
Which of the following cyanohydrins on hydrolysis give optically active acid that gives an iodoform reaction?
A. Acetone cyanohydrin
B. Propionaldehyde cyanohydrin
C. Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin
D. Formaldehyde cyanohydrin
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: Think about the compounds which give iodoform reaction. What are compounds formed on the hydrolysis of the cyano group? Compounds having a chiral center and do not have any symmetry elements are optically active.
Complete answer:
- We know that aldehyde or ketone group-containing compounds on reaction hydrogen cyanide give cyanohydrins. Cyanohydrins contain a hydroxyl group and a cyanide group.
- Iodoform reaction is given by compounds containing methyl groups connected to the aldehyde group or keto group i.e. the carbonyl carbon or when a hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary carbon atom that has a methyl group on one side and any other group on the other. So, the structures of the groups that give a positive iodoform test are:
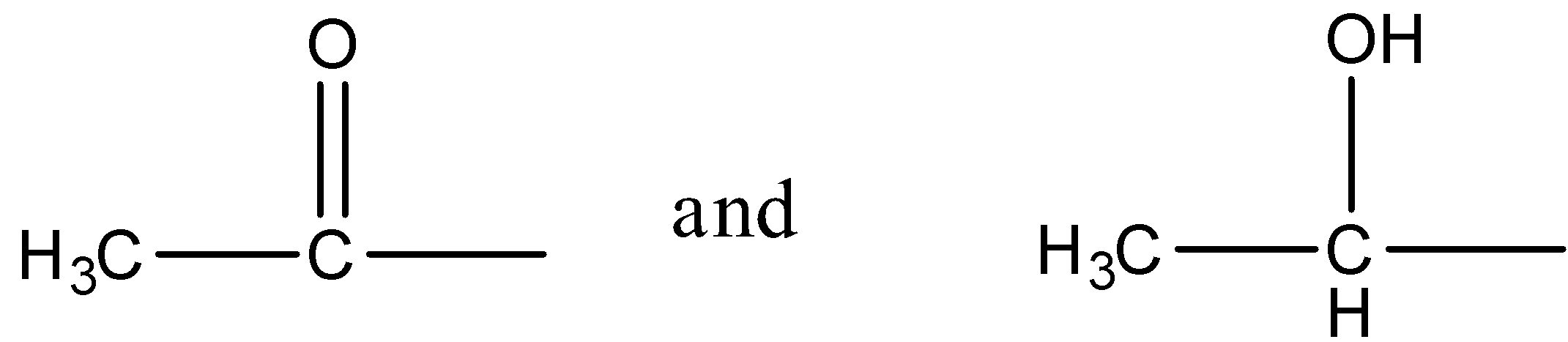
We will now write the reaction mechanism for the iodoform reaction using an arbitrary compound.
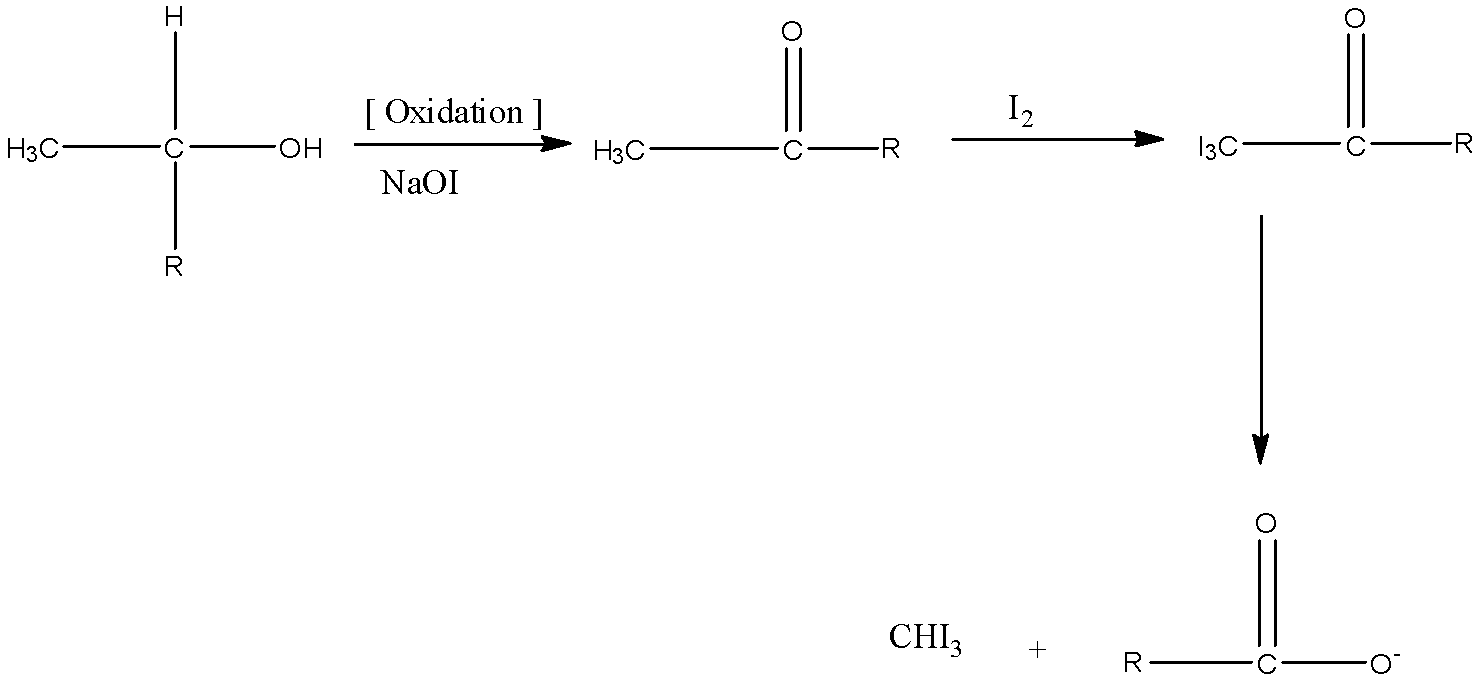
- Cyanohydrin on reaction with iodine in presence of base first oxidizes hydroxyl group to aldehyde or keto group. Then methyl aldehydes or methyl ketones give iodoform tests. The cyanide group on hydrolysis gives the carboxylic acid group.
- Let us verify the given options to find which compound gives the desired product.
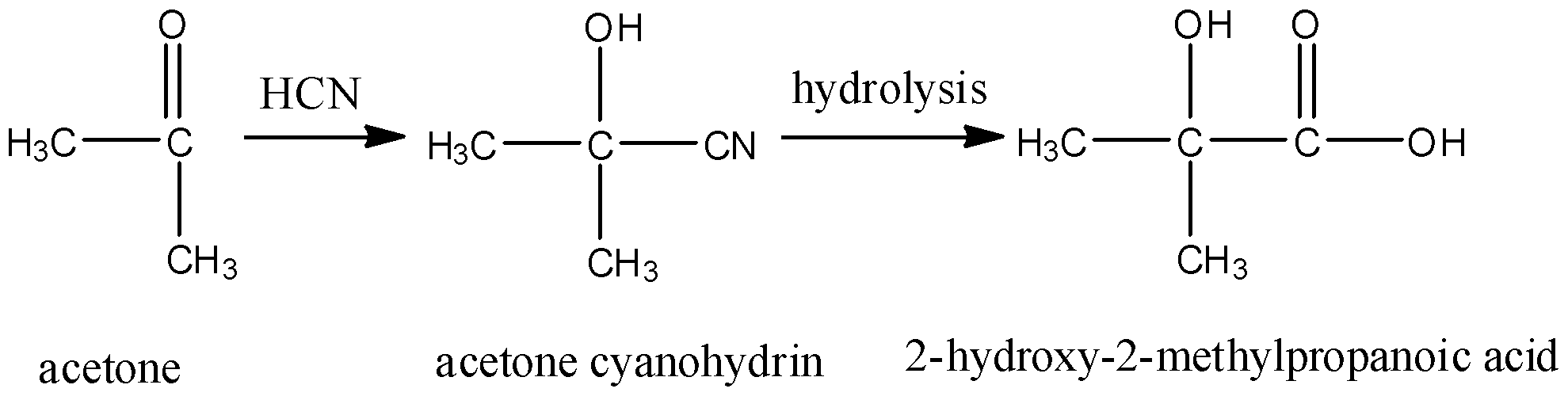
- Acetone cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid. In which, one carbon atom is attached to 2 methyl groups so it will be optically inactive. It will also not give a positive iodoform test due to the absence of the methyl group that should be attached to the carbonyl carbon. So, it is not the correct answer.
