
Which device works on the principle of Mutual induction?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Mutual inductance occurs when one magnetic field interacts with another. The mutual inductance concept governs the operation of transformers, motors, generators, and other electrical equipment. Mutual induction occurs when a current flows through one coil or winding and induces a voltage in another coil.
Complete answer:
A transformer is a device that operates on the principle of mutual induction. A transformer is a device that converts alternating current (AC) from one voltage to another.
A transformer consists of two coils, known as the primary and secondary coils. The coils wrapped around a soft iron core. To reduce eddy currents, the iron core is laminated. The transformer's input is applied across the primary coil, and its output is acquired via the secondary coil.
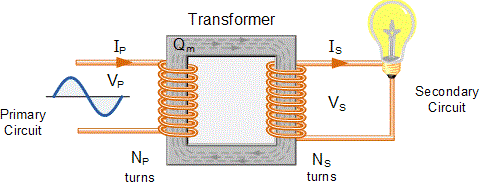
The transformer's principle working concept is based on mutual inductance between primary and secondary circuits that are linked by a shared magnetic flux. The two coils are electrically isolated yet magnetically coupled via a reluctance channel.
Additional information:
Transformer:
In its most basic form, a transformer is something that steps up or steps down voltage. However, when we investigate it further and concerning electric current, it is defined as a static device that changes the level of voltage between circuits. The transformer is essentially a voltage control device that is frequently utilized in alternating current power distribution and transmission.
Michael Faraday first proposed the concept of a transformer in 1831, and it has since been advanced by several other famous scientific thinkers. The general objective of utilizing transformers, however, was to maintain a balance between the electricity generated at very high voltages and the electricity used at very low voltages.
Note: Overall, a transformer performs the following functions:
Electric power transmission from one circuit to the other.
Electromagnetic induction is a method of transferring electrical electricity.
Transfer of electric power with no change in frequency
Mutual induction connects two circuits.
Complete answer:
A transformer is a device that operates on the principle of mutual induction. A transformer is a device that converts alternating current (AC) from one voltage to another.
A transformer consists of two coils, known as the primary and secondary coils. The coils wrapped around a soft iron core. To reduce eddy currents, the iron core is laminated. The transformer's input is applied across the primary coil, and its output is acquired via the secondary coil.

The transformer's principle working concept is based on mutual inductance between primary and secondary circuits that are linked by a shared magnetic flux. The two coils are electrically isolated yet magnetically coupled via a reluctance channel.
Additional information:
Transformer:
In its most basic form, a transformer is something that steps up or steps down voltage. However, when we investigate it further and concerning electric current, it is defined as a static device that changes the level of voltage between circuits. The transformer is essentially a voltage control device that is frequently utilized in alternating current power distribution and transmission.
Michael Faraday first proposed the concept of a transformer in 1831, and it has since been advanced by several other famous scientific thinkers. The general objective of utilizing transformers, however, was to maintain a balance between the electricity generated at very high voltages and the electricity used at very low voltages.
Note: Overall, a transformer performs the following functions:
Electric power transmission from one circuit to the other.
Electromagnetic induction is a method of transferring electrical electricity.
Transfer of electric power with no change in frequency
Mutual induction connects two circuits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




