
Which is optically active molecule:-
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)




Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: The optically active molecule rotates the plane polarized light either on the left hand side or right hand side. The optical activity is shown by chiral compounds where the chiral carbon is bonded to four different atoms or groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Optically active compounds are those compounds which can rotate the plane polarized light either on the left side or right. If the compound rotates the plane polarized light to the right side then it is called dextrorotatory and when the compound rotates the plane polarized light to the left side then it is laevorotatory.
The optical activity is shown by chiral compounds. The chiral carbon is also known asymmetric carbon where the chiral carbon is attached to four different groups.
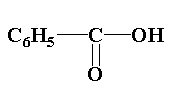
In compound (1), the central carbon is attached to three groups one is phenyl group, second is oxygen atom and third is hydroxyl group. Thus it is not an optically active molecule.
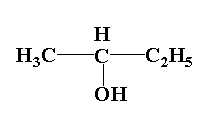
In compound (2), the central carbon is attached to four groups one is methyl group, second is ethyl group and third is hydroxyl group and forth is hydrogen atom. Thus it is an optically active molecule.
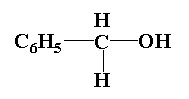
In compound (3), the central carbon is attached to three groups one is phenyl group, second is hydroxyl group and third is two hydrogen atoms. Thus it is not an optically active molecule.
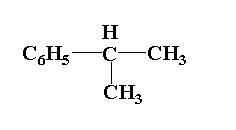
In compound (4), the central carbon is attached to three groups one is phenyl group, second is hydrogen atom and third is two methyl groups. Thus it is not an optically active molecule.
Therefore, the correct option is 2.
Note:
The chiral molecules are always asymmetric in nature. The chiral compounds are those compounds which give non-superimposable mirror image.
Complete step by step answer:
Optically active compounds are those compounds which can rotate the plane polarized light either on the left side or right. If the compound rotates the plane polarized light to the right side then it is called dextrorotatory and when the compound rotates the plane polarized light to the left side then it is laevorotatory.
The optical activity is shown by chiral compounds. The chiral carbon is also known asymmetric carbon where the chiral carbon is attached to four different groups.
In compound (1), the central carbon is attached to three groups one is phenyl group, second is oxygen atom and third is hydroxyl group. Thus it is not an optically active molecule.
In compound (2), the central carbon is attached to four groups one is methyl group, second is ethyl group and third is hydroxyl group and forth is hydrogen atom. Thus it is an optically active molecule.
In compound (3), the central carbon is attached to three groups one is phenyl group, second is hydroxyl group and third is two hydrogen atoms. Thus it is not an optically active molecule.
In compound (4), the central carbon is attached to three groups one is phenyl group, second is hydrogen atom and third is two methyl groups. Thus it is not an optically active molecule.
Therefore, the correct option is 2.
Note:
The chiral molecules are always asymmetric in nature. The chiral compounds are those compounds which give non-superimposable mirror image.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




