
Which compound in the above pair undergoes faster ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction?

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: A unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate of reaction depends on only one reactant is known as ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction. Identify if the given halides are primary, secondary or tertiary and then decide which of them reacts faster.
Complete step by step answer:
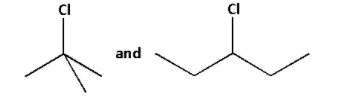
The given halides are as follows:
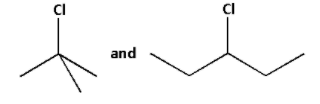
The simplified forms of the given halides are as follows:
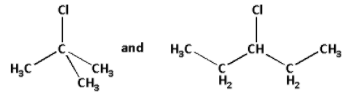
In the first halide, the carbon atom to which the chlorine atom is attached to three more carbons. Thus, the first halide is a tertiary halide.
In the second halide, the carbon atom to which the chlorine atom is attached to two more carbons. Thus, the second halide is a secondary halide.
When the chloride group leaves the structure, a carbocation will be formed. The tertiary halide will form tertiary carbocation and the secondary halide will form secondary carbocation.
The carbocation having more number of adjacent carbon atoms is the most stable. Thus, the tertiary carbocation is more stable.
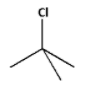
The tertiary alkyl halide leads to the formation of a more stable tertiary carbocation. Thus, the tertiary alkyl halide undergoes a faster ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction.
Thus, the compound that undergoes faster ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction is,
Note: The order of stability of alkyl halides is as follows:
Tertiary halide > secondary halide > primary halide
The order of stability of carbocations is as follows:
Tertiary carbocation > secondary carbocation > primary carbocation
Thus, a tertiary halide prefers a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction. And a primary halide prefers a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction. A bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate of reaction depends on two reactants is known as ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The given halides are as follows:

The simplified forms of the given halides are as follows:

In the first halide, the carbon atom to which the chlorine atom is attached to three more carbons. Thus, the first halide is a tertiary halide.
In the second halide, the carbon atom to which the chlorine atom is attached to two more carbons. Thus, the second halide is a secondary halide.
When the chloride group leaves the structure, a carbocation will be formed. The tertiary halide will form tertiary carbocation and the secondary halide will form secondary carbocation.
The carbocation having more number of adjacent carbon atoms is the most stable. Thus, the tertiary carbocation is more stable.
The tertiary alkyl halide leads to the formation of a more stable tertiary carbocation. Thus, the tertiary alkyl halide undergoes a faster ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction.
Thus, the compound that undergoes faster ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction is,

Note: The order of stability of alkyl halides is as follows:
Tertiary halide > secondary halide > primary halide
The order of stability of carbocations is as follows:
Tertiary carbocation > secondary carbocation > primary carbocation
Thus, a tertiary halide prefers a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{1}}$ reaction. And a primary halide prefers a ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction. A bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the rate of reaction depends on two reactants is known as ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}{\text{2}}$ reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




