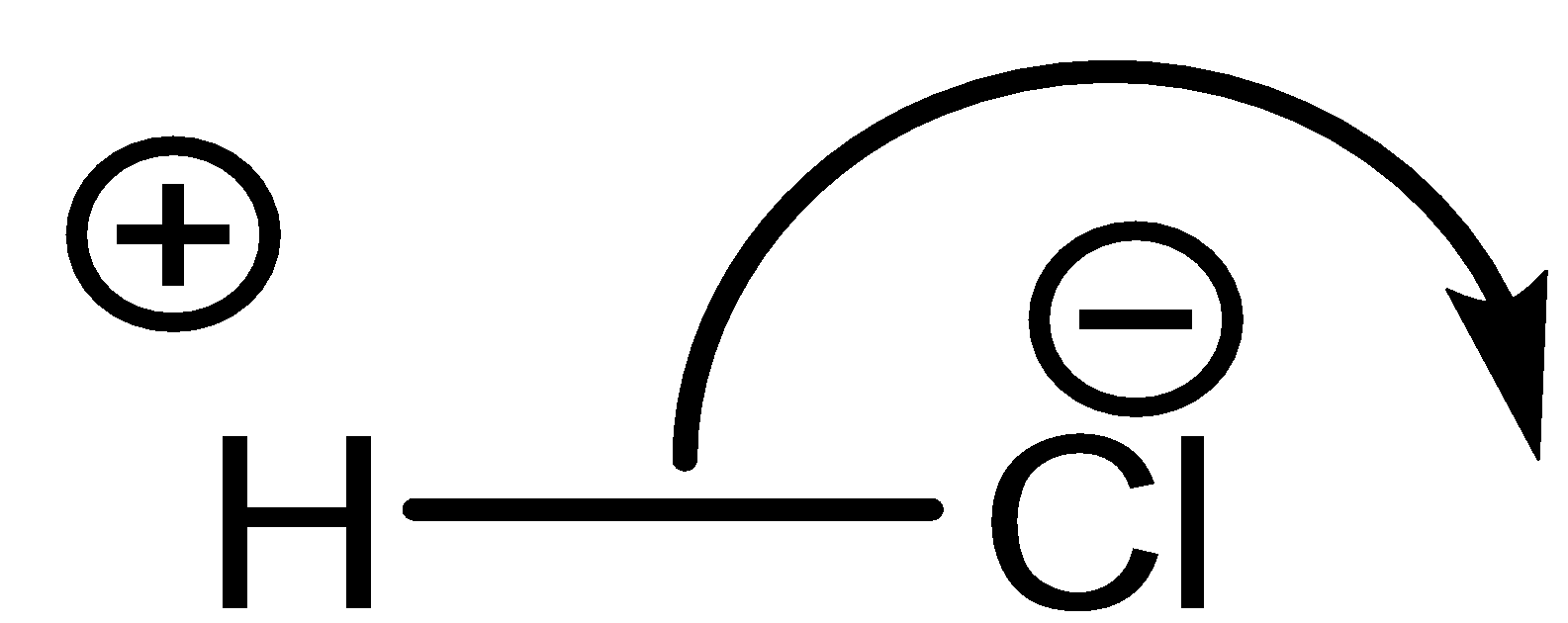
A nonpolar molecule is one where there is an equal share of electrons between the bonded atoms of a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other’s dipole moment out.

Let us now look at each molecule with diagram and find out the polar molecule:
Each hydrogen atom has one electron and needs one electron to complete its first energy level. Since both the atoms are identical, the electrons are shared equally, so hydrogen is non-polar.