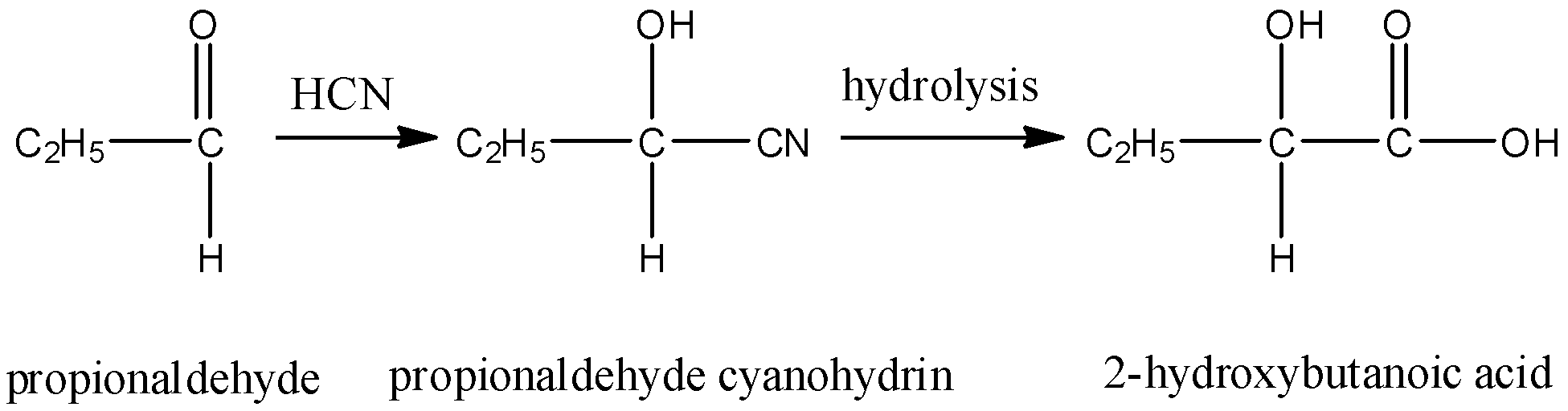
- Propionaldehyde cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxybutanoic acid. This compound is optically active due to the presence of a chiral carbon but will not show a positive iodoform test due to the absence of methyl group on carbonyl carbon.
- Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. This compound is optically active and also contains a methyl group attached to a secondary carbon atom that is further attached to a hydroxyl group. So, this will give a positive iodoform test. So, this is the correct answer.
