
What is the quadratic formula?
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: A polynomial of the form \[a{x^2} + bx + c,a \ne 0\] and when we equate this polynomial to zero i.e.\[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0,a \ne 0\], then the equation/formula we get is known as quadratic equation or quadratic formula.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us take an example of blackboard of our school which usually has rectangular shape,
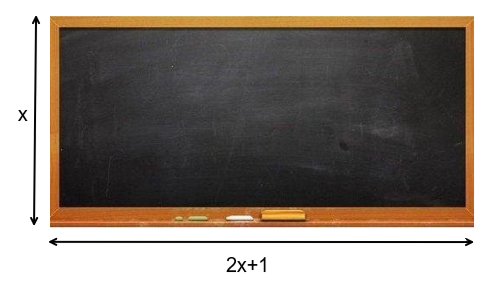
Now we have two information regarding the blackboard, first is the area of blackboard is \[10{m^2}\] and the length is one meter more than twice its breadth
As we know that,
Area of rectangle \[ = length \times breadth\]
So we have,
Area of rectangle \[ = (2x + 1) \times (x)\]
\[(2x + 1) \times (x) = 10\] (Given)
After multiplication we get,
\[2{x^2} + x = 10\]
Therefore, \[2{x^2} + x - 10 = 0\]
So, the breadth of the blackboard should satisfy the equation \[2{x^2} + x - 10 = 0\] which is a quadratic equation.
A quadratic equation is an equation of the form \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\], where a, b, c are real numbers and \[a \ne 0\]. For example, \[2{x^2} + x - 10 = 0\] is a quadratic equation. We can also say that, any equation of the form \[p(x) = 0\], where \[p(x)\] is a polynomial of degree $2$ , is a quadratic equation. But by writing the terms of \[p(x)\] in descending order of their degrees, we get the standard form of the equation. \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] , \[a \ne 0\] is called the standard form of a quadratic equation.
The Solution of quadratic equation and relation between roots and coefficient:
> The solutions of the quadratic equation, \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] is given by \[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}\]
> The expression \[{b^2} - 4ac = D\] is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
> If \[\alpha {\text{ }}\& {\text{ }}\beta \] are the roots of the quadratic equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] then;
1) \[\alpha + \beta = - \dfrac{b}{a}\]
2) \[\alpha \beta = \dfrac{c}{a}\]
3) \[\left| {\alpha - \beta } \right| = \dfrac{{\sqrt D }}{{\left| a \right|}}\]
> Quadratic equation whose roots are \[\alpha {\text{ }}\& {\text{ }}\beta \] is \[(x - \alpha )(x - \beta ) = 0\] i.e.
\[{x^2} - (\alpha + \beta )x + \alpha \beta = 0\] i.e. \[{x^2} - \] (sum of roots) \[x\]\[ + \] product of roots \[ = 0\]
Nature of Roots: Consider the quadratic equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] where \[a,b,c \in R\& a \ne 0\] then;
> \[D > 0 \Leftrightarrow \] Roots are real & distinct (unequal).
> \[D = 0 \Leftrightarrow \] Roots are real & coincident (equal).
> \[D < 0 \Leftrightarrow \] Roots are imaginary.
Note: To solve a quadratic equation by factoring,
> Rearrange the equation and take all terms on one side of the equal sign and zero on the other side.
> Factorize the equation.
> Take each factor equal to zero and solve each equation.
> Check the calculated answer by putting it in the original equation.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us take an example of blackboard of our school which usually has rectangular shape,

Now we have two information regarding the blackboard, first is the area of blackboard is \[10{m^2}\] and the length is one meter more than twice its breadth
As we know that,
Area of rectangle \[ = length \times breadth\]
So we have,
Area of rectangle \[ = (2x + 1) \times (x)\]
\[(2x + 1) \times (x) = 10\] (Given)
After multiplication we get,
\[2{x^2} + x = 10\]
Therefore, \[2{x^2} + x - 10 = 0\]
So, the breadth of the blackboard should satisfy the equation \[2{x^2} + x - 10 = 0\] which is a quadratic equation.
A quadratic equation is an equation of the form \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\], where a, b, c are real numbers and \[a \ne 0\]. For example, \[2{x^2} + x - 10 = 0\] is a quadratic equation. We can also say that, any equation of the form \[p(x) = 0\], where \[p(x)\] is a polynomial of degree $2$ , is a quadratic equation. But by writing the terms of \[p(x)\] in descending order of their degrees, we get the standard form of the equation. \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] , \[a \ne 0\] is called the standard form of a quadratic equation.
The Solution of quadratic equation and relation between roots and coefficient:
> The solutions of the quadratic equation, \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] is given by \[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}\]
> The expression \[{b^2} - 4ac = D\] is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
> If \[\alpha {\text{ }}\& {\text{ }}\beta \] are the roots of the quadratic equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] then;
1) \[\alpha + \beta = - \dfrac{b}{a}\]
2) \[\alpha \beta = \dfrac{c}{a}\]
3) \[\left| {\alpha - \beta } \right| = \dfrac{{\sqrt D }}{{\left| a \right|}}\]
> Quadratic equation whose roots are \[\alpha {\text{ }}\& {\text{ }}\beta \] is \[(x - \alpha )(x - \beta ) = 0\] i.e.
\[{x^2} - (\alpha + \beta )x + \alpha \beta = 0\] i.e. \[{x^2} - \] (sum of roots) \[x\]\[ + \] product of roots \[ = 0\]
Nature of Roots: Consider the quadratic equation \[a{x^2} + bx + c = 0\] where \[a,b,c \in R\& a \ne 0\] then;
> \[D > 0 \Leftrightarrow \] Roots are real & distinct (unequal).
> \[D = 0 \Leftrightarrow \] Roots are real & coincident (equal).
> \[D < 0 \Leftrightarrow \] Roots are imaginary.
Note: To solve a quadratic equation by factoring,
> Rearrange the equation and take all terms on one side of the equal sign and zero on the other side.
> Factorize the equation.
> Take each factor equal to zero and solve each equation.
> Check the calculated answer by putting it in the original equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




