
Which of the following depicts the process of translocation in plants?
(a)Physiologic loading of sucrose into the phloem
(b)Unloading sucrose at the sink
(c)Control of pressure flow of the sap in the phloem driven by osmosis
(d)All the above
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Ernst Münch suggested the 'pressure-flow' theory in 1930 to describe the mechanism of phloem translocation. Leaves photosynthesize, creating sugars. Water passes through osmosis through the sugar-laden sieve-tube cells with sugar. This creates pressure that forces the sap down the tube of the sieve. As sugar enters the cells that need it, sugar is effectively transferred by the cells from the elements of the sieve channel.
Complete answer:
The movement of organic molecules and some mineral ions mean translocation in vascular plants. In xylem vessels, water movement from the soil to the leaves occurs as a result of transpiration. Because of the forces of cohesion between water molecules formed due to hydrogen bonds that allow the water to flow upwards, transpiration, the evaporation of water from leaves, creates a pull on the water column.
In the living cells of the phloem, organic materials, primarily formed in the leaves, are transported around the plant through a process called translocation.
The phloem is composed of still-living cells that carry sap, unlike xylem (which is made up of dead cells). The sap is a water-based solution rich in photosynthesis-made sugars. These sugars are transported to areas of the plant that are not photosynthetic, such as the roots, or into storage systems, such as tubers or bulbs.
Phloem loading is the transfer of sugars (photosynthetic) from mesophyll cells to the elements of the sieve tube in the leaf. On the other hand, the transfer of sugars (photosynthetic) from elements of the sieve tube to the end-consumption recipient cells ( i.e. sink organs) is called phloem unloading. Both are processes that require energy.
Storage organs such as the roots are sugar sources during the plant's growth cycle, usually during the spring, and sugar sinks are the many growing areas of the plant.
So, the correct answer is option ‘D’.
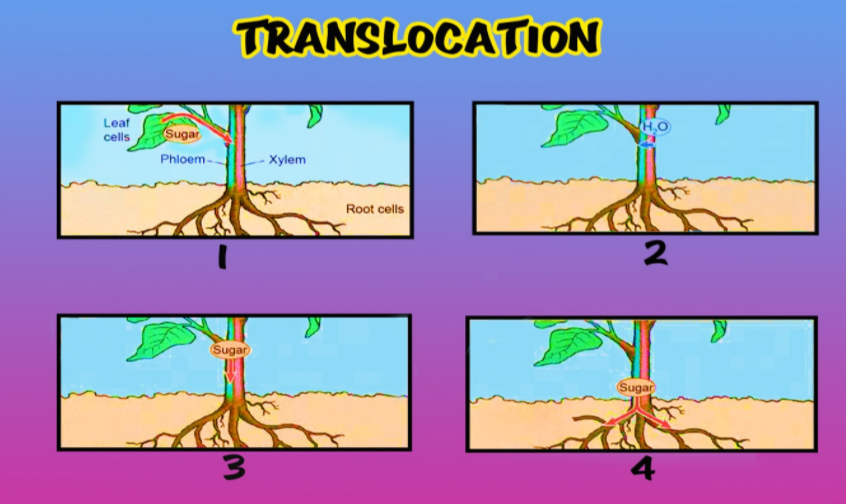
Note: -In the phloem, other molecules such as amino acids, hormones, and even messenger RNAs are also transmitted by elements of the sieve channel.
-The phloem movement is multi-directional, while it is one-directional (upwards) in xylem cells.
Complete answer:
The movement of organic molecules and some mineral ions mean translocation in vascular plants. In xylem vessels, water movement from the soil to the leaves occurs as a result of transpiration. Because of the forces of cohesion between water molecules formed due to hydrogen bonds that allow the water to flow upwards, transpiration, the evaporation of water from leaves, creates a pull on the water column.
In the living cells of the phloem, organic materials, primarily formed in the leaves, are transported around the plant through a process called translocation.
The phloem is composed of still-living cells that carry sap, unlike xylem (which is made up of dead cells). The sap is a water-based solution rich in photosynthesis-made sugars. These sugars are transported to areas of the plant that are not photosynthetic, such as the roots, or into storage systems, such as tubers or bulbs.
Phloem loading is the transfer of sugars (photosynthetic) from mesophyll cells to the elements of the sieve tube in the leaf. On the other hand, the transfer of sugars (photosynthetic) from elements of the sieve tube to the end-consumption recipient cells ( i.e. sink organs) is called phloem unloading. Both are processes that require energy.
Storage organs such as the roots are sugar sources during the plant's growth cycle, usually during the spring, and sugar sinks are the many growing areas of the plant.
So, the correct answer is option ‘D’.

Note: -In the phloem, other molecules such as amino acids, hormones, and even messenger RNAs are also transmitted by elements of the sieve channel.
-The phloem movement is multi-directional, while it is one-directional (upwards) in xylem cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




