
Which of the following are symmetrical ethers?
Diethyl ether, propoxybenzene, anisole, phenetole, ethyl methyl ether, furan, tetrahydrofuran.
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The general formula for ether is $R-O-R’$ or $R-O-R$. Symmetrical ethers are the ethers that have exactly similar groups on both sides of the oxygen atom, which means ethers with the general formula $R-O-R$ are called symmetrical ethers. The word symmetry means two halves.
Complete step by step answer:
Ethers which can be divided into two halves, taking the $O-$ atom as the center of division, are called symmetrical ethers.
1. Diethyl ether - Diethyl means two molecules of ethyl group $(C_2H_5)$ are present. The chemical formula for diethyl ether is $C_2H_5-O-C_2H_5$. As we see, there are two groups of ethyl molecules present on either side of the oxygen atom. It means that on dividing the compound vertically across the center ( $O-$ atom), we get exactly two halves of two ethyl groups. So, the compound, diethyl ether is symmetrical.
2. Propoxybenzene – As the name suggests, the compound propoxybenzene consists of a propyl group and a benzene ring on either side of the $O-$ atom (oxy group). The chemical structure for propoxybenzene can be shown as under:
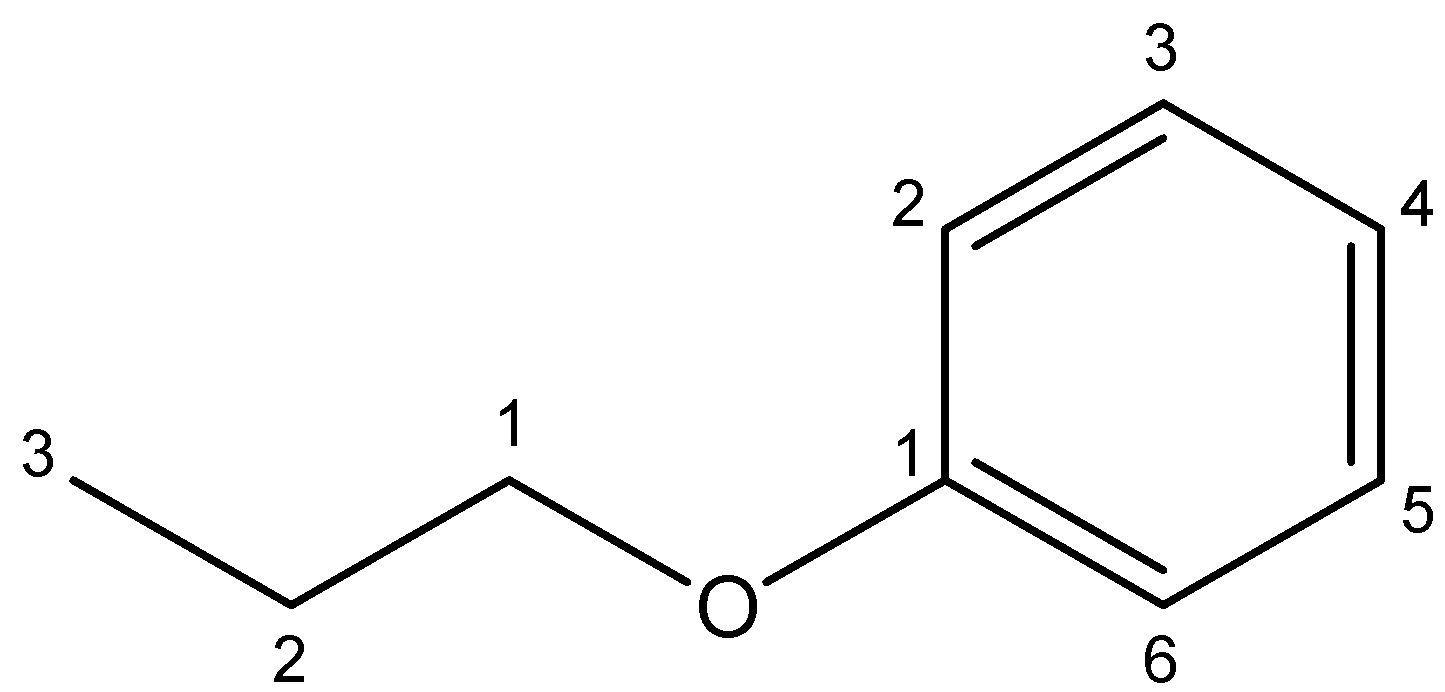
As we see, there is a propyl group of three carbon atoms on the left side of the $O-$ atom and a benzene ring containing six carbon atoms on the right side of the $O-$ atom. On dividing the compound through the oxygen atom, we find different groups on the left and right sides of the atom. So, the compound propoxybenzene is not a symmetrical ether.
