
Which of the following compounds is a constituent of the polymer?
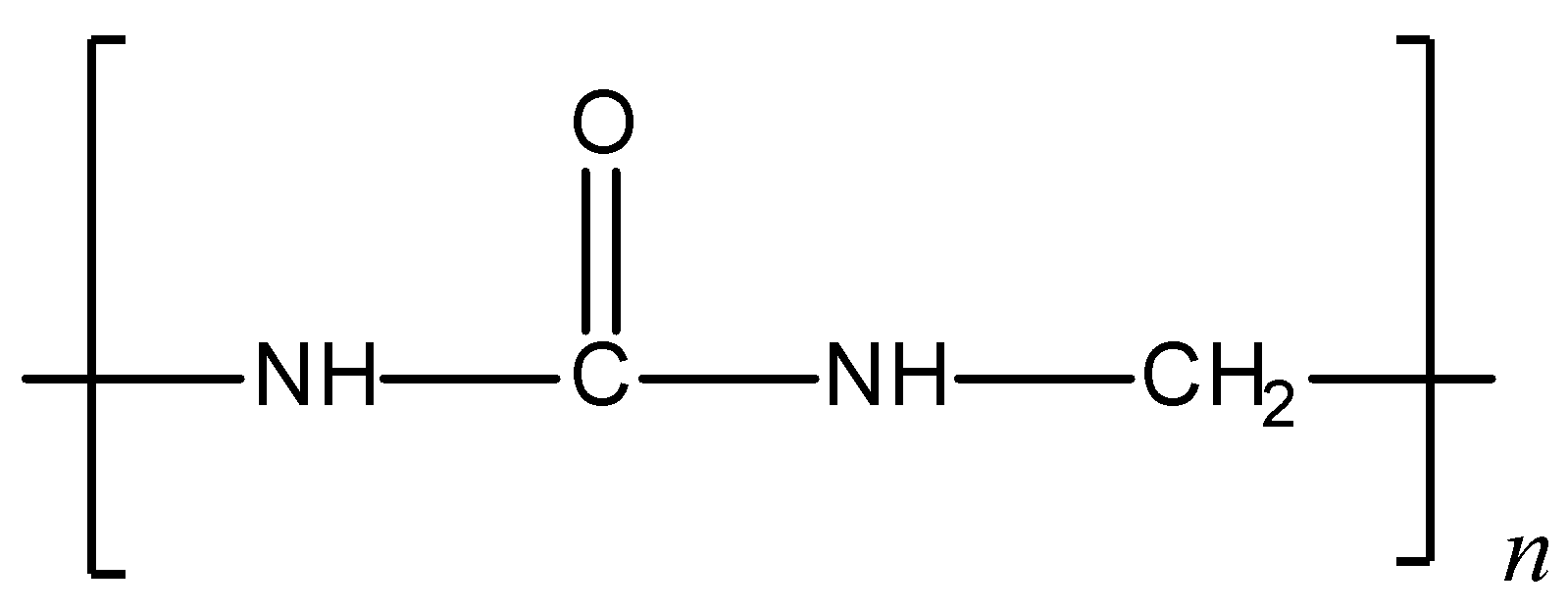
A) Formaldehyde
B) Ammonia
C) Methylamine
D) N-Methyl urea

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question you should know the various condensation polymers and their monomer units. Condensation polymers include the combination of two different molecules. Given polymer structure gives hint about the use of one molecule i.e., urea since it contains $ - NH(CO)NH - $ linkage.
Complete step by step solution:
A polymer is defined as a large molecule of high molecular weight formed by the combination of a number of one or more types of molecules of low molecular weight. The smaller molecules, which occur as repeating units to make up a polymer, are known as monomers. In other words, a polymer can be defined as a number of repeating units of chemical units called monomers held together by covalent bonds. The process by which monomers combine to form a polymer is known as polymerization.
