
What will be S :
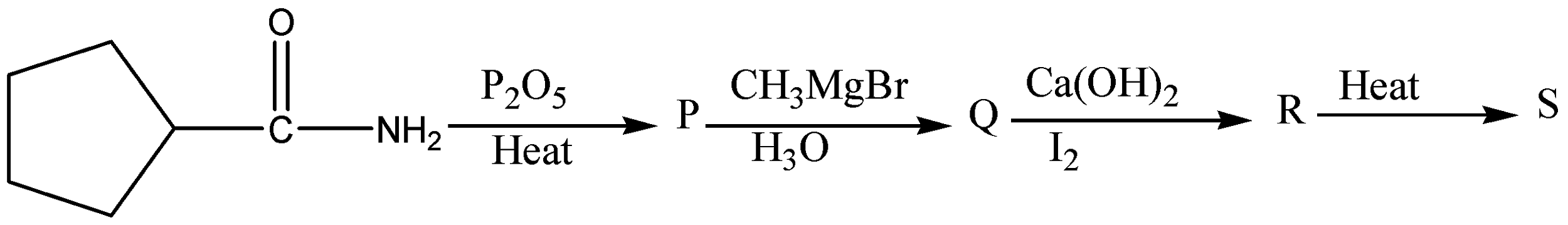
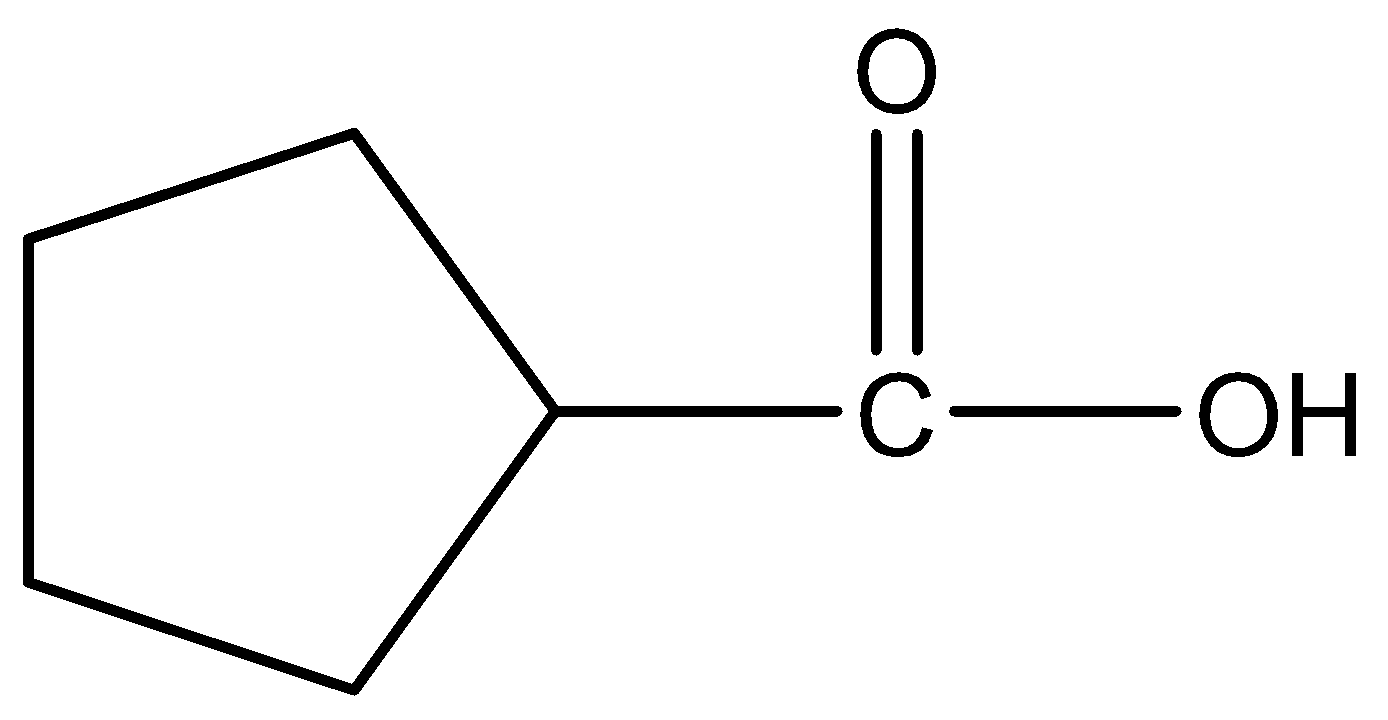
A.