3. Anisole – The IUPAC name for anisole is methoxybenzene. It consists of a methyl group on one side of the oxygen atom and a benzene ring on the other side. Its chemical structure can be drawn as below:
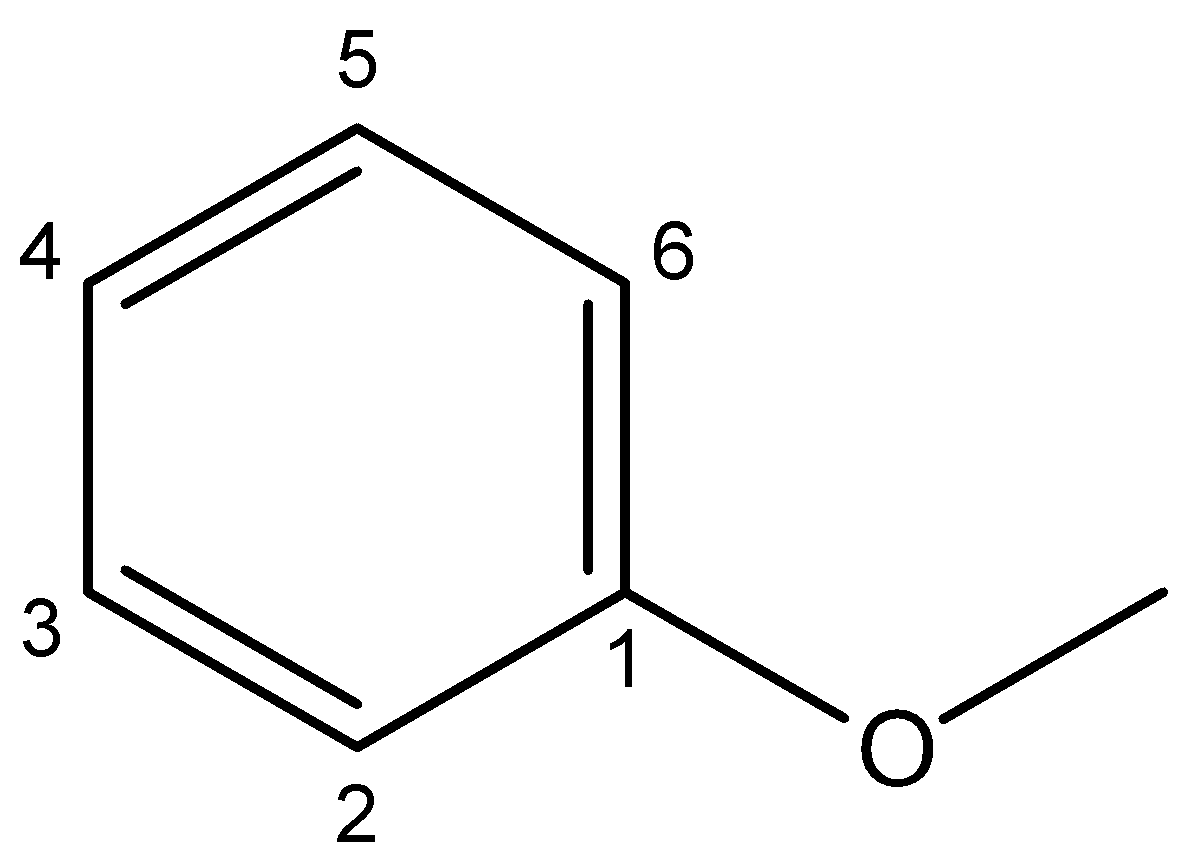
On dividing the compound through the oxygen atom, it does not cut into two halves. So, anisole is not a symmetrical ether.