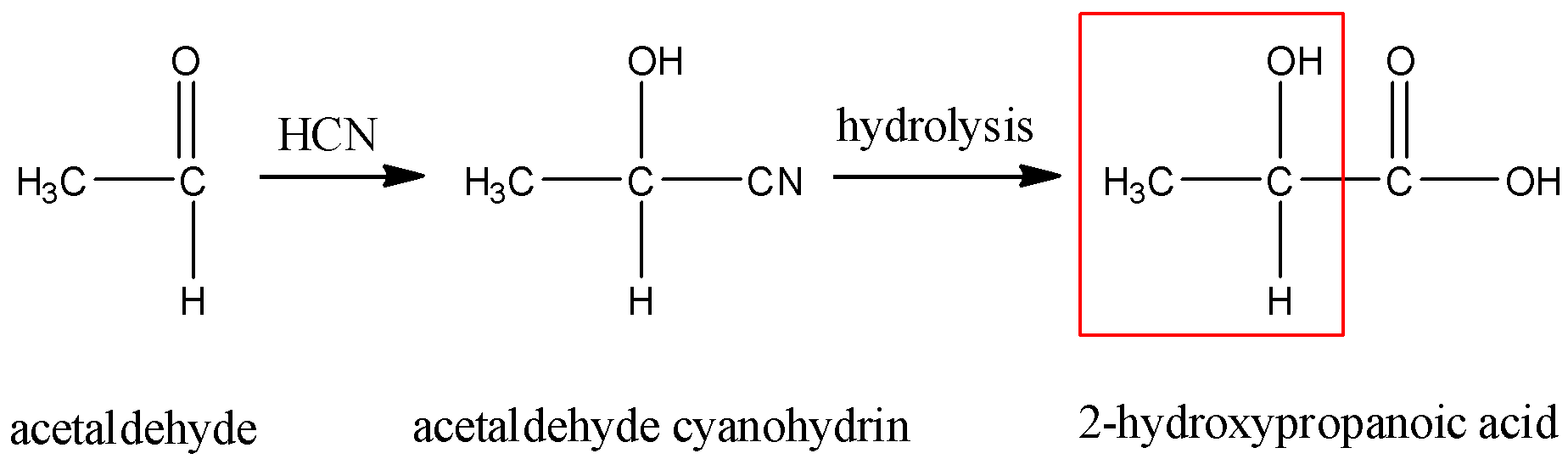
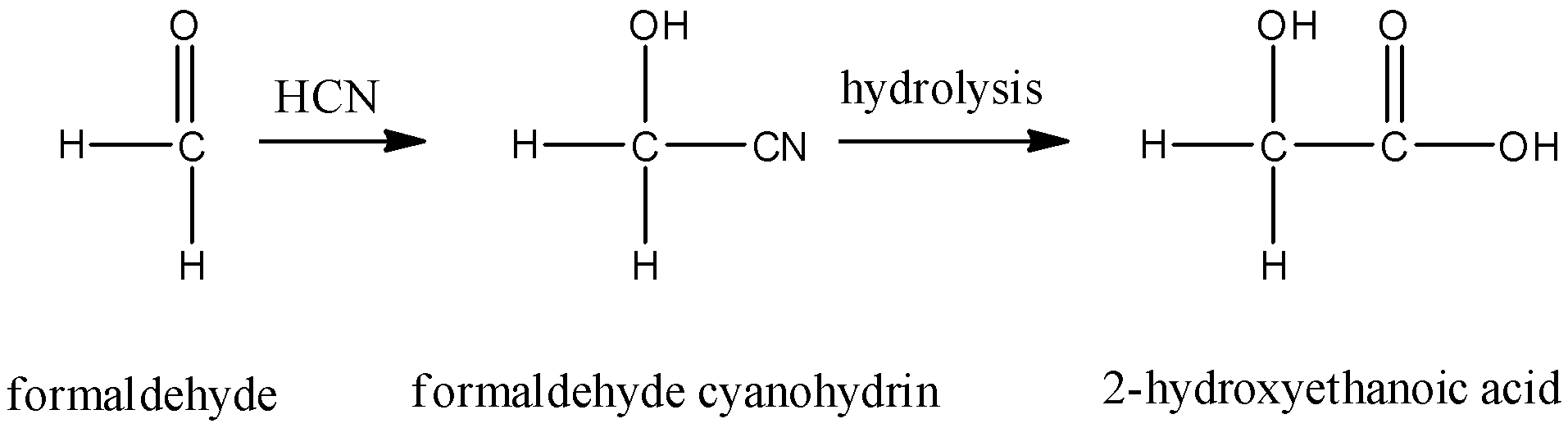
- Formaldehyde cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxyethanoic acid. This compound is neither optically active nor does it show a positive iodoform test. So, this is not the correct answer.
