
Which of the following is a biodegradable polymer?
(A)
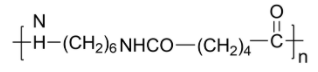
(B)
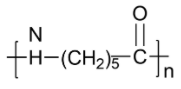
(C)
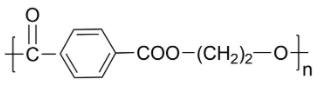
(D)
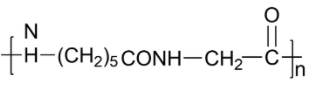

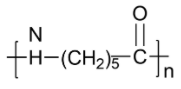

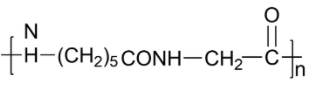
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Biodegradable polymers are the polymers that can be decomposed by microbial action yielding natural by-products such as gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, water, biomass, and inorganic salts.
Complete step by step solution:
-A substance or a material consisting of very large molecules, or macromolecules, which are composed of many repeating units are called polymers.
-The word polymer is derived from the Greek word ‘polus’ meaning many or much and ‘meros’ meaning part.
-A polymer-based on the origin of source, can be of three classes, natural polymers, synthetic polymers, and semi-synthetic polymers.
-Additionally, polymers are divided into two special classes as biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
-The polymers that break down after its intended purpose by bacterial decomposition either by an aerobic or anaerobic process, giving natural and simpler by-products are called Biodegradable polymers.
-Non-biodegradable polymers are the polymers that cannot be or very slowly decomposed by the action of microorganisms.
-Most common examples of biodegradable polymers are aliphatic polyesters.
-The structure in option A is Nylon 6,6 polymer. Nylon 6,6 also known as nylon 66 obtained by the polymerization of adipic acid with hexamethylene diamine is a non-biodegradable polymer.
-The structure in option B is Nylon 6 polymer which was developed to reduce the properties of nylon 66 polymer. The presence of amide bonds in the molecules makes the molecule non-biodegradable.
-The structure in option C is Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polymer used as an insulator in electrical and electronics industries. PBT is not a biodegradable polymer.
-The structure in option D is Nylon-2-Nylon-6 which is a copolymer of glycine and w-aminocaproic acid along with polyamide linkages. This is a biodegradable polymer.
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note: Biodegradable polymers have significant applications in various fields including medicine, agriculture, and packaging. One of the most and trending uses of biodegradable polymers are in controlled drug delivery and release.
Complete step by step solution:
-A substance or a material consisting of very large molecules, or macromolecules, which are composed of many repeating units are called polymers.
-The word polymer is derived from the Greek word ‘polus’ meaning many or much and ‘meros’ meaning part.
-A polymer-based on the origin of source, can be of three classes, natural polymers, synthetic polymers, and semi-synthetic polymers.
-Additionally, polymers are divided into two special classes as biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers.
-The polymers that break down after its intended purpose by bacterial decomposition either by an aerobic or anaerobic process, giving natural and simpler by-products are called Biodegradable polymers.
-Non-biodegradable polymers are the polymers that cannot be or very slowly decomposed by the action of microorganisms.
-Most common examples of biodegradable polymers are aliphatic polyesters.
-The structure in option A is Nylon 6,6 polymer. Nylon 6,6 also known as nylon 66 obtained by the polymerization of adipic acid with hexamethylene diamine is a non-biodegradable polymer.
-The structure in option B is Nylon 6 polymer which was developed to reduce the properties of nylon 66 polymer. The presence of amide bonds in the molecules makes the molecule non-biodegradable.
-The structure in option C is Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polymer used as an insulator in electrical and electronics industries. PBT is not a biodegradable polymer.
-The structure in option D is Nylon-2-Nylon-6 which is a copolymer of glycine and w-aminocaproic acid along with polyamide linkages. This is a biodegradable polymer.
Hence the correct answer is option D.
Note: Biodegradable polymers have significant applications in various fields including medicine, agriculture, and packaging. One of the most and trending uses of biodegradable polymers are in controlled drug delivery and release.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