4. Phenetole – The IUPAC name for phenetole is ethyl phenyl ether. Its chemical structure can be shown as under:
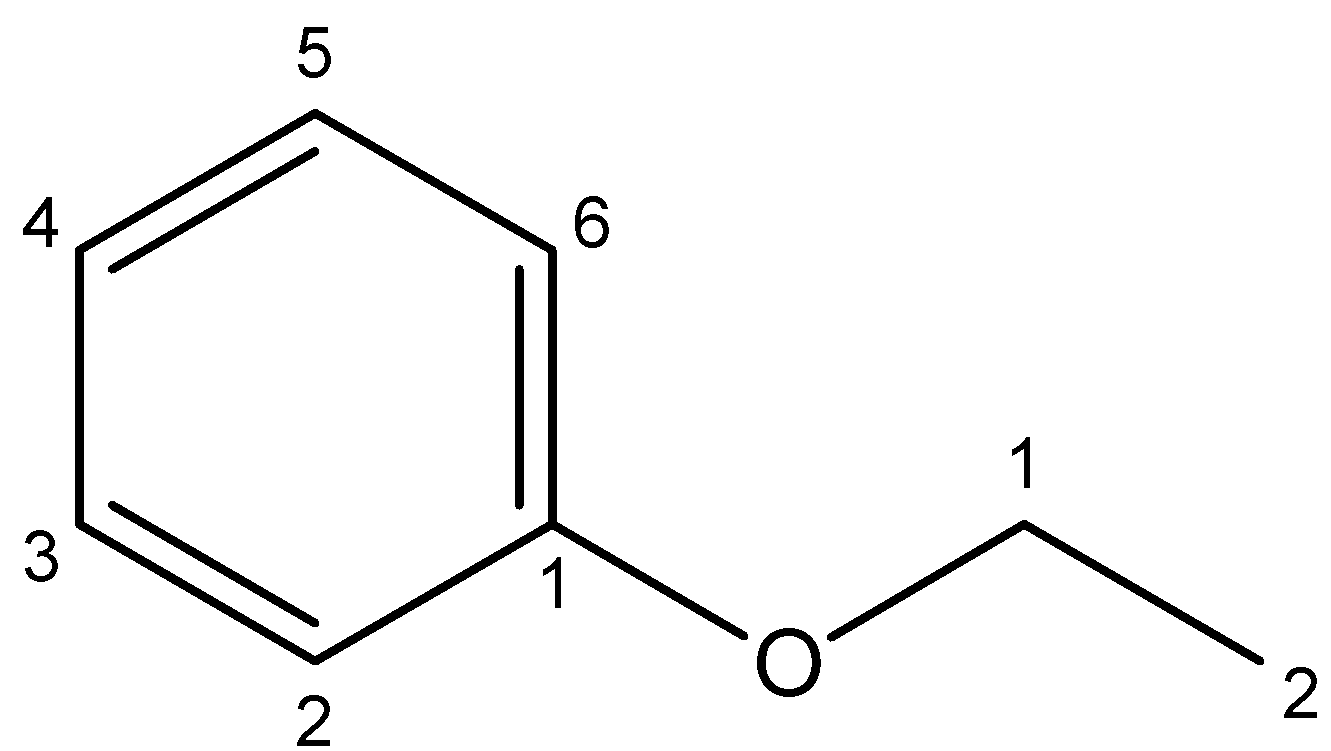
On dividing the compound through the oxygen atom, we get the benzene ring on the left and ethyl group on the right. Since the compound cannot be divided into two halves, phenetole is not a symmetrical ether.
