
Which law describes; ${n_1}\sin i = {n_2}\sin r$ $\to$ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ (Newton’s, Snell’s ) Law.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Light shows different phenomena when it travels such as reflection, refraction, polarisation, diffraction etc. We can solve this problem with the help of refraction phenomena of light. In optical physics, refraction is the change in the direction of light waves when it travels from one medium to another medium. The other waves in nature also follow the refraction phenomena as sound waves and water waves.
Complete answer:
Refraction can be seen in our everyday life, for example rainbow and mirages are natural optical phenomena. Refraction follows the Snell’s law. When a light rays travels from one medium to another, it deflects from its original position. The Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of the angle of incidence ${\theta _1}$ to the angel of refraction ${\theta _2}$ is equal to the constant ($\mu $) which is the refractive index of the medium 2 relative to the medium1. This is expressed as:
$\dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} = \mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$ where ${n_1}$ is the refractive index of medium 1, ${n_2}$ is the refractive index of medium 2, $i$ is the angle of incidence and $r$ is the angle of refraction.
The diagrammatic representation is as follows:
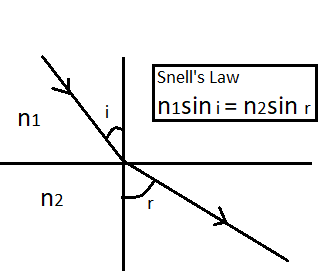
So for the given question , Snell’s law is the suitable word for space given.
Note:
This law has a wide range of applications in the optical branch of physics. When the refraction occurs at the intersecting point, the speed of light and the wavelength of the light wave is changed but the frequency will remain the same in both the medium. Refraction is responsible for many natural phenomena such as mirages, rainbow.
Complete answer:
Refraction can be seen in our everyday life, for example rainbow and mirages are natural optical phenomena. Refraction follows the Snell’s law. When a light rays travels from one medium to another, it deflects from its original position. The Snell’s law states that the ratio of the sines of the angle of incidence ${\theta _1}$ to the angel of refraction ${\theta _2}$ is equal to the constant ($\mu $) which is the refractive index of the medium 2 relative to the medium1. This is expressed as:
$\dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} = \mu = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}}$ where ${n_1}$ is the refractive index of medium 1, ${n_2}$ is the refractive index of medium 2, $i$ is the angle of incidence and $r$ is the angle of refraction.
The diagrammatic representation is as follows:

So for the given question , Snell’s law is the suitable word for space given.
Note:
This law has a wide range of applications in the optical branch of physics. When the refraction occurs at the intersecting point, the speed of light and the wavelength of the light wave is changed but the frequency will remain the same in both the medium. Refraction is responsible for many natural phenomena such as mirages, rainbow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