Given structure of polymer is:
The given polymer is urea-formaldehyde polymer or also called urea-formaldehyde resin. It is a condensation polymer. Preparation of urea- formaldehyde polymer: Urea on condensation with formaldehyde results in the formation of urea-formaldehyde resin. Initially, the reaction results in the formation of monomethylol, which further condenses with urea and formaldehyde to give the polymer. The polymerisation reaction can be shown as follows:
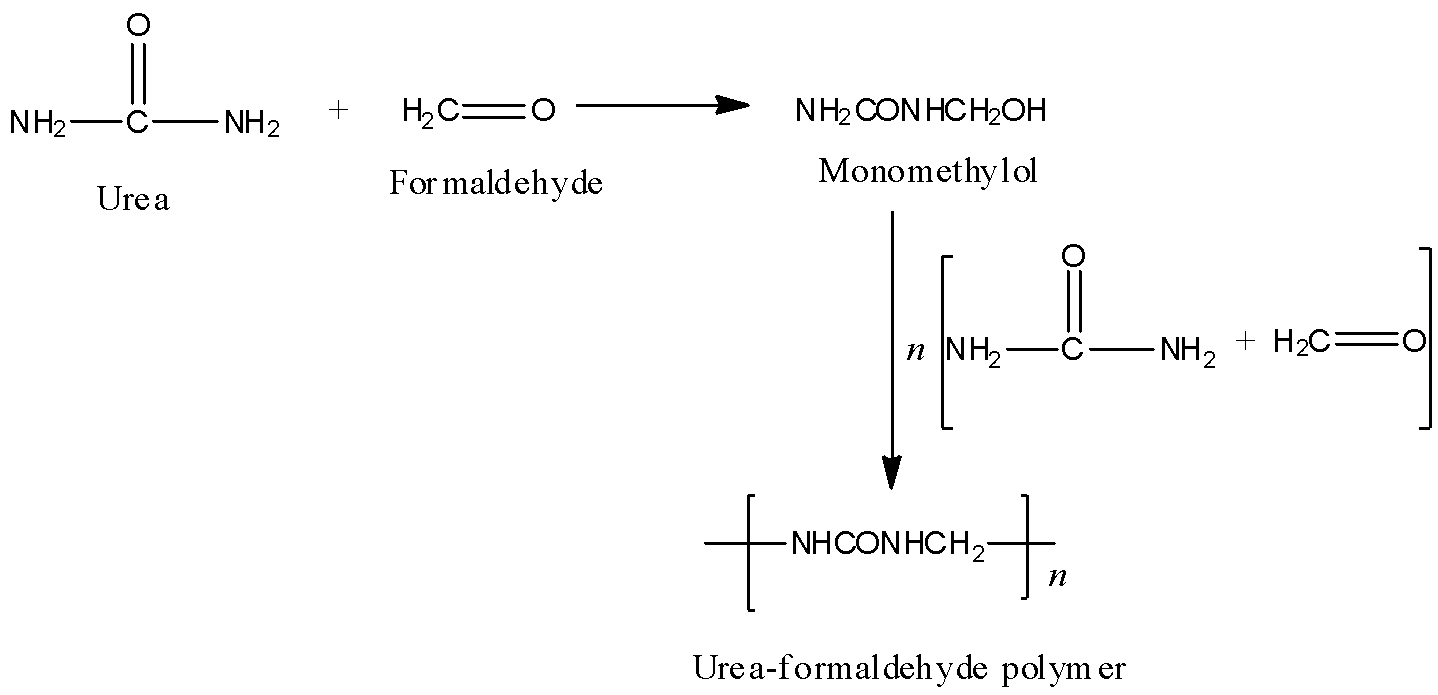
Hence, formaldehyde is a constituent for the given structure i.e., urea-formaldehyde polymer.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Additional information: Common uses of urea-formaldehyde resin are: Ion exchange resin, adhesives, electrical fittings, grease resistant textile, laminations and foams.
Note: Urea-formaldehyde polymer is a condensation polymer. In condensation polymers, the monomer units contain two or more functional groups and generally the condensation occurs between two different monomeric units. Condensation polymerisation is a step growth polymerisation. It generally proceeds with the elimination of simple molecules, like water, ammonia and so on.
Complete step by step solution:
A polymer is defined as a large molecule of high molecular weight formed by the combination of a number of one or more types of molecules of low molecular weight. The smaller molecules, which occur as repeating units to make up a polymer, are known as monomers. In other words, a polymer can be defined as a number of repeating units of chemical units called monomers held together by covalent bonds. The process by which monomers combine to form a polymer is known as polymerization.