5. Ethyl methyl ether – the structure of ethyl methyl ether can be drawn as follows:
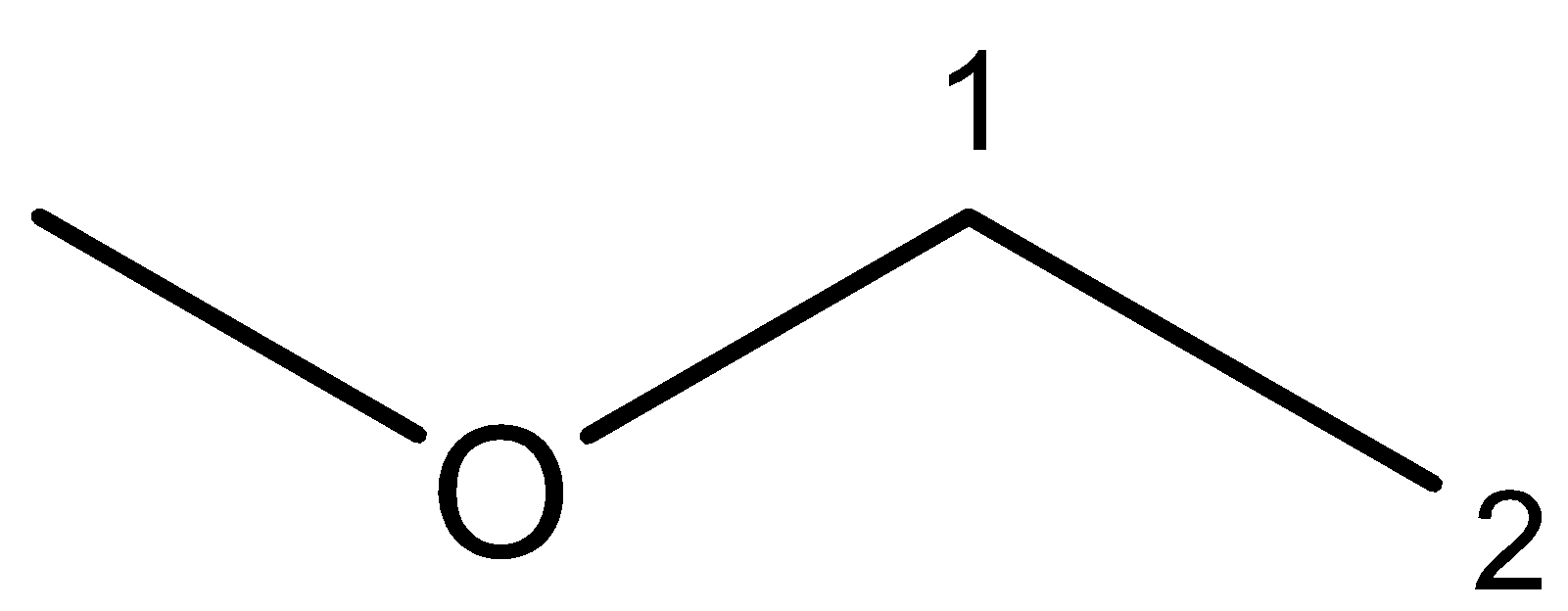
In ethyl methyl ether, there is a methyl group on the left and an ethyl group on the right side of the oxygen atom. So, on dividing the compound through the center, it will give us two different groups of methyl and ethyl. So, ethyl methyl ether is not a symmetrical ether.
6. Furan – The chemical name for furan is $1-oxacyclopenta-2,4-diene$, whose structure can be shown as follows:
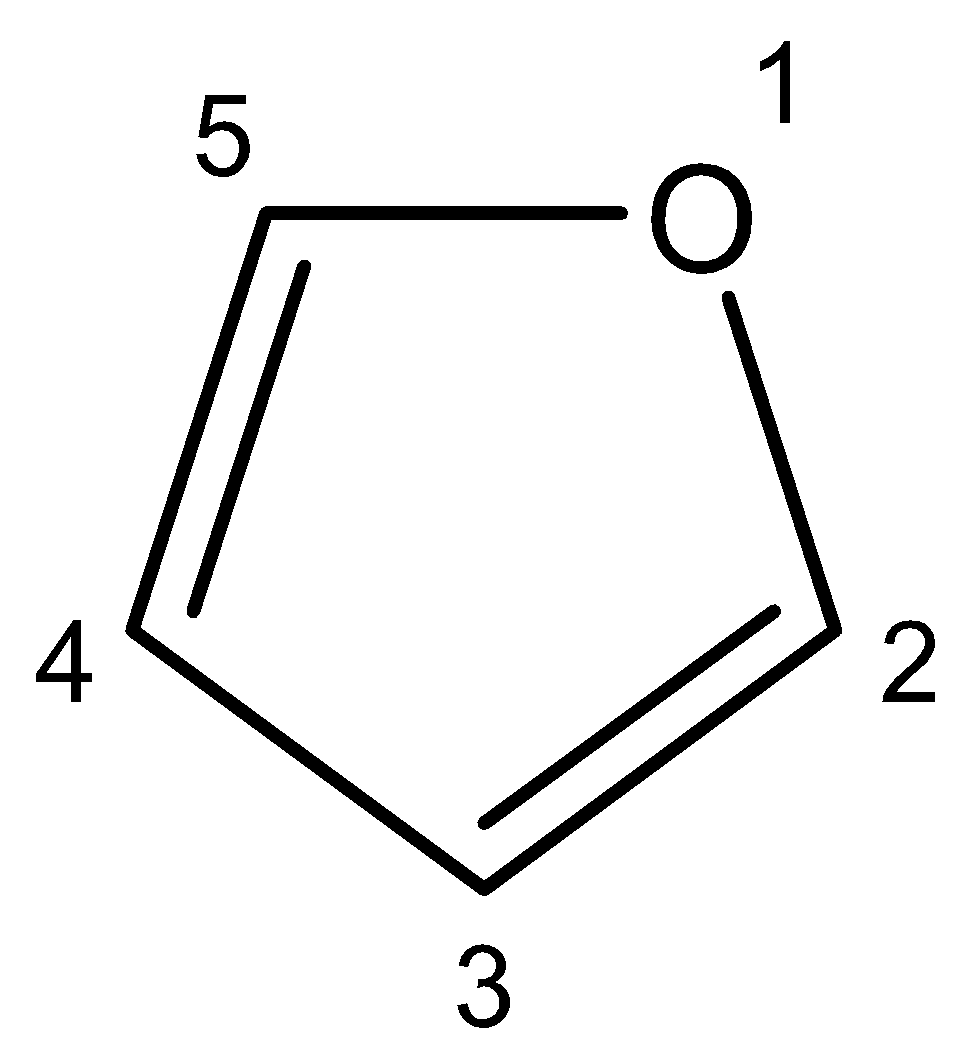