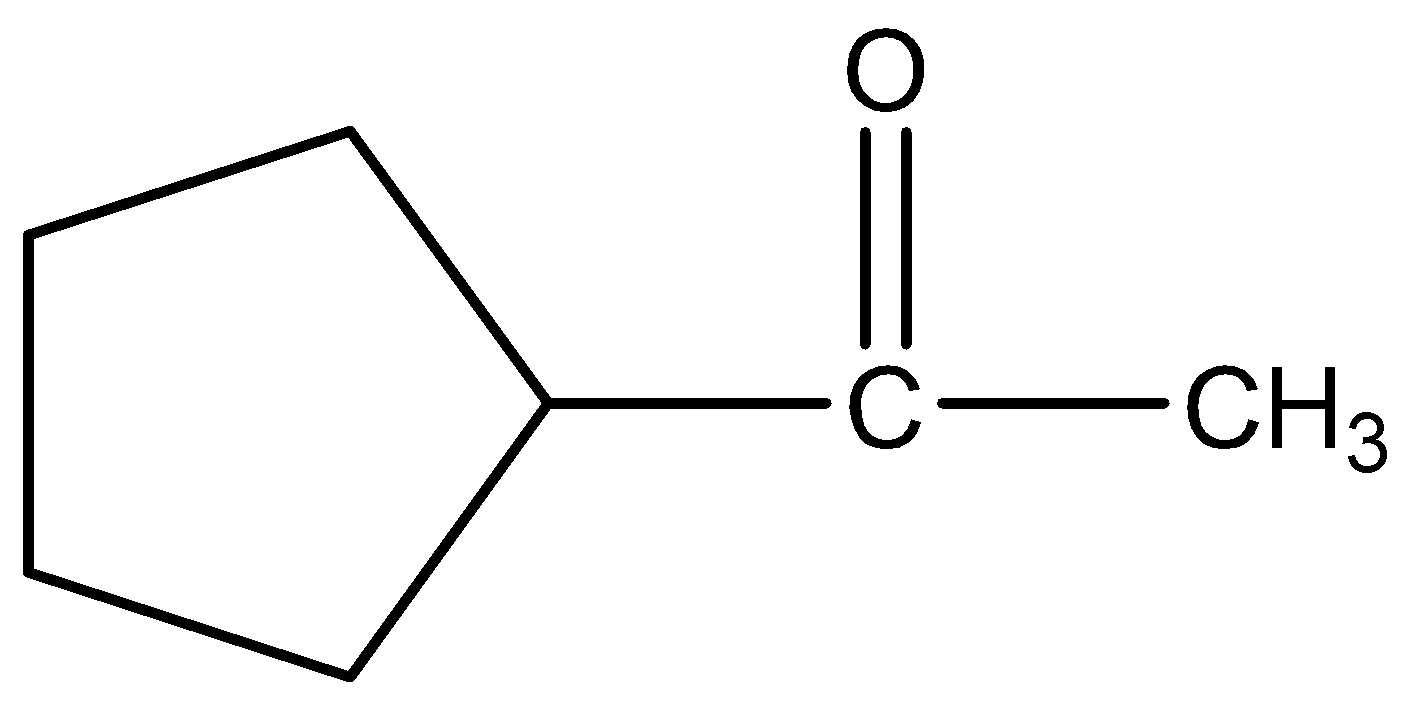
B.
