
Which of the following has +R (resonance) effect?
a.) \[-CN\]
b.) \[-CHO\]
c.) \[-N{{H}_{2}}\]
d.) \[-N{{O}_{2}}\]
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: +R effect is the positive resonance effect and it is shown by electron donating groups. We can take help of canonical structures to see how there is a withdrawal or releasing effect of electrons attributed to a particular substituent through the delocalization of π or pi-electron.
Complete step by step answer:
The two types of resonance or mesomeric effects. They are-
+R or +M
-R or -M
Negative resonance or mesomeric effect (-M or -R): It is shown by the groups that withdraw electrons by delocalization mechanism from the rest of the conjugated molecule and are denoted by -M or -R. The electron density on the rest of the molecular entity is decreased due to this effect.
Examples of groups showing negative resonance are \[N{{O}_{2}}\], CO, COOH, CN, CHO etc.
Positive resonance or mesomeric effect (+M or +R): It is shown by the groups that donates or releases electrons to the rest of the conjugated molecule by delocalization. These groups are denoted by +M or +R. Due to this effect, the electron density on the rest of the molecular entity is increased.
Examples of groups showing positive resonance are \[N{{H}_{2}}\], OR, SH, OH etc.
Now, let us see the options given and check if they are electron donating or withdrawing.
At first we have –CN. Cyanide group has a positive group i.e. C directly attached to the benzene ring. Therefore, it will show –R resonance effect.
Then we have –CHO. Here also we have a positive group carbon directly attached to the benzene ring and it will pull electrons towards it. Thus, it will show –R effect.
Next we have \[-N{{H}_{2}}\] . Here, the negative group is attached to the benzene ring and thus will donate its electron cloud resulting in +R effect.
The mechanism can be given as below.
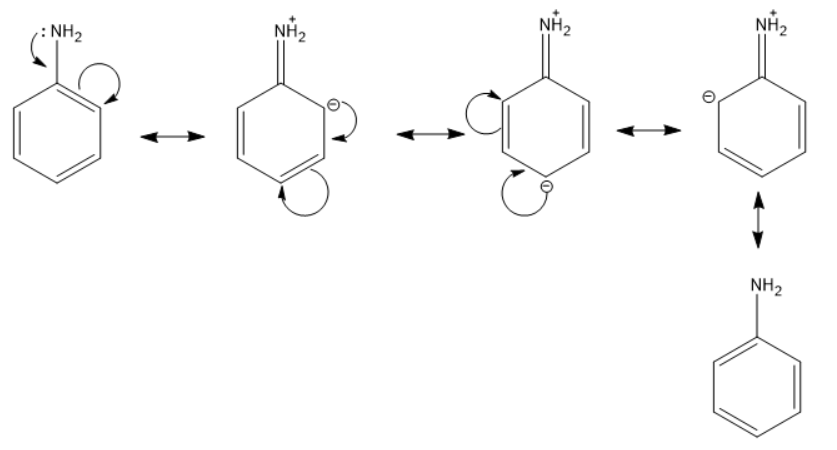
And lastly we have $-N{{O}_{2}}$. If we compare nitrogen and oxygen, nitrogen is more electropositive therefore it will show –R effect.
We can understand from the above discussion that $-N{{H}_{2}}$ will show +R.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: There is polarity produced in a molecule by the interaction between a lone electron pair and a pi bond. It is generally found in molecules with conjugated double bonds or in molecules having at least one lone pair and one double bond.
A carbocation is stabilised through +R effect i.e. resonance of the positive charge around the ring. But there are some cases where an alkyl carbocation with a +I effect is more stable than a carbocation with +R group although resonance effect has higher priority.
Complete step by step answer:
The two types of resonance or mesomeric effects. They are-
+R or +M
-R or -M
Negative resonance or mesomeric effect (-M or -R): It is shown by the groups that withdraw electrons by delocalization mechanism from the rest of the conjugated molecule and are denoted by -M or -R. The electron density on the rest of the molecular entity is decreased due to this effect.
Examples of groups showing negative resonance are \[N{{O}_{2}}\], CO, COOH, CN, CHO etc.
Positive resonance or mesomeric effect (+M or +R): It is shown by the groups that donates or releases electrons to the rest of the conjugated molecule by delocalization. These groups are denoted by +M or +R. Due to this effect, the electron density on the rest of the molecular entity is increased.
Examples of groups showing positive resonance are \[N{{H}_{2}}\], OR, SH, OH etc.
Now, let us see the options given and check if they are electron donating or withdrawing.
At first we have –CN. Cyanide group has a positive group i.e. C directly attached to the benzene ring. Therefore, it will show –R resonance effect.
Then we have –CHO. Here also we have a positive group carbon directly attached to the benzene ring and it will pull electrons towards it. Thus, it will show –R effect.
Next we have \[-N{{H}_{2}}\] . Here, the negative group is attached to the benzene ring and thus will donate its electron cloud resulting in +R effect.
The mechanism can be given as below.

And lastly we have $-N{{O}_{2}}$. If we compare nitrogen and oxygen, nitrogen is more electropositive therefore it will show –R effect.
We can understand from the above discussion that $-N{{H}_{2}}$ will show +R.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: There is polarity produced in a molecule by the interaction between a lone electron pair and a pi bond. It is generally found in molecules with conjugated double bonds or in molecules having at least one lone pair and one double bond.
A carbocation is stabilised through +R effect i.e. resonance of the positive charge around the ring. But there are some cases where an alkyl carbocation with a +I effect is more stable than a carbocation with +R group although resonance effect has higher priority.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




