
What is transistor and symbol?
Answer
550.8k+ views
Hint: Nowadays, transistors are found in mostly all the electrical devices. One of the prominent uses of the transistors is in the making of the amplifiers. Transistors are of two types, namely, NPN and PNP transistors. We shall analyze the NPN transistor in depth as the PNP transistor also works on the same principle.
Complete answer:
A transistor consists of three main regions. Here, we shall discuss an NPN transistor but these regions have the same name and function even in the case for the PNP transistor. The names given to these regions are based on their functions.
The emitter is the N-side of the transistor which is grounded. It emits electrons into the transistor. The collector is the other N-side of the transistor which is connected to the positive terminal of the battery or power supply. It is called so because it collects the electrons.
The thin P-region in between the two N-sides is called the base.
Due to the forward bias, the electrons emitted from the emitter base junction are going all the way into the collector base junction and before they have any time to recombine because of very small of holes in the base, most of the electrons get swept across and collected over on the collector mainly due to the positive voltage that is being supplied.
The symbol of a transistor in electrical circuits is given as:
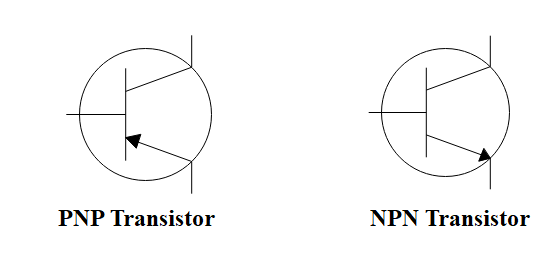
Therefore, we understand that transistors have become an important component of the electric circuits due to their working properties.
Note:
For the transistor to work as an amplifier, the emitter base has to be forward biased and the collector base has to be reverse biased because the N-type is connected to more positively than the P-type. Also, if we reverse bias the emitter base junction, then majority charge carriers would not be able to diffuse through and as a result the electrons will not get emitted and nothing will happen.
Complete answer:
A transistor consists of three main regions. Here, we shall discuss an NPN transistor but these regions have the same name and function even in the case for the PNP transistor. The names given to these regions are based on their functions.
The emitter is the N-side of the transistor which is grounded. It emits electrons into the transistor. The collector is the other N-side of the transistor which is connected to the positive terminal of the battery or power supply. It is called so because it collects the electrons.
The thin P-region in between the two N-sides is called the base.
Due to the forward bias, the electrons emitted from the emitter base junction are going all the way into the collector base junction and before they have any time to recombine because of very small of holes in the base, most of the electrons get swept across and collected over on the collector mainly due to the positive voltage that is being supplied.
The symbol of a transistor in electrical circuits is given as:

Therefore, we understand that transistors have become an important component of the electric circuits due to their working properties.
Note:
For the transistor to work as an amplifier, the emitter base has to be forward biased and the collector base has to be reverse biased because the N-type is connected to more positively than the P-type. Also, if we reverse bias the emitter base junction, then majority charge carriers would not be able to diffuse through and as a result the electrons will not get emitted and nothing will happen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




