
What is the founder's effect?
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The more adaptable an organism is the greater its probability to survive. To adapt to a certain environment organisms need to evolve (develop certain characteristics over a period of time). Evolutionary biology is the study of these traits (characteristics) that are passed on to consecutive generations. An integral part of evolutionary biology is population genetics. It is a branch that focuses on the genetic diversity within a population.
Complete answer:
Founder’s effect is a phenomenon that affects the genetic diversity within a population. A group of individuals separates from a larger population to form a new group. This is known as the founder’s effect. The newly formed group may distinctly vary from its original population. In 1942, Ernst Mayr, an evolutionary biologist had studied this effect.
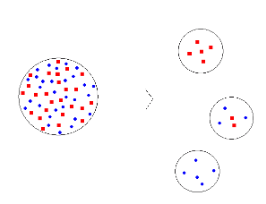
Illustration of the founder’s effect
This effect is caused due to mutations in the gene, migration, or isolation of a particular group due to geographical barriers. The smaller this new group, the lower is the probability of its genotype being represented in the original population. Over a period this may lead to the formation of new species.
Inbreeding is usually observed in this new population. As the population is small inbreeding could also lead to their extinction. Due to inbreeding, the individuals may inherit a defective gene which is not a desirable outcome. With each successive generation, the individuals in this group could all together lose the traits prevalent in the parent population. The founder’s effect leads to less genetic diversity in the population.
Note: Genetic drift is a phenomenon that involves a change in the frequency of any trait (allele) in the genotype of individuals belonging to a particular population. Founder’s effect is considered a type of genetic drift. However, genetic drift involves the random selection of individuals.
Complete answer:
Founder’s effect is a phenomenon that affects the genetic diversity within a population. A group of individuals separates from a larger population to form a new group. This is known as the founder’s effect. The newly formed group may distinctly vary from its original population. In 1942, Ernst Mayr, an evolutionary biologist had studied this effect.

Illustration of the founder’s effect
This effect is caused due to mutations in the gene, migration, or isolation of a particular group due to geographical barriers. The smaller this new group, the lower is the probability of its genotype being represented in the original population. Over a period this may lead to the formation of new species.
Inbreeding is usually observed in this new population. As the population is small inbreeding could also lead to their extinction. Due to inbreeding, the individuals may inherit a defective gene which is not a desirable outcome. With each successive generation, the individuals in this group could all together lose the traits prevalent in the parent population. The founder’s effect leads to less genetic diversity in the population.
Note: Genetic drift is a phenomenon that involves a change in the frequency of any trait (allele) in the genotype of individuals belonging to a particular population. Founder’s effect is considered a type of genetic drift. However, genetic drift involves the random selection of individuals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




