
Which among the following is not a planar molecule?
A. ${\text{BC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$
B. ${{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4}$
C. ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$
D. ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals with different energy, shape than the atomic orbitals suitable for pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds.
There are three types of hybridization-\[{\text{sp}},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}_3}{\text{d}},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{{\text{d}}^2},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{{\text{d}}^3}\]
Complete step by step answer:
A.
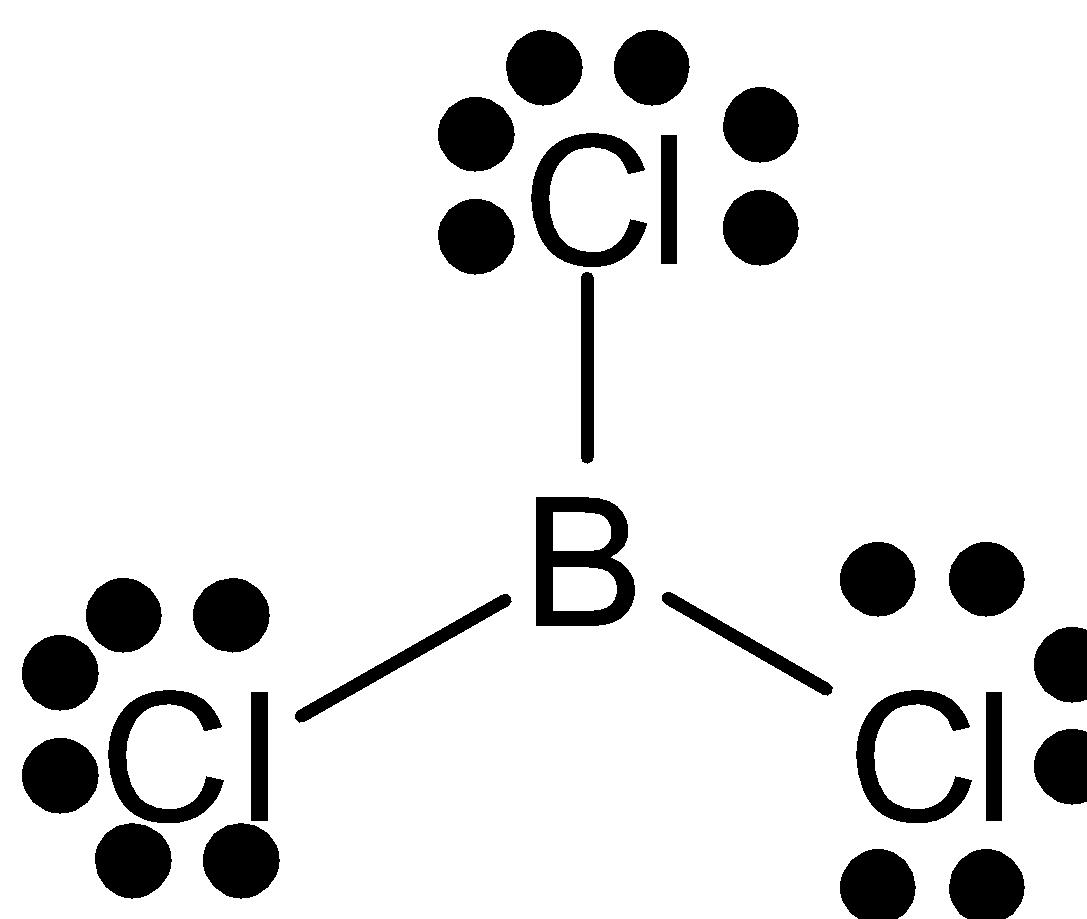
In this compound, the central atom is boron. It is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybridized. Boron has an electronic configuration $1{{\text{s}}^2}2{{\text{s}}^2}2{{\text{p}}^1}$. For bonding boron with three chlorines, it needs three unpaired electrons. One electron is moved from $2{\text{s}}$ to $2{\text{p}}$. Thus these form three half-filled ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybrid orbitals. This will overlap with the chlorine’s unpaired electron. The bond angle is ${120^ \circ }$ and its geometry is trigonal planar.
B.