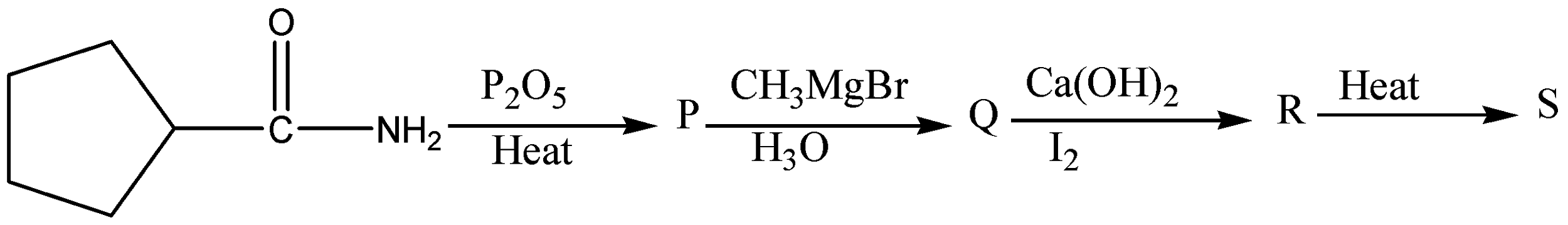


Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: When an amide is treated with dehydrating agents it gets converted into nitriles. Nitriles will get converted to imines in the presence of Grignard reagents and imines on treatment with aqueous acid \[\left( {{H_3}O} \right)\] to give ketones. When a methyl ketone is treated with base and a halogen such as \[\;{I_2},{\text{ }}B{r_2},\] or \[C{l_2}\], it is converted into a carboxylic acid, along with a haloform \[\left( {HC{X_3}} \right)\]
Complete step by step answer:
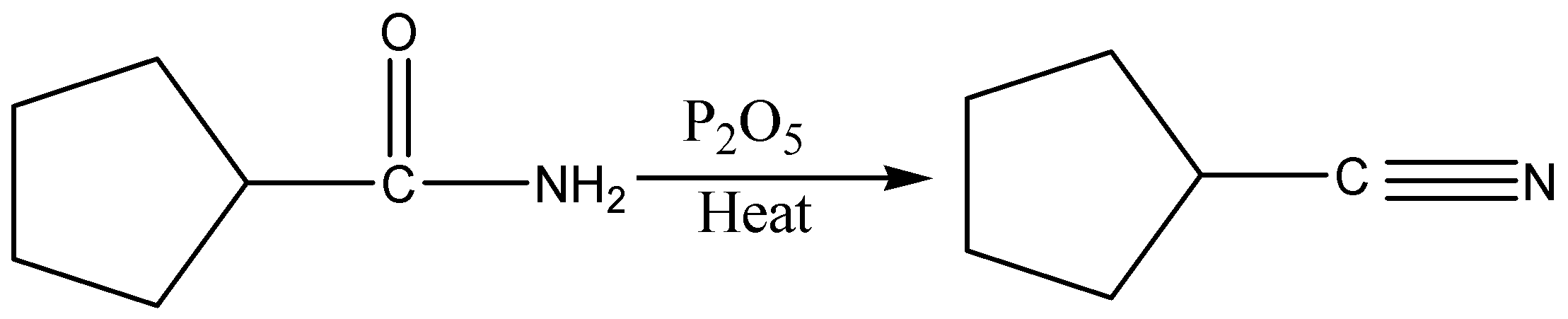
When an amide is treated with dehydrating agents it gets converted into nitriles.
In the given case, \[{P_2}{O_5}\] is a dehydrating agent. When they are heated, amide gets converted into nitriles. Phosphorus pentoxide \[({P_2}{O_5})\] has a strong affinity for water and therefore, acts as a powerful dehydrating agent.
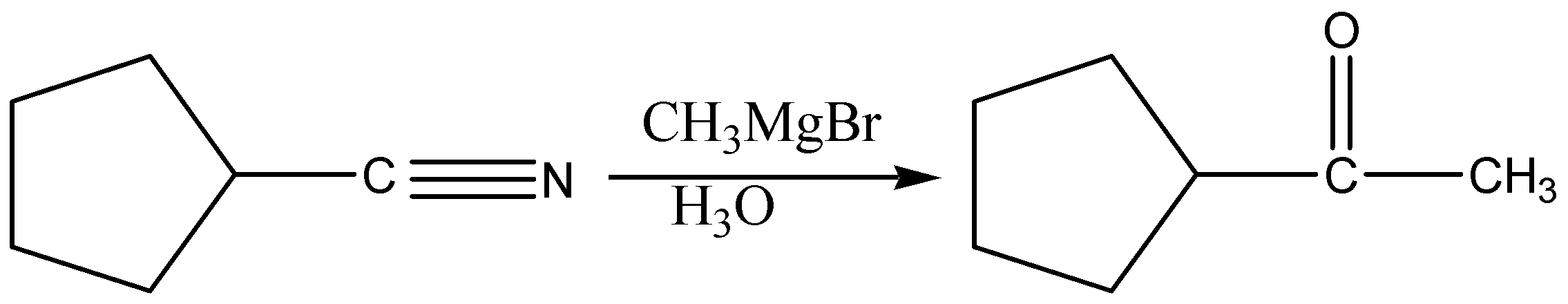
Grignard reagents \[\left( {C{H_3}MgBr} \right)\] will add once to nitriles to form imines. The imines can be treated with aqueous acid (H3O) to give ketones.