Since there are two different groups on either side of the oxygen atom, furan is a symmetrical ether. The compound consists of four carbon atoms, two on each side of the oxygen atom. On putting a plane across the oxygen atom, we get two identical groups on either side of the atom. So, it is a symmetrical ether.
7. Tetrahydrofuran – Tetrahydrofuran is a furan containing four hydrogen atoms. The chemical name for tetrahydrofuran is as follows:
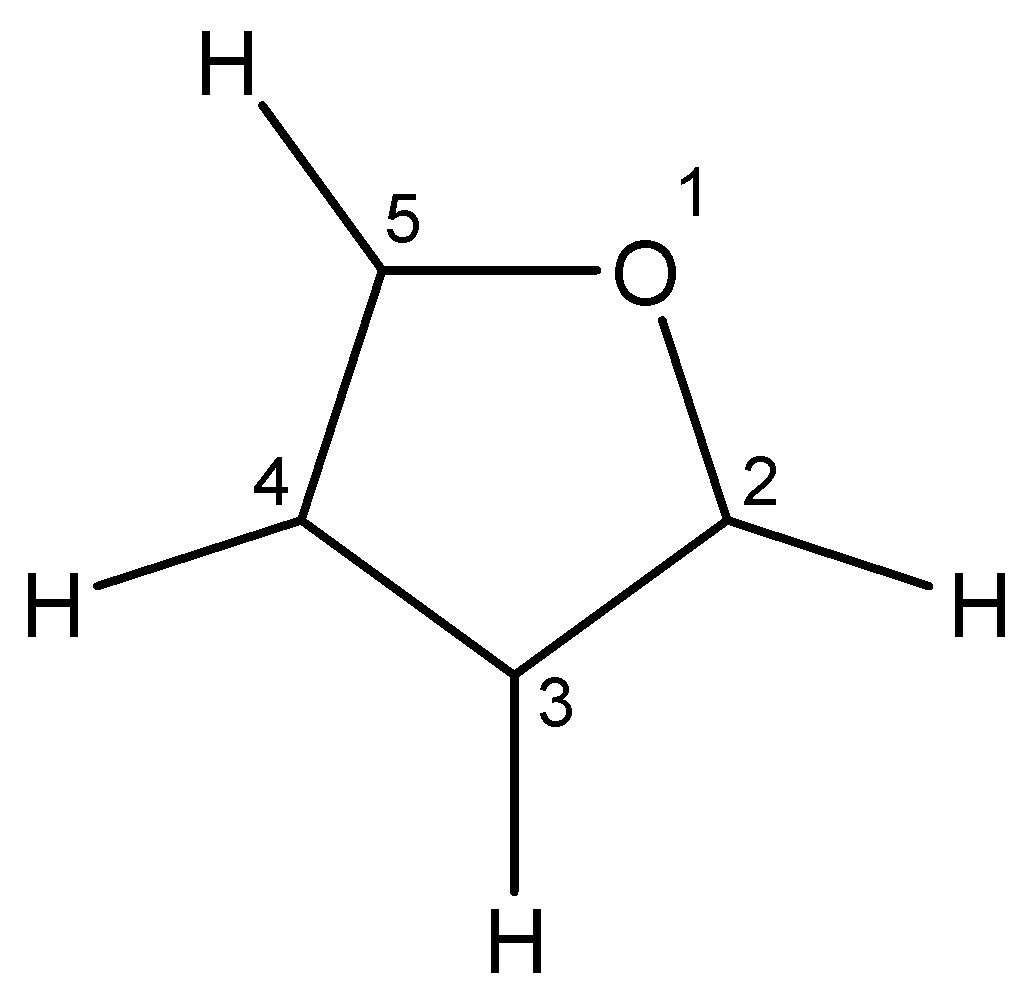
Like furan, tetrahydrofuran is also symmetrical as it contains two identical groups on both sides of the oxygen atom.
