
which monomer would polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms?
(This question has multiple correct options)
(A) $C{ H }_{ 2 }=C{ Cl }_{ 2}$
(B) ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$
(C) $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$
(D) All of the above
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Tacticity refers to the steric order of the polymer backbone. For a polymer to display tacticity it should be asymmetric. To determine whether a polymer chain is asymmetric or not, look for the presence of chiral centers in the polymer chain.
Complete step by step solution: Let us first understand tacticity in a polymer. Polymers are composed of monomers and these monomers can produce chiral centers in a polymer chain when they undergo polymerisation. If we have a linear asymmetric polymer chain, then the side groups (also called the pendant groups) can be arranged on either side of the chain such that it gives rise to three different types of arrangement. Let us understand it with a simple example. Suppose we have a monomer $R-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$. If we consider the ${ CH }_{ 2 }$ end of the monomer as the head and the $R-CH$ end as tail, then a head to tail polymerization will lead to the following polymer chain:

Where C’ are the asymmetric carbon atoms. The side group R present on these asymmetric carbon atoms can have different spatial arrangement around their carbon centers as a result of which three different arrangements will arise:
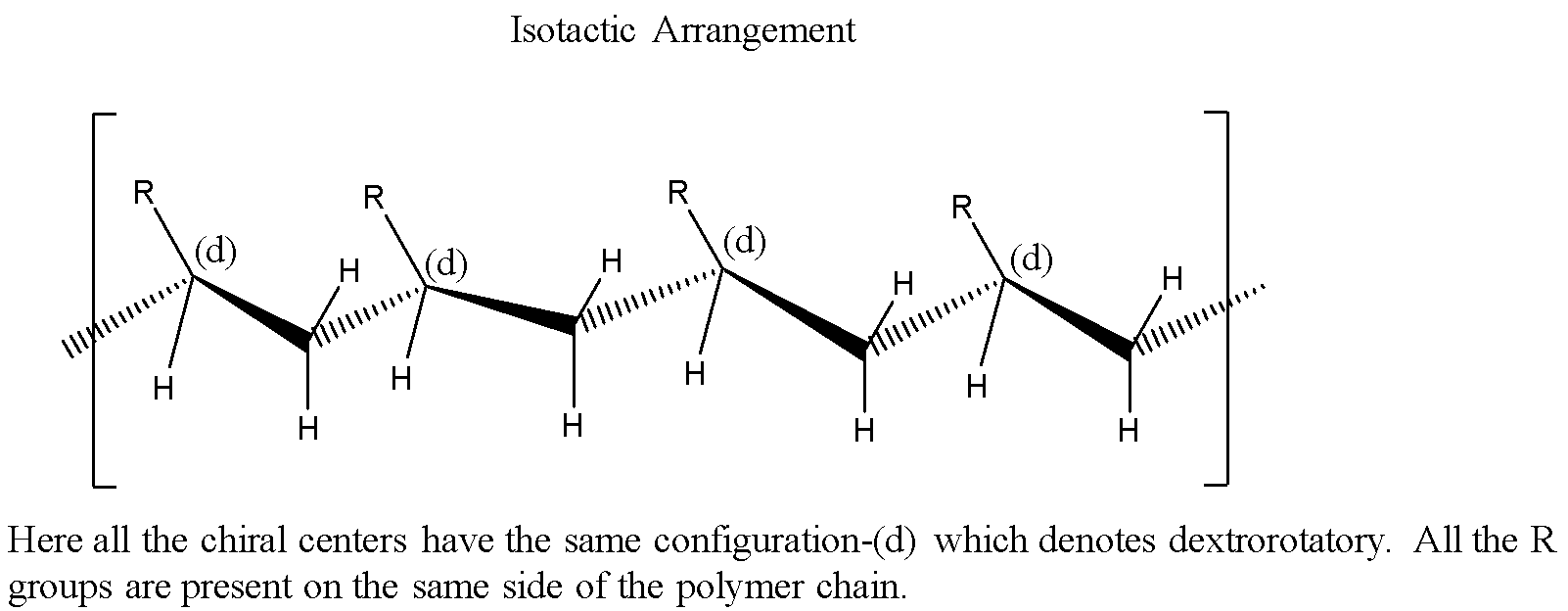
