
what is the suffix of an ester?
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The IUPAC nomenclature system consists of three parts: word root, suffix, and prefix. The suffix is linked to the word root. Esters are the derivative of acid. Thus esters can be divided into two parts one as the acid part and the alcohol part. The general IUPAC nomenclature of the ester is alkyl alkanoate.
Complete Solution :
Esters have distinctive odour. They are commonly used for characteristic aroma and fragrance. Esters are the derivatives of carboxylic acid. This is obtained by the reaction of acid and alcohol followed by the removal of a water molecule. The general representation of ester is $\text{ R}-\text{COO}-\text{R }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$ .
The following step can be employed to name an ester. These steps are as follows:
Step 1) first, determine the oxygen atom of the continuous chain which is bonded to the carbon atom on both sides. (On one side it is a carbonyl carbon).

Step 2) let’s start numbering the carbon chain on either side of the identified oxygen atom. The number will be given in such a way that carbon on either side of the oxygen will have a 1 position.

Step 3) To name a compound using a simple format.
(Alkyl on the side without carbonyl group) (Alkane on the side with carbonyl group)
Step 4) in the last step, the ending of alkane (which is on the same side that of the carboxyl or carbonyl-containing chain) is changed from –e to –oate.
$\text{ Alkyl Alkane -e + oate = Alkyl Alkanoate }$
Thus, esters have a suffix as ‘-oate’.
Let's consider an example:
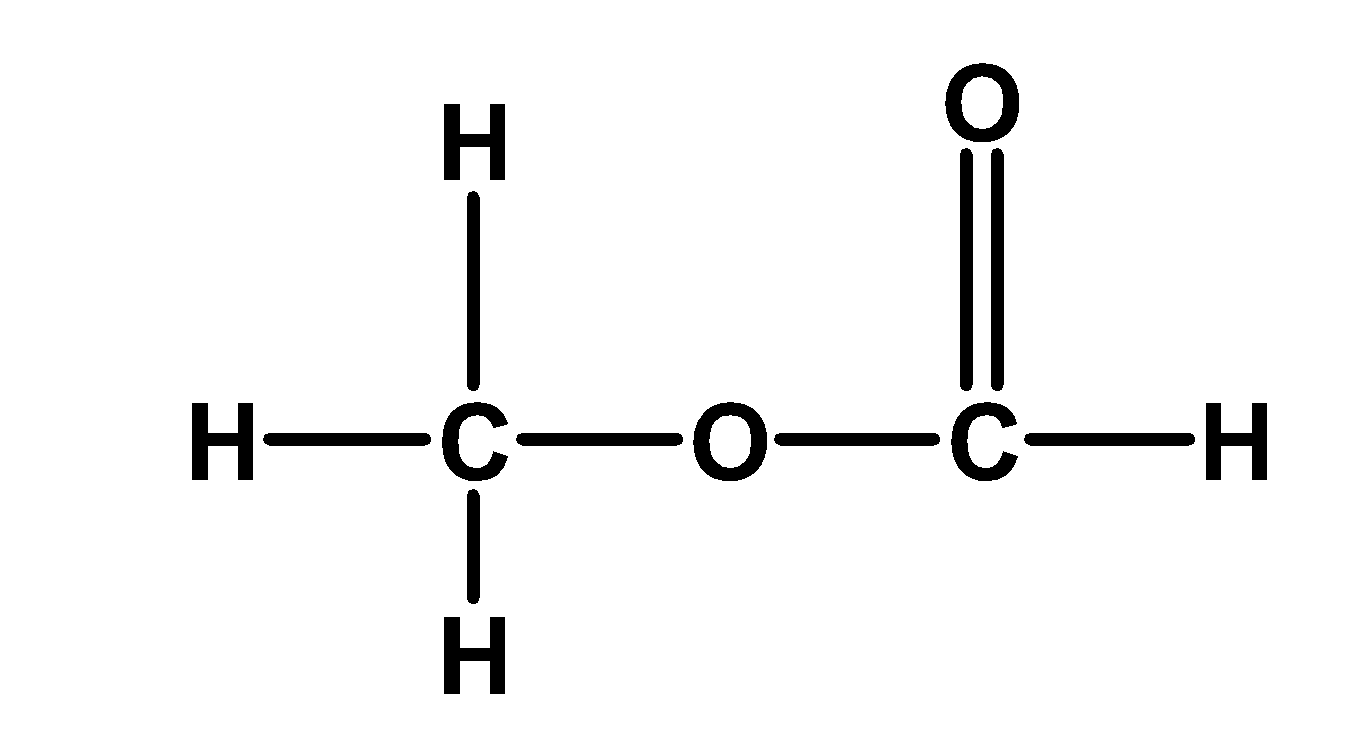
The compound has an IUPAC name as methyl methanoate.
Note: Remember that the ester is made of two parts: acid and alcohol. The alcohol part always ends with the ‘yl’ as the ending. However the IUPAC name ends is written in such a way that ‘oic acid ‘ of acid is changed to ‘oate’.Similarly, amides are also derivative of acid. In amides, the oic acid is replaced by the name ‘amide’.
Complete Solution :
Esters have distinctive odour. They are commonly used for characteristic aroma and fragrance. Esters are the derivatives of carboxylic acid. This is obtained by the reaction of acid and alcohol followed by the removal of a water molecule. The general representation of ester is $\text{ R}-\text{COO}-\text{R }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$ .
The following step can be employed to name an ester. These steps are as follows:
Step 1) first, determine the oxygen atom of the continuous chain which is bonded to the carbon atom on both sides. (On one side it is a carbonyl carbon).

Step 2) let’s start numbering the carbon chain on either side of the identified oxygen atom. The number will be given in such a way that carbon on either side of the oxygen will have a 1 position.

Step 3) To name a compound using a simple format.
(Alkyl on the side without carbonyl group) (Alkane on the side with carbonyl group)
Step 4) in the last step, the ending of alkane (which is on the same side that of the carboxyl or carbonyl-containing chain) is changed from –e to –oate.
$\text{ Alkyl Alkane -e + oate = Alkyl Alkanoate }$
Thus, esters have a suffix as ‘-oate’.
Let's consider an example:

The compound has an IUPAC name as methyl methanoate.
Note: Remember that the ester is made of two parts: acid and alcohol. The alcohol part always ends with the ‘yl’ as the ending. However the IUPAC name ends is written in such a way that ‘oic acid ‘ of acid is changed to ‘oate’.Similarly, amides are also derivative of acid. In amides, the oic acid is replaced by the name ‘amide’.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




