
Which of the following describes the major difference between the production of egg cells (oogenesis) and the production of sperm cells (spermatogenesis)?
(a)During spermatogenesis, 4 diploid cells are produced, but during oogenesis, 4 haploid cells are produced.
(b)During spermatogenesis, 3 polar bodies are produced along with one sperm cell, while oogenesis produces 4 egg cells
(c)During spermatogenesis 4 diploid sperm cells are produced, and during oogenesis 4 diploid egg cells are produced
(d)During spermatogenesis, 4 haploid sperm cells are produced while oogenesis produces 1 haploid egg cell and 3 polar bodies
(e)During spermatogenesis, 4 haploid sperm cells are produced while oogenesis produces 4 haploid egg cells
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are both processes of gametogenesis because they result in the formation of the male gamete (sperm) and the female gamete (ovum) respectively. Since gametes are haploid in nature, gametogenesis occurs through meiosis.
Complete answer:
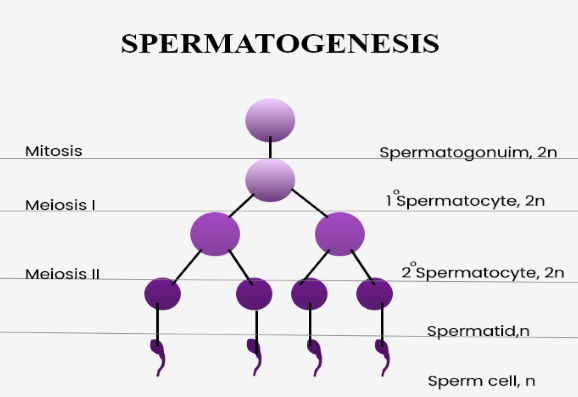
In spermatogenesis, the primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis-I resulting in the production of two haploid secondary spermatocytes. The secondary spermatocytes each undergo meiosis-II and result in the formation of four haploid sperm cells.
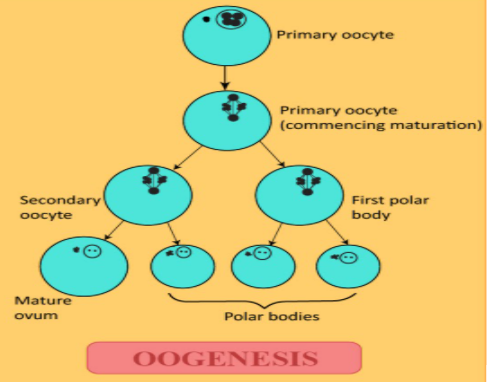
Whereas in oogenesis, the diploid primary oocyte undergoes an unequal meiosis-I to form a larger haploid secondary oocyte and a smaller polar body. This happens to ensure the majority of the cytoplasm and food are retained by the egg. This secondary oocyte and the polar body both undergo meiosis-II to produce an ovum and a secondary polar body and two secondary polar bodies respectively.
Additional Information:
Let us look at the process of spermatogenesis and oogenesis in detail:
Spermatogenesis: The primary spermatocytes are formed by the mitotic division and growth by the spermatogonium. When secondary spermatocytes are formed by meiosis-I of primary spermatocytes, they further divide to form 4 haploid spermatids. These spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm cells) through a process known as spermiogenesis. The process of release of sperm cells from the seminiferous tubules is known as spermiation.
Oogenesis: Oogonia divide by meiosis and get temporarily arrested at the stage of prophase-I and are known as primary oocytes. The primary oocyte gets surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells over time to form the primary follicle followed by the secondary follicle. With time, this converts into a tertiary follicle which has a fluid-filled cavity called the antrum. At this stage, the primary oocyte completes meiosis-I to give a secondary oocyte and a polar body. The second meiosis takes place when a sperm enters the plasma membrane of the secondary oocyte.
So, the correct option is ‘During spermatogenesis, 4 haploid sperm cells are produced while oogenesis produces 1 haploid egg cell and 3 polar bodies’.
Note: -Spermatogenesis starts at the age of puberty whereas oogenesis starts at the time of embryonic development.
-The primary hormones responsible for regulating spermatogenesis are the gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and androgens.
-The primary hormones responsible for stimulating oogenesis are again gonadotropins LH and FSH as well as estrogens.
Complete answer:
In spermatogenesis, the primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis-I resulting in the production of two haploid secondary spermatocytes. The secondary spermatocytes each undergo meiosis-II and result in the formation of four haploid sperm cells.
Whereas in oogenesis, the diploid primary oocyte undergoes an unequal meiosis-I to form a larger haploid secondary oocyte and a smaller polar body. This happens to ensure the majority of the cytoplasm and food are retained by the egg. This secondary oocyte and the polar body both undergo meiosis-II to produce an ovum and a secondary polar body and two secondary polar bodies respectively.
Additional Information:
Let us look at the process of spermatogenesis and oogenesis in detail:
Spermatogenesis: The primary spermatocytes are formed by the mitotic division and growth by the spermatogonium. When secondary spermatocytes are formed by meiosis-I of primary spermatocytes, they further divide to form 4 haploid spermatids. These spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm cells) through a process known as spermiogenesis. The process of release of sperm cells from the seminiferous tubules is known as spermiation.
Oogenesis: Oogonia divide by meiosis and get temporarily arrested at the stage of prophase-I and are known as primary oocytes. The primary oocyte gets surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells over time to form the primary follicle followed by the secondary follicle. With time, this converts into a tertiary follicle which has a fluid-filled cavity called the antrum. At this stage, the primary oocyte completes meiosis-I to give a secondary oocyte and a polar body. The second meiosis takes place when a sperm enters the plasma membrane of the secondary oocyte.
So, the correct option is ‘During spermatogenesis, 4 haploid sperm cells are produced while oogenesis produces 1 haploid egg cell and 3 polar bodies’.
Note: -Spermatogenesis starts at the age of puberty whereas oogenesis starts at the time of embryonic development.
-The primary hormones responsible for regulating spermatogenesis are the gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and androgens.
-The primary hormones responsible for stimulating oogenesis are again gonadotropins LH and FSH as well as estrogens.


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




