
Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
A.
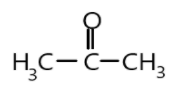
B.
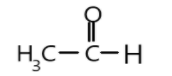
C.
D.

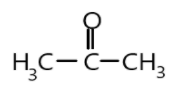
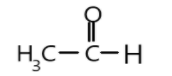


Answer
522.5k+ views
Hint: As we all know that the carbonyl compounds undergo nucleophilic addition reaction and this type of reaction are typical of aldehydes and ketones. If the atom or group is attached with the carbonyl carbon it will decrease the electron density due to negative inductive effect.
Complete answer:
As we are already aware of the fact that addition reactions brought about by a nucleophile are called nucleophilic addition reactions and these reactions are typically found in ketones and aldehydes. We know that the carbonyl compounds of aldehydes and ketones undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction and if there is any atom or group attached with the carbonyl carbon that shows negative inductive effect, then it will decrease the electron density on carbonyl carbon and facilitate the attack of nucleophiles hence reactivity of carbonyl compound increases.
In the first option, we can see that methyl group is attached to the carbonyl carbon which will hinder the attack of nucleophile and due to positive its positive inductive effect electron density increases which will decrease the attacking tendency of the nucleophile, hence it is a bit less reactive compound.
In the second potion we can see that an atom attached with carbonyl carbon will decrease the electron density due to its negative inductive effect thereby increasing the attack of nucleophiles and hence making the carbonyl compound more reactive.
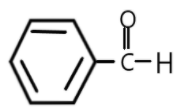
In aromatic aldehydes as we can see in the third and fourth option they show a positive resonance or negative mesomeric effect of benzene ring and thus the carbonyl compounds in aromatic compounds are much less reactive as compared to aliphatic compounds.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say that ethanol will be most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
Hence the correct answer is (B).
Note:
There are two important factors that help in comparing the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reaction and these are steric factor and the electronic factor. More the number of alkyl groups attached to carbonyl carbon more will be the steric hindrance hence less will be the tendency to attack the nucleophile. And if these alkyl groups show positive inductive effect the tendency to attack will be decreased as the electron density increases on carbonyl carbon, thus more the positive inductive effect lesser will be the carbonyl carbon reactivity.
Complete answer:
As we are already aware of the fact that addition reactions brought about by a nucleophile are called nucleophilic addition reactions and these reactions are typically found in ketones and aldehydes. We know that the carbonyl compounds of aldehydes and ketones undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction and if there is any atom or group attached with the carbonyl carbon that shows negative inductive effect, then it will decrease the electron density on carbonyl carbon and facilitate the attack of nucleophiles hence reactivity of carbonyl compound increases.
In the first option, we can see that methyl group is attached to the carbonyl carbon which will hinder the attack of nucleophile and due to positive its positive inductive effect electron density increases which will decrease the attacking tendency of the nucleophile, hence it is a bit less reactive compound.
In the second potion we can see that an atom attached with carbonyl carbon will decrease the electron density due to its negative inductive effect thereby increasing the attack of nucleophiles and hence making the carbonyl compound more reactive.
In aromatic aldehydes as we can see in the third and fourth option they show a positive resonance or negative mesomeric effect of benzene ring and thus the carbonyl compounds in aromatic compounds are much less reactive as compared to aliphatic compounds.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say that ethanol will be most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction.
Hence the correct answer is (B).
Note:
There are two important factors that help in comparing the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones in nucleophilic addition reaction and these are steric factor and the electronic factor. More the number of alkyl groups attached to carbonyl carbon more will be the steric hindrance hence less will be the tendency to attack the nucleophile. And if these alkyl groups show positive inductive effect the tendency to attack will be decreased as the electron density increases on carbonyl carbon, thus more the positive inductive effect lesser will be the carbonyl carbon reactivity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