\[C{{O}_{2}}\] has two polar bonds, but the net dipole moment in the linear molecule cancels each other out making \[C{{O}_{2}}\] a nonpolar molecule.
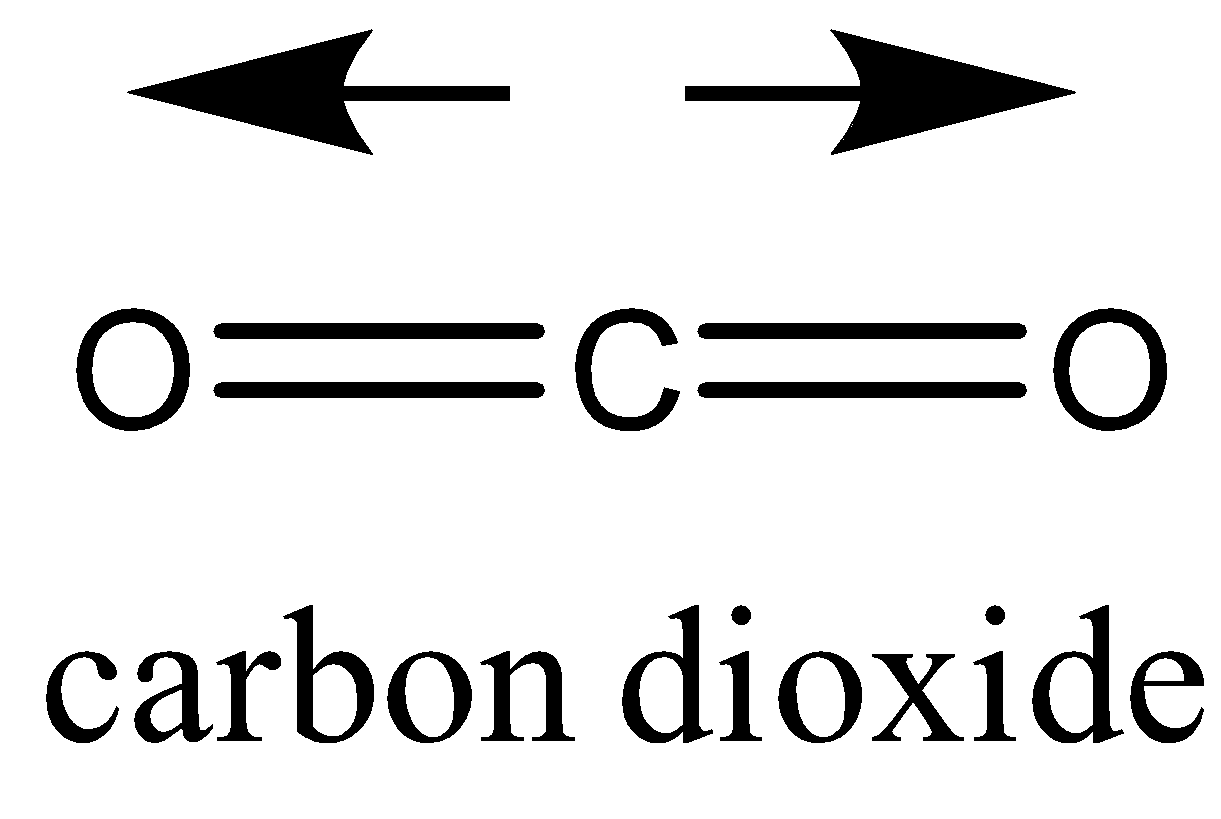
\[{{H}_{2}}O\] has two polar bonds, but the polar bonds in the bent molecule results in a net dipole moment making \[{{H}_{2}}O\] a polar molecule.

\[NaCl\] is a polar molecule due to large electronegativity difference, so electrons transfer from sodium to chlorine atom completely.
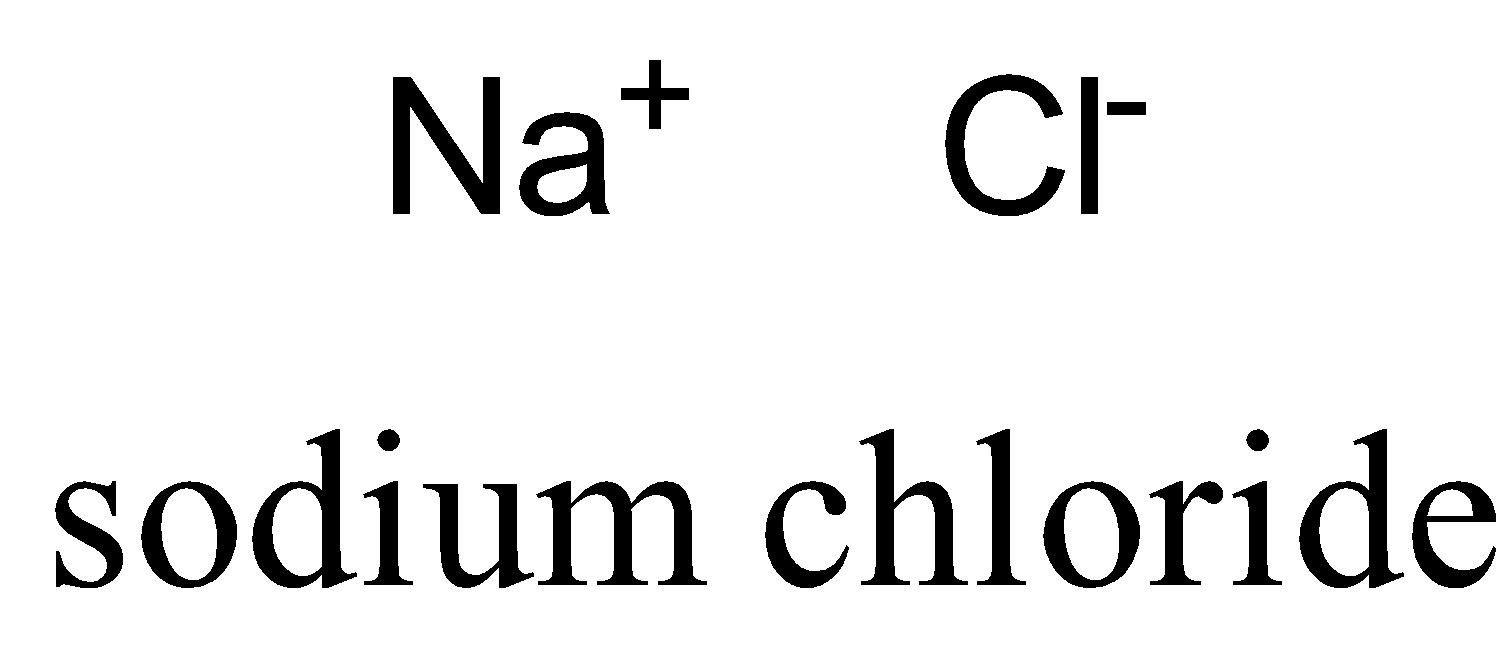
Due to the small electronegativity difference between C and H, it is slightly polar but the molecule is symmetrical around its centre and results in an even distribution of electrons, making it non-polar.