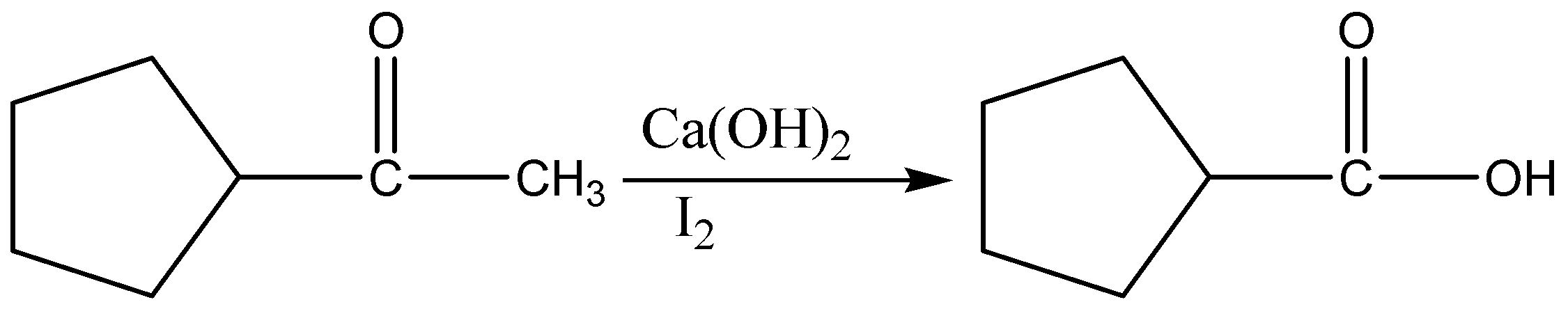
When a methyl ketone is treated with base and a halogen such as \[{I_2},{\text{ }}B{r_2},\] or \[C{l_2}\], it is converted into a carboxylic acid, along with a haloform \[\left( {HC{X_3}} \right)\].
The reaction proceeds through three successive cycles of deprotonation and halogenation at the alpha carbon, followed by addition of base to the carbonyl and expulsion of \[C{X_3}\] as a leaving group.
The final breakage of the \[C - C\] bond only happens with methyl ketones, however! Alkyl ketones with alpha \[C - H\] bonds just give products from alpha-halogenation.
Since a \[C - C\] bond is being exchanged for a \[C - O\] bond, this is a net oxidation – indeed, one of the few methods we learn in introductory organic chemistry for the oxidation of a ketone.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The Grignard reagent adds to the carbon of the nitrile, forming a new carbon-carbon bond. This is stable until water and acid is added which forms the imine. Protonation of the imine nitrogen results in the formation of the iminium ion, which undergoes 1,2-addition by water. This species then undergoes proton transfer to allow for the loss of ammonia \[\left( {N{H_3}} \right)\] in a subsequent 1,2-elimination. Deprotonation of the carbonyl oxygen then results in the ketone.
Complete step by step answer:
When an amide is treated with dehydrating agents it gets converted into nitriles.
In the given case, \[{P_2}{O_5}\] is a dehydrating agent. When they are heated, amide gets converted into nitriles. Phosphorus pentoxide \[({P_2}{O_5})\] has a strong affinity for water and therefore, acts as a powerful dehydrating agent.

Grignard reagents \[\left( {C{H_3}MgBr} \right)\] will add once to nitriles to form imines. The imines can be treated with aqueous acid (H3O) to give ketones.

When a methyl ketone is treated with base and a halogen such as \[{I_2},{\text{ }}B{r_2},\] or \[C{l_2}\], it is converted into a carboxylic acid, along with a haloform \[\left( {HC{X_3}} \right)\].
The reaction proceeds through three successive cycles of deprotonation and halogenation at the alpha carbon, followed by addition of base to the carbonyl and expulsion of \[C{X_3}\] as a leaving group.
The final breakage of the \[C - C\] bond only happens with methyl ketones, however! Alkyl ketones with alpha \[C - H\] bonds just give products from alpha-halogenation.
Since a \[C - C\] bond is being exchanged for a \[C - O\] bond, this is a net oxidation – indeed, one of the few methods we learn in introductory organic chemistry for the oxidation of a ketone.

Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The Grignard reagent adds to the carbon of the nitrile, forming a new carbon-carbon bond. This is stable until water and acid is added which forms the imine. Protonation of the imine nitrogen results in the formation of the iminium ion, which undergoes 1,2-addition by water. This species then undergoes proton transfer to allow for the loss of ammonia \[\left( {N{H_3}} \right)\] in a subsequent 1,2-elimination. Deprotonation of the carbonyl oxygen then results in the ketone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