Therefore, the symmetrical ethers among the given ethers are diethyl ether, furan, and tetrahydrofuran.
Note: It is important to remember the IUPAC names of different ethers to be able to draw their chemical structures. Ethers can either contain either two alkyl groups on both sides of the oxygen atom, or two aryl groups on both sides of the oxygen atom, or one alkyl group and one aryl group on either side of the oxygen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Ethers which can be divided into two halves, taking the $O-$ atom as the center of division, are called symmetrical ethers.
1. Diethyl ether - Diethyl means two molecules of ethyl group $(C_2H_5)$ are present. The chemical formula for diethyl ether is $C_2H_5-O-C_2H_5$. As we see, there are two groups of ethyl molecules present on either side of the oxygen atom. It means that on dividing the compound vertically across the center ( $O-$ atom), we get exactly two halves of two ethyl groups. So, the compound, diethyl ether is symmetrical.
2. Propoxybenzene – As the name suggests, the compound propoxybenzene consists of a propyl group and a benzene ring on either side of the $O-$ atom (oxy group). The chemical structure for propoxybenzene can be shown as under:

As we see, there is a propyl group of three carbon atoms on the left side of the $O-$ atom and a benzene ring containing six carbon atoms on the right side of the $O-$ atom. On dividing the compound through the oxygen atom, we find different groups on the left and right sides of the atom. So, the compound propoxybenzene is not a symmetrical ether.
3. Anisole – The IUPAC name for anisole is methoxybenzene. It consists of a methyl group on one side of the oxygen atom and a benzene ring on the other side. Its chemical structure can be drawn as below:

On dividing the compound through the oxygen atom, it does not cut into two halves. So, anisole is not a symmetrical ether.
4. Phenetole – The IUPAC name for phenetole is ethyl phenyl ether. Its chemical structure can be shown as under:

On dividing the compound through the oxygen atom, we get the benzene ring on the left and ethyl group on the right. Since the compound cannot be divided into two halves, phenetole is not a symmetrical ether.
5. Ethyl methyl ether – the structure of ethyl methyl ether can be drawn as follows:

In ethyl methyl ether, there is a methyl group on the left and an ethyl group on the right side of the oxygen atom. So, on dividing the compound through the center, it will give us two different groups of methyl and ethyl. So, ethyl methyl ether is not a symmetrical ether.
6. Furan – The chemical name for furan is $1-oxacyclopenta-2,4-diene$, whose structure can be shown as follows:

Since there are two different groups on either side of the oxygen atom, furan is a symmetrical ether. The compound consists of four carbon atoms, two on each side of the oxygen atom. On putting a plane across the oxygen atom, we get two identical groups on either side of the atom. So, it is a symmetrical ether.
7. Tetrahydrofuran – Tetrahydrofuran is a furan containing four hydrogen atoms. The chemical name for tetrahydrofuran is as follows:

Like furan, tetrahydrofuran is also symmetrical as it contains two identical groups on both sides of the oxygen atom.
Therefore, the symmetrical ethers among the given ethers are diethyl ether, furan, and tetrahydrofuran.
Note: It is important to remember the IUPAC names of different ethers to be able to draw their chemical structures. Ethers can either contain either two alkyl groups on both sides of the oxygen atom, or two aryl groups on both sides of the oxygen atom, or one alkyl group and one aryl group on either side of the oxygen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