So, correct options are C, D.
Note: Apart from electron distribution and electronegativity difference, you have to see the net dipole moment and shape of the molecule to determine the polarity of the molecule. Students often forget to consider the shape of the molecule which can lead them to make a mistake on polarity of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
A polar molecule is a molecule where there is transfer of electrons from less electronegative to more electronegative atom. In other words, we can say that there is a considerable electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.

A nonpolar molecule is one where there is an equal share of electrons between the bonded atoms of a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other’s dipole moment out.

Let us now look at each molecule with diagram and find out the polar molecule:
Each hydrogen atom has one electron and needs one electron to complete its first energy level. Since both the atoms are identical, the electrons are shared equally, so hydrogen is non-polar.

\[C{{O}_{2}}\] has two polar bonds, but the net dipole moment in the linear molecule cancels each other out making \[C{{O}_{2}}\] a nonpolar molecule.
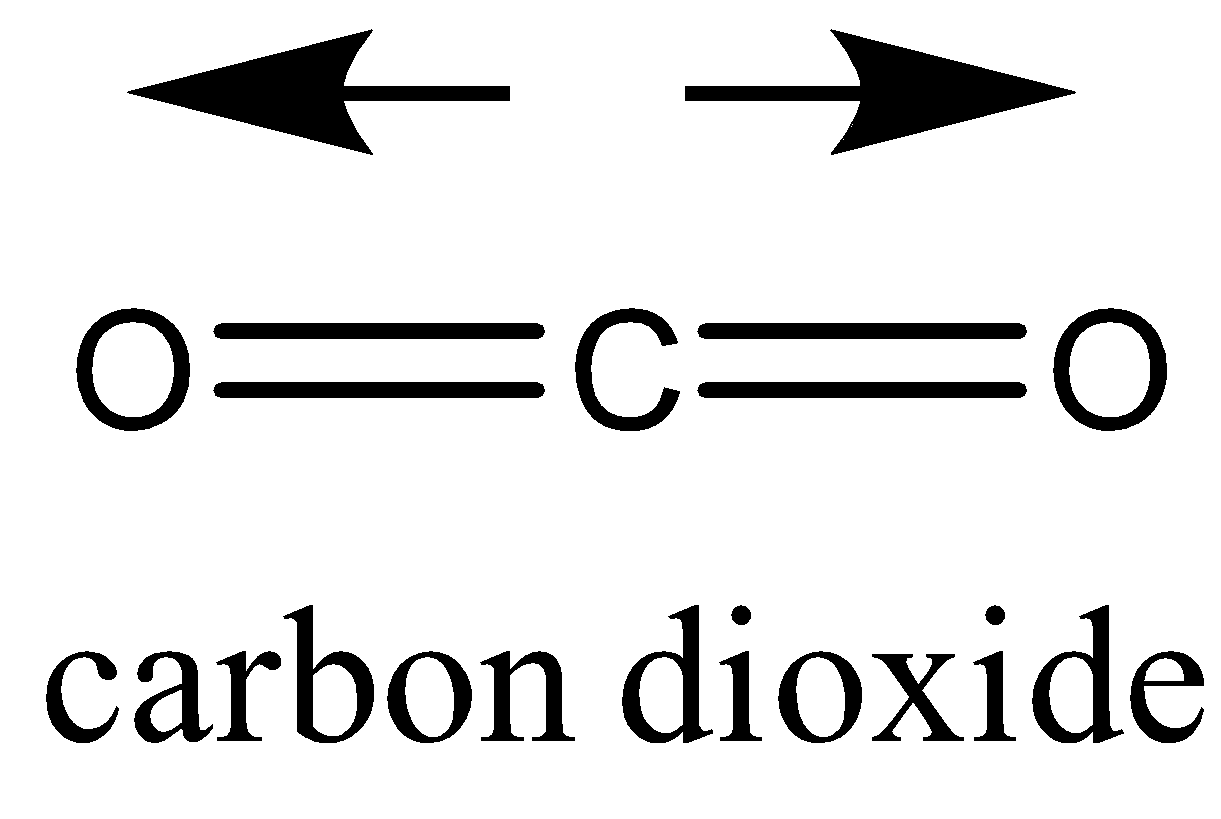
\[{{H}_{2}}O\] has two polar bonds, but the polar bonds in the bent molecule results in a net dipole moment making \[{{H}_{2}}O\] a polar molecule.