There are two carbons in this molecule and both of them are ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybridized. Each carbon is in trigonal planar geometry. In this compound, carbon-hydrogen has $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bonds. $\pi $ bonds are formed by side to side overlap. The side-to side overlap is between unhybridized p orbital of one carbon to other carbon.
Hence it is planar.
C.
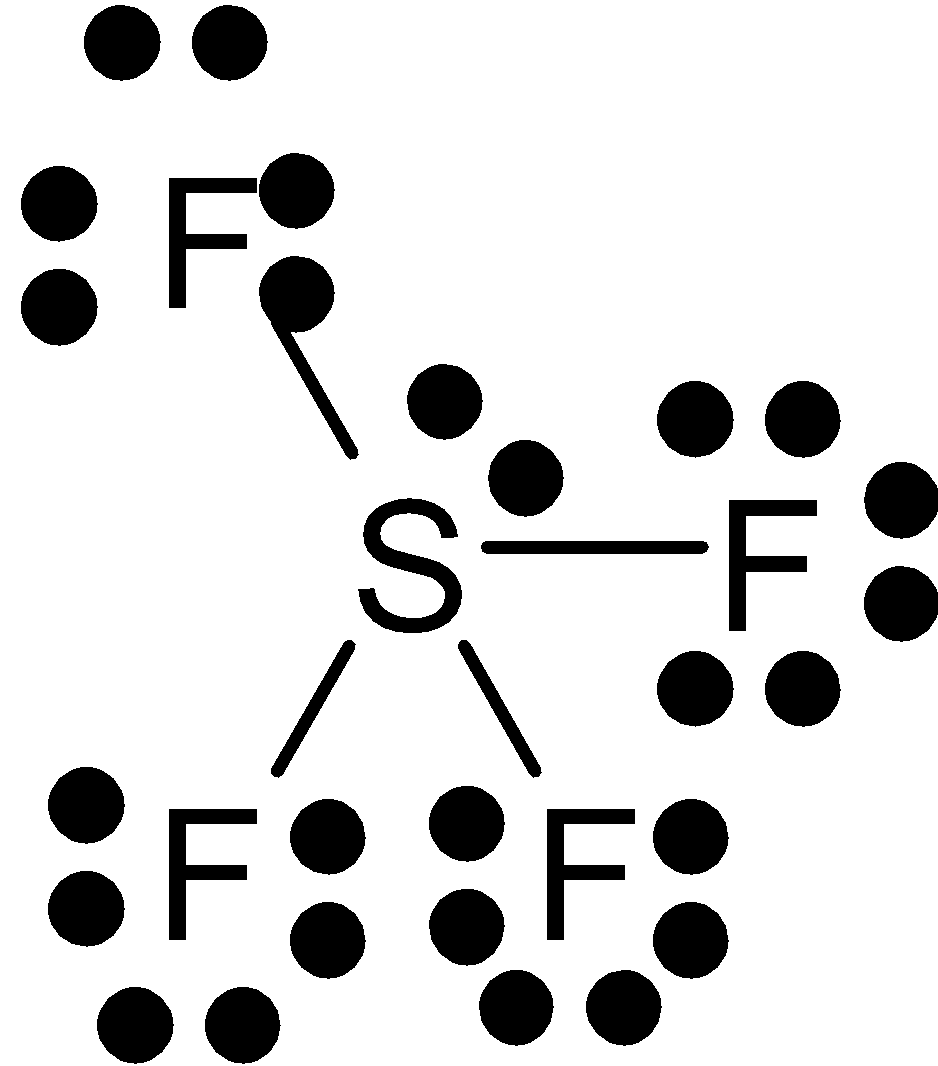
Sulfur has a lone pair of electrons since five of the pair of electrons bonded with fluorine. Its geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. It has two bond angles. The lone pair of electrons are at equatorial position because it needs more space than the bonds. Thus it is not planar.
D.

It has a V or bent shape. It lies in a plane.
Hence only ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ molecule is not planar.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
Valence bond theory is responsible for this concept. It explains about different hybridization and thereby determining the geometry of the molecules. It explains the formation of covalent bonds using quantum mechanics.
There are three types of hybridization-\[{\text{sp}},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}_3}{\text{d}},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{{\text{d}}^2},{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{{\text{d}}^3}\]
Complete step by step answer:
A.

In this compound, the central atom is boron. It is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybridized. Boron has an electronic configuration $1{{\text{s}}^2}2{{\text{s}}^2}2{{\text{p}}^1}$. For bonding boron with three chlorines, it needs three unpaired electrons. One electron is moved from $2{\text{s}}$ to $2{\text{p}}$. Thus these form three half-filled ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybrid orbitals. This will overlap with the chlorine’s unpaired electron. The bond angle is ${120^ \circ }$ and its geometry is trigonal planar.
B.

There are two carbons in this molecule and both of them are ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}$ hybridized. Each carbon is in trigonal planar geometry. In this compound, carbon-hydrogen has $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bonds. $\pi $ bonds are formed by side to side overlap. The side-to side overlap is between unhybridized p orbital of one carbon to other carbon.
Hence it is planar.
C.

Sulfur has a lone pair of electrons since five of the pair of electrons bonded with fluorine. Its geometry is trigonal bipyramidal. It has two bond angles. The lone pair of electrons are at equatorial position because it needs more space than the bonds. Thus it is not planar.
D.

It has a V or bent shape. It lies in a plane.
Hence only ${\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ molecule is not planar.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
Valence bond theory is responsible for this concept. It explains about different hybridization and thereby determining the geometry of the molecules. It explains the formation of covalent bonds using quantum mechanics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




