
What is the angle of twist?
Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint:Torsion is the twisting of an object caused by a moment acting about the object’s longitudinal axis. This is a type of deformation. A moment that tends to cause is called torque. If we apply a torque to a circular bar with one end fixed, the torque causes the free end to deform or rotate through an angle this angle is called the Angle of twist.
Formula Used
\[\varphi = \dfrac{{TL}}{{JG}}\] Radians
Complete step by step solution:
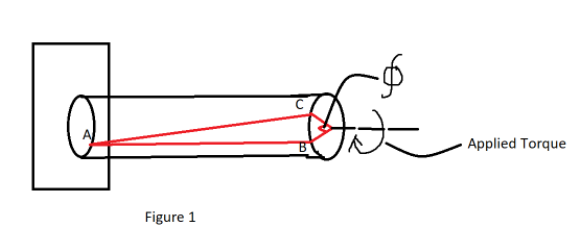
From figure 1 we can see that if we apply torque to a cylindrical bar it causes the bar to deform by twisting. The above cylindrical bar is fixed at one end and the other is left free. While applying the torque if we notice the line AB, the line rotates by angle Phi\[(\varphi )\]. This angle is called the angle of twist.
We can calculate the angle of twist from the following equation.
\[\varphi = \dfrac{{TL}}{{JG}}radians\]
Where\[(\varphi )\] is the angle of twist. Its unit is radians.
\[T\] Is the applied torque. Its unit is Nm
\[L\] Is the length of the circular bar. Its unit is m.
\[J\] Is the polar moment of inertia. Its unit is \[{m^4}\]
\[G\] Is the shear modulus. Its unit is GPA.
Note:The polar moment of inertia is the object’s capacity to resist the internal torque which is applied to the circular bar.
The angle of twist is usually measured in radians. But in the end, they will be converted to degrees.
The shear modulus G is the material’s property. In some cases, the above formula can be rearranged to find the material’s shear modulus.
The general formula for the angle of twist is given below
Formula: \[\varphi = \int_0^L {\dfrac{{T(x)}}{{J(x)G(x)}}} dx\] Units radians.
Formula Used
\[\varphi = \dfrac{{TL}}{{JG}}\] Radians
Complete step by step solution:

From figure 1 we can see that if we apply torque to a cylindrical bar it causes the bar to deform by twisting. The above cylindrical bar is fixed at one end and the other is left free. While applying the torque if we notice the line AB, the line rotates by angle Phi\[(\varphi )\]. This angle is called the angle of twist.
We can calculate the angle of twist from the following equation.
\[\varphi = \dfrac{{TL}}{{JG}}radians\]
Where\[(\varphi )\] is the angle of twist. Its unit is radians.
\[T\] Is the applied torque. Its unit is Nm
\[L\] Is the length of the circular bar. Its unit is m.
\[J\] Is the polar moment of inertia. Its unit is \[{m^4}\]
\[G\] Is the shear modulus. Its unit is GPA.
Note:The polar moment of inertia is the object’s capacity to resist the internal torque which is applied to the circular bar.
The angle of twist is usually measured in radians. But in the end, they will be converted to degrees.
The shear modulus G is the material’s property. In some cases, the above formula can be rearranged to find the material’s shear modulus.
The general formula for the angle of twist is given below
Formula: \[\varphi = \int_0^L {\dfrac{{T(x)}}{{J(x)G(x)}}} dx\] Units radians.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