\[NaCl\] is a polar molecule due to large electronegativity difference, so electrons transfer from sodium to chlorine atom completely.
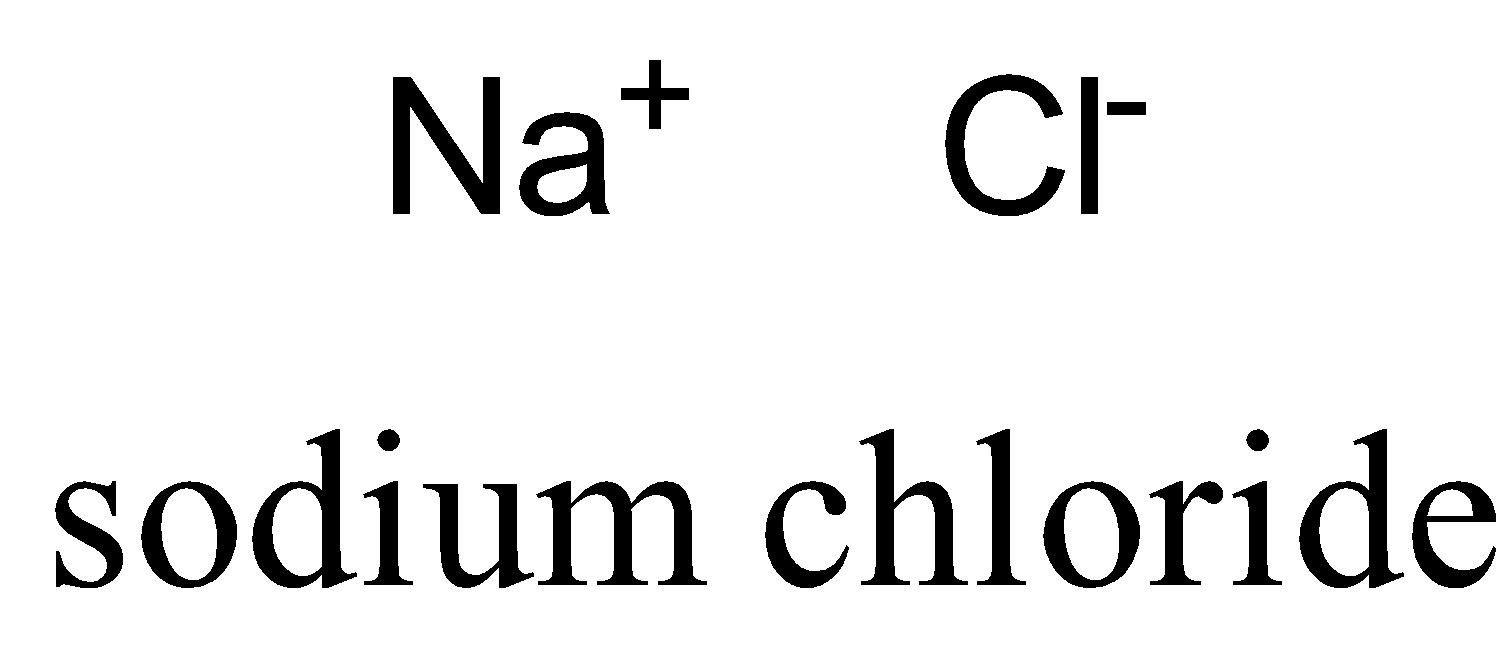
Due to the small electronegativity difference between C and H, it is slightly polar but the molecule is symmetrical around its centre and results in an even distribution of electrons, making it non-polar.

So, correct options are C, D.
Note: Apart from electron distribution and electronegativity difference, you have to see the net dipole moment and shape of the molecule to determine the polarity of the molecule. Students often forget to consider the shape of the molecule which can lead them to make a mistake on polarity of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




