
Which of the following best describes the diagram of a molecular orbital?
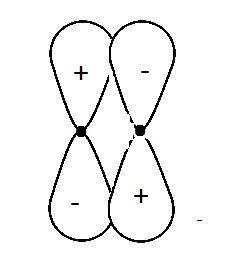
A.A bonding \[\pi \] orbital
B.A non bonding orbital
C.An antibonding $\sigma $ orbital
D.An antibonding $\pi $ orbital

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: When atomic orbitals interact with each other they produce molecular orbitals, basically molecular orbitals are the wave functions which describe the position and the probability of the moving electrons in an orbital.
Complete step by step answer:
The mathematical function which is used to describe the position and probability of a particle is known as molecular orbital. It basically shows us the wave-like behavior of electrons.
Molecular orbitals are formed from the interactions of atomic orbitals. The number of atomic orbitals are equal to the number of molecular orbitals always.
Molecular orbitals are of three types:
First is bonding orbital, these have energy lower than the atomic orbitals, second are antibonding orbitals, these have energy more than that of atomic orbitals and the third one are non bonding orbitals, these molecular orbitals have energy equal to their atomic orbitals.
As we have given in the structure that two \[P\] orbitals are overlapping. If orbitals overlap axially, a sigma bond is produced and if the orbitals overlap laterally pi bond formation takes place. Whether the molecular orbital is bonding or antibonding, it depends on the charges written in the atomic orbitals. If the positive charge overlaps the positive charge then it is bonding and if positive charge overlaps the negative charge then it is antibonding molecular orbital.
So as given in the diagram the opposite charges are overlapping each other hence it is a pi antibonding molecular orbital.
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note:
The atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals both show the probability of the finding electron in a molecule. Each molecular orbital has two electrons with the opposite spin. The bonding of atomic orbitals depend on the way, how these atomic orbitals overlap.
Complete step by step answer:
The mathematical function which is used to describe the position and probability of a particle is known as molecular orbital. It basically shows us the wave-like behavior of electrons.
Molecular orbitals are formed from the interactions of atomic orbitals. The number of atomic orbitals are equal to the number of molecular orbitals always.
Molecular orbitals are of three types:
First is bonding orbital, these have energy lower than the atomic orbitals, second are antibonding orbitals, these have energy more than that of atomic orbitals and the third one are non bonding orbitals, these molecular orbitals have energy equal to their atomic orbitals.
As we have given in the structure that two \[P\] orbitals are overlapping. If orbitals overlap axially, a sigma bond is produced and if the orbitals overlap laterally pi bond formation takes place. Whether the molecular orbital is bonding or antibonding, it depends on the charges written in the atomic orbitals. If the positive charge overlaps the positive charge then it is bonding and if positive charge overlaps the negative charge then it is antibonding molecular orbital.
So as given in the diagram the opposite charges are overlapping each other hence it is a pi antibonding molecular orbital.
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note:
The atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals both show the probability of the finding electron in a molecule. Each molecular orbital has two electrons with the opposite spin. The bonding of atomic orbitals depend on the way, how these atomic orbitals overlap.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