Isotactic: All the chiral centers have the same spatial configuration.
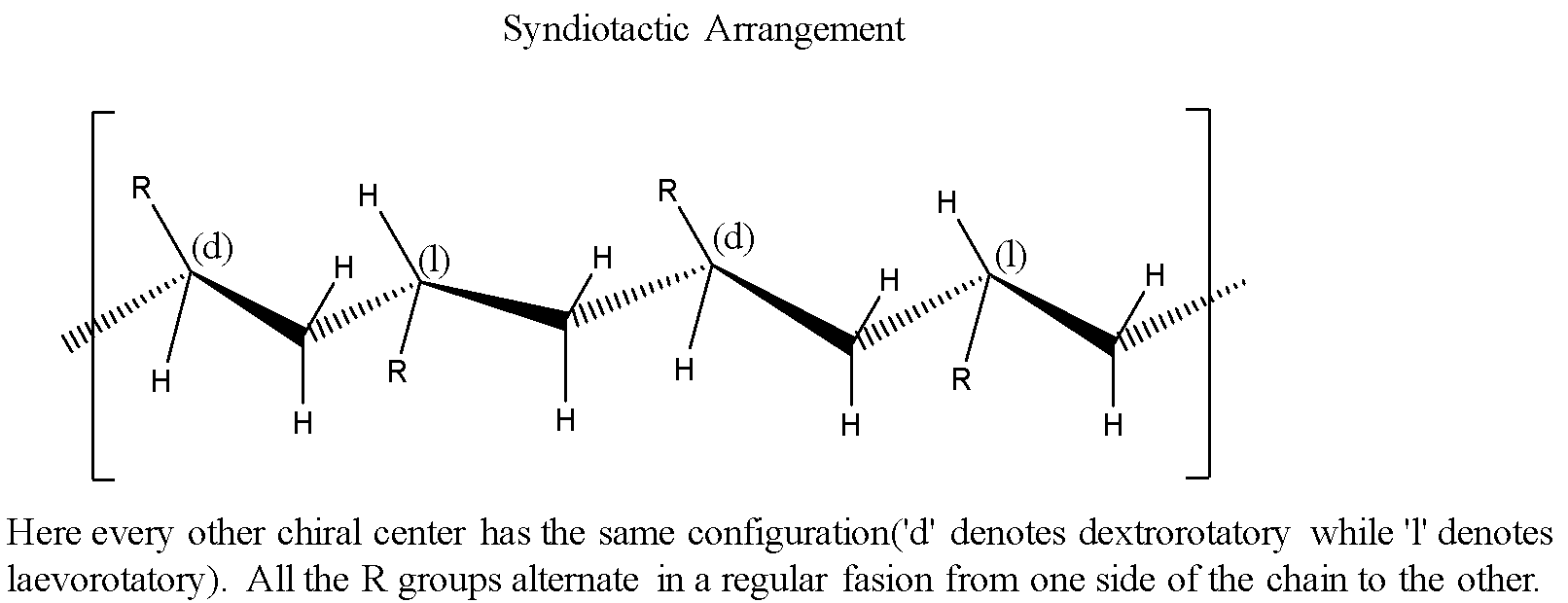
Syndiotactic: Every other chiral center has the same spatial configuration.
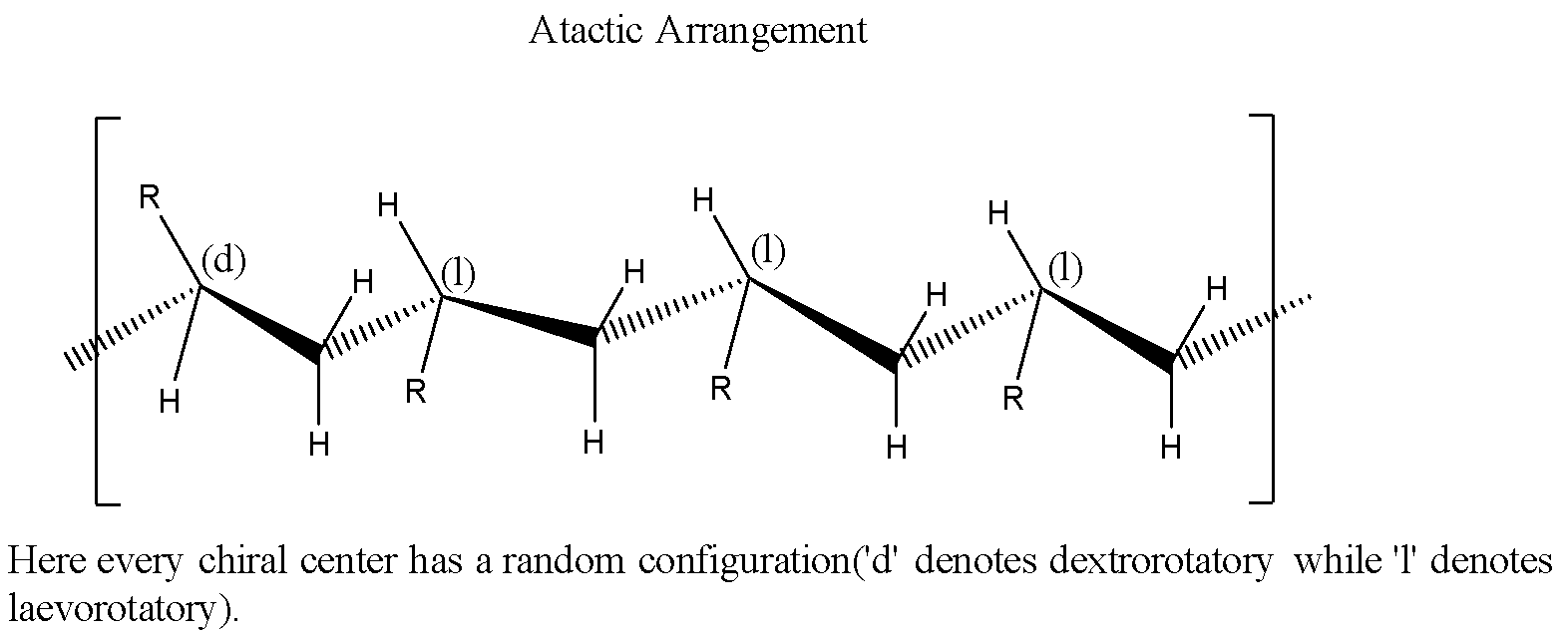
Atactic: The chiral centers will have random spatial configurations.
If $C{ H }_{ 2 }=C{ Cl }_{ 2}$ polymerises in a head to tail fashion, it will have the following structure:
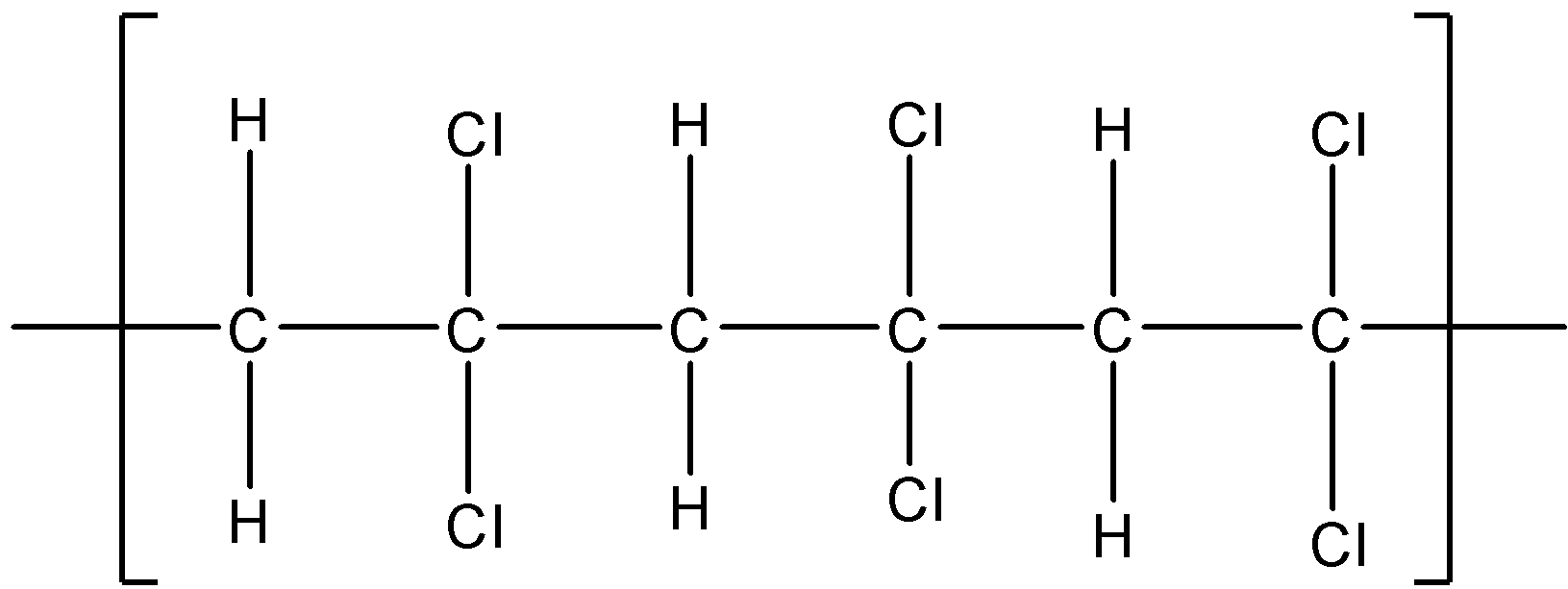
The above structure is not asymmetric since it does not have any chiral center. Therefore $C{ H }_{ 2 }=C{ Cl }_{ 2}$ will not polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms.
If ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ polymerises in a head to tail fashion, it will have the following structure:

