
Which of the following is a polar molecule ?
(a) Ammonia $(N{H_3})$
(b) Methane $(C{H_4})$
(c) Ethylene $({C_2}{H_4})$
(d) Carbon Tetrachloride $(CC{l_4})$
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint: A polar molecule is a molecule in which there is an electronegativity difference between atoms and hence shared pairs of electrons are not at equal distance between these atoms. In this way a polar covalent bond is formed. Polar molecules always have some net quantity of dipole moment.
Complete answer:
A polar molecule has some net dipole moment. In this molecule, the net dipole moment can never be zero. A polar molecule always contains an electronegative element so that there is an electronegativity difference between atoms and hence shared pairs of electrons are not at equal distance between these atoms. Hence, in this way a polar covalent bond is formed.
Now, we will discuss each given molecule one by one:
a) Ammonia $(N{H_3})$
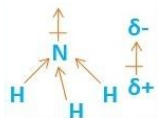
As we can see that in the $N{H_3}$ molecule, there is an electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. As nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen atoms so it pulls electron density towards itself and hence there is a net dipole moment in the upward direction.
Hence, we can say that Ammonia is a polar molecule.
b) Methane $(C{H_4})$
In methane molecules, there are four hydrogen-carbon bonds and there is some electronegativity difference between these atoms. But, the structure of the methane molecule is tetrahedral and all the $C - H$ bonds are at ${90^o}$ to each other. Hence all the four bonds cancel out each other’s dipole moment and the net dipole moment of the methane molecule is zero.
Hence, it is a nonpolar molecule.
c) Ethylene $({C_2}{H_4})$
In ethylene molecules, all the four $C - H$ bonds cancel out each other’s dipole moment as they all are in plane and the net dipole moment of the methane molecule is zero.
Hence, we can say that ethylene molecules are nonpolar.
d) Carbon Tetrachloride $(CC{l_4})$
Carbon tetrachloride is the same as methane as we have discussed above. It has tetrahedral structure and all the four bonds cancel out each other’s dipole moment and the net dipole moment of the methane molecule is zero.
Hence, it is a nonpolar molecule.
Therefore, only ammonia is a polar molecule from given options.
Hence, Option (a) Ammonia $(N{H_3})$ is correct.
Note:
Therefore, a polar molecule is one whose one end is slightly positive and the other end is slightly negative. There is always an electronegativity difference between the atoms of a molecule and a shared pair of electrons will be attracted by the more electronegative one. Hence, there will be a permanent dipole moment in a polar molecule.
Complete answer:
A polar molecule has some net dipole moment. In this molecule, the net dipole moment can never be zero. A polar molecule always contains an electronegative element so that there is an electronegativity difference between atoms and hence shared pairs of electrons are not at equal distance between these atoms. Hence, in this way a polar covalent bond is formed.
Now, we will discuss each given molecule one by one:
a) Ammonia $(N{H_3})$

As we can see that in the $N{H_3}$ molecule, there is an electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. As nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen atoms so it pulls electron density towards itself and hence there is a net dipole moment in the upward direction.
Hence, we can say that Ammonia is a polar molecule.
b) Methane $(C{H_4})$
In methane molecules, there are four hydrogen-carbon bonds and there is some electronegativity difference between these atoms. But, the structure of the methane molecule is tetrahedral and all the $C - H$ bonds are at ${90^o}$ to each other. Hence all the four bonds cancel out each other’s dipole moment and the net dipole moment of the methane molecule is zero.
Hence, it is a nonpolar molecule.
c) Ethylene $({C_2}{H_4})$
In ethylene molecules, all the four $C - H$ bonds cancel out each other’s dipole moment as they all are in plane and the net dipole moment of the methane molecule is zero.
Hence, we can say that ethylene molecules are nonpolar.
d) Carbon Tetrachloride $(CC{l_4})$
Carbon tetrachloride is the same as methane as we have discussed above. It has tetrahedral structure and all the four bonds cancel out each other’s dipole moment and the net dipole moment of the methane molecule is zero.
Hence, it is a nonpolar molecule.
Therefore, only ammonia is a polar molecule from given options.
Hence, Option (a) Ammonia $(N{H_3})$ is correct.
Note:
Therefore, a polar molecule is one whose one end is slightly positive and the other end is slightly negative. There is always an electronegativity difference between the atoms of a molecule and a shared pair of electrons will be attracted by the more electronegative one. Hence, there will be a permanent dipole moment in a polar molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