Hence, the correct option is ‘C. Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin’
Note:
Remember that the presence of the $-CHO$ group before hydrolysis, in general, indicates that the compound will show a negative iodoform test but 2-hydroxypropanoic acid is an exception to this rule due to the presence of the hydroxyl group attached to the secondary carbon atom and one of its branches is a methyl group. Keep the conditions for the iodoform test in your mind before you answer the question.
Complete answer:
- We know that aldehyde or ketone group-containing compounds on reaction hydrogen cyanide give cyanohydrins. Cyanohydrins contain a hydroxyl group and a cyanide group.
- Iodoform reaction is given by compounds containing methyl groups connected to the aldehyde group or keto group i.e. the carbonyl carbon or when a hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary carbon atom that has a methyl group on one side and any other group on the other. So, the structures of the groups that give a positive iodoform test are:
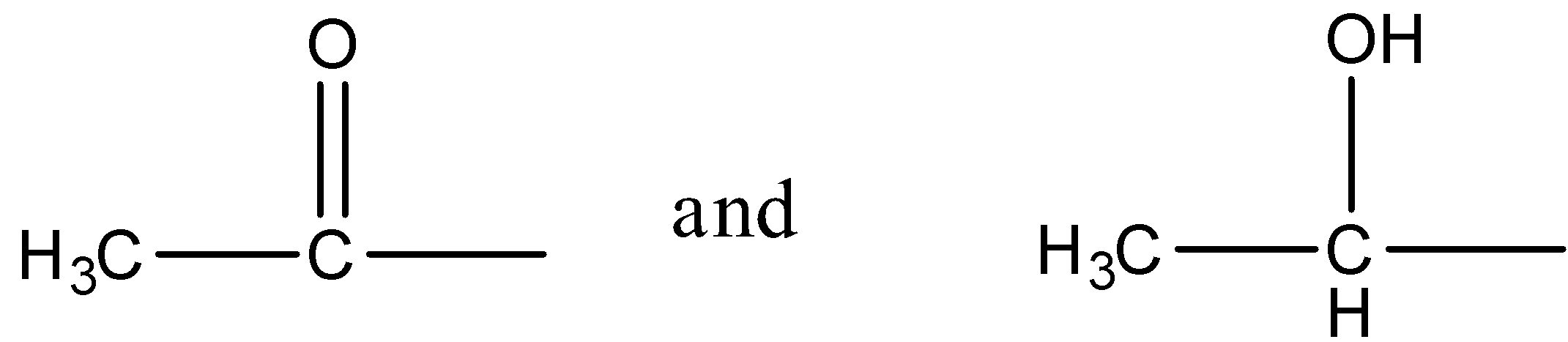
We will now write the reaction mechanism for the iodoform reaction using an arbitrary compound.

- Cyanohydrin on reaction with iodine in presence of base first oxidizes hydroxyl group to aldehyde or keto group. Then methyl aldehydes or methyl ketones give iodoform tests. The cyanide group on hydrolysis gives the carboxylic acid group.
- Let us verify the given options to find which compound gives the desired product.
- Acetone cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanoic acid. In which, one carbon atom is attached to 2 methyl groups so it will be optically inactive. It will also not give a positive iodoform test due to the absence of the methyl group that should be attached to the carbonyl carbon. So, it is not the correct answer.

- Propionaldehyde cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxybutanoic acid. This compound is optically active due to the presence of a chiral carbon but will not show a positive iodoform test due to the absence of methyl group on carbonyl carbon.

- Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. This compound is optically active and also contains a methyl group attached to a secondary carbon atom that is further attached to a hydroxyl group. So, this will give a positive iodoform test. So, this is the correct answer.

- Formaldehyde cyanohydrin on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxyethanoic acid. This compound is neither optically active nor does it show a positive iodoform test. So, this is not the correct answer.

Hence, the correct option is ‘C. Acetaldehyde cyanohydrin’
Note:
Remember that the presence of the $-CHO$ group before hydrolysis, in general, indicates that the compound will show a negative iodoform test but 2-hydroxypropanoic acid is an exception to this rule due to the presence of the hydroxyl group attached to the secondary carbon atom and one of its branches is a methyl group. Keep the conditions for the iodoform test in your mind before you answer the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