Here the carbon atoms labelled in red colour are asymmetric and therefore this polymer chain is asymmetric. So, ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ will polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms.
If $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ polymerises in a head to tail fashion, it will have the following structure:

Here the carbon atoms labelled in red colour are asymmetric and therefore this polymer chain is asymmetric. So, $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ will polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms.
Therefore the correct answers are (B) ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ and (C) $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$.
Note: The monomers of the polymer chain can not only polymerise in a head to tail fashion but also in head to head; tail to tail fashion and random orientation of monomer units along the polymer chain. Also 1,2-disubstituted monomers can also polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms; such as a disubstituted olefin having two different side groups.
Complete step by step solution: Let us first understand tacticity in a polymer. Polymers are composed of monomers and these monomers can produce chiral centers in a polymer chain when they undergo polymerisation. If we have a linear asymmetric polymer chain, then the side groups (also called the pendant groups) can be arranged on either side of the chain such that it gives rise to three different types of arrangement. Let us understand it with a simple example. Suppose we have a monomer $R-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$. If we consider the ${ CH }_{ 2 }$ end of the monomer as the head and the $R-CH$ end as tail, then a head to tail polymerization will lead to the following polymer chain:

Where C’ are the asymmetric carbon atoms. The side group R present on these asymmetric carbon atoms can have different spatial arrangement around their carbon centers as a result of which three different arrangements will arise:
Isotactic: All the chiral centers have the same spatial configuration.

Syndiotactic: Every other chiral center has the same spatial configuration.

Atactic: The chiral centers will have random spatial configurations.

If $C{ H }_{ 2 }=C{ Cl }_{ 2}$ polymerises in a head to tail fashion, it will have the following structure:

The above structure is not asymmetric since it does not have any chiral center. Therefore $C{ H }_{ 2 }=C{ Cl }_{ 2}$ will not polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms.
If ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ polymerises in a head to tail fashion, it will have the following structure:

Here the carbon atoms labelled in red colour are asymmetric and therefore this polymer chain is asymmetric. So, ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ will polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms.
If $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ polymerises in a head to tail fashion, it will have the following structure:

Here the carbon atoms labelled in red colour are asymmetric and therefore this polymer chain is asymmetric. So, $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ will polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms.
Therefore the correct answers are (B) ${ CH }_{ 3 }-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$ and (C) $Ph-CH={ CH }_{ 2 }$.
Note: The monomers of the polymer chain can not only polymerise in a head to tail fashion but also in head to head; tail to tail fashion and random orientation of monomer units along the polymer chain. Also 1,2-disubstituted monomers can also polymerise in isotactic, syndiotactic and atactic forms; such as a disubstituted olefin having two different side groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