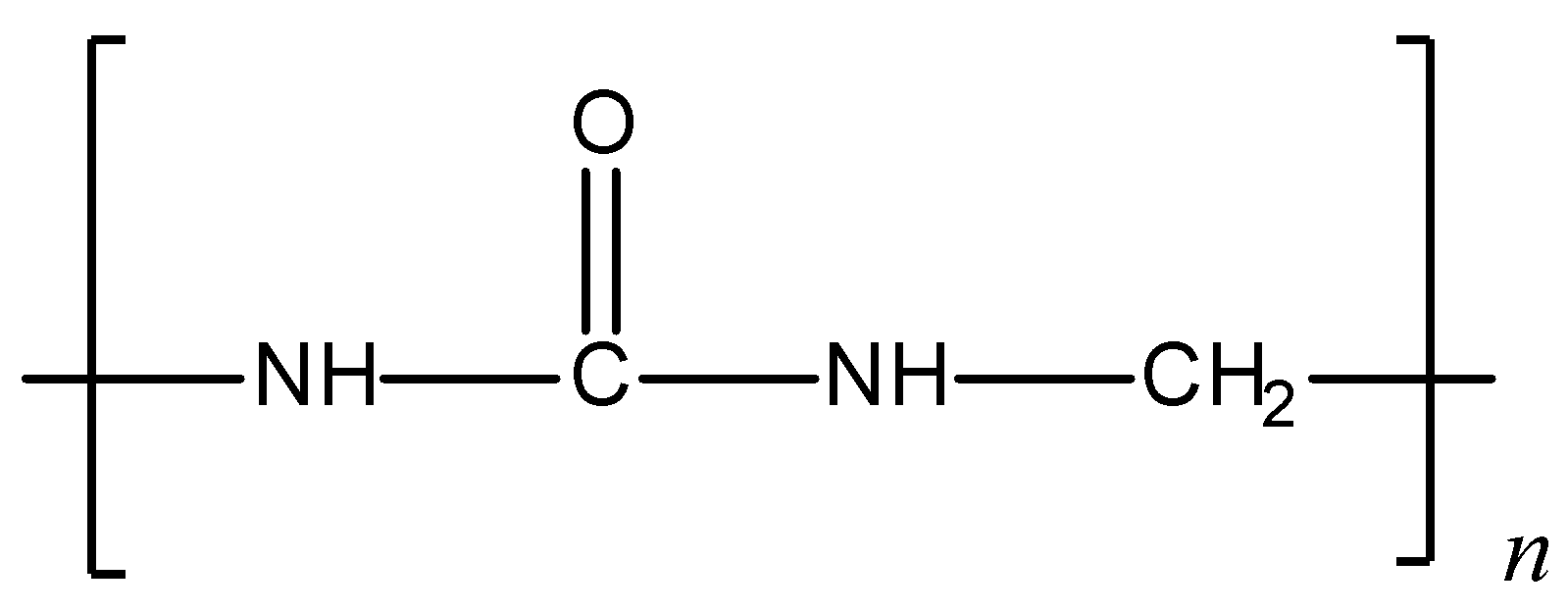
Given structure of polymer is:

The given polymer is urea-formaldehyde polymer or also called urea-formaldehyde resin. It is a condensation polymer. Preparation of urea- formaldehyde polymer: Urea on condensation with formaldehyde results in the formation of urea-formaldehyde resin. Initially, the reaction results in the formation of monomethylol, which further condenses with urea and formaldehyde to give the polymer. The polymerisation reaction can be shown as follows:

Hence, formaldehyde is a constituent for the given structure i.e., urea-formaldehyde polymer.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Additional information: Common uses of urea-formaldehyde resin are: Ion exchange resin, adhesives, electrical fittings, grease resistant textile, laminations and foams.
Note: Urea-formaldehyde polymer is a condensation polymer. In condensation polymers, the monomer units contain two or more functional groups and generally the condensation occurs between two different monomeric units. Condensation polymerisation is a step growth polymerisation. It generally proceeds with the elimination of simple molecules, like water, ammonia and so on.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




