
What is spermatogonium?
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: To continue every living population,living beings undergo fertilisation to produce their offspring. Fertilisation is of many types and the single fertilized cell is produced by the organisms to continue their generation. At puberty human beings are capable of producing germ cells . In males it continues throughout life but in females it terminates at the age of about 45 years.
Step by step answer:
A spermatogonium is mainly an undifferentiated male germ cell which is diploid. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. Spermatogonium produces mature sperm cells which are haploid through successive mitotic and meiotic division which fertilise an egg to produce a zygote.
The testis is the primary sex organ of the male that produces large numbers of sperm and it is found in nearly all animal species. Spermatogonia are a group of proliferative cells in the testis that further divide to produce mature sperm cells. Like stem cells, spermatogonium cells are also capable of replicating and hence male are continuously producing sperm . All the process of maturation and formation of sperm takes place in the scrotal sac which is situated outside the body. As the formation and maturation of sperm cells require lower temperature than our body.
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell development. Immature sperm cells undergo successive mitotic and meiotic division to produce mature sperm cells.
At puberty, hormones stimulate these cells to begin dividing by mitosis. Some of the daughter cells produced by mitosis remain at the periphery as spermatogonia.
Spermatogenesis occurs within the seminiferous tubules of the testes. Male germ cell differentiation occurs continuously in the seminiferous tubules of the testes throughout the life of a normal animal.
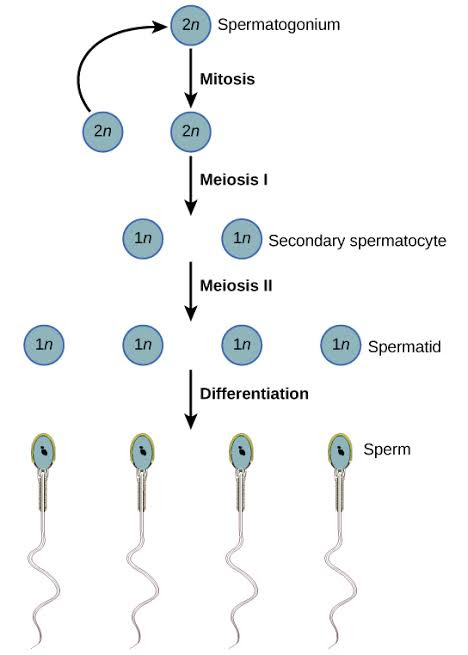
The spermatogonium cells (2n) undergo first mitotic division to produce primary spermatocytes which further undergo first meiotic division to produce primary spermatids and undergoes second meiotic division to produce spermatids which upon further maturation to form mature spermatozoa or sperm cells (1n).
Note:
Mature sperm cells ejaculate from the seminiferous tubules to epididymis and from there it excretes out through the urethra. Millions of sperm enter the vagina during copulation. In the vaginal environment the sperm cells become active and only one cell reaches an egg and is capable of fertilising an egg.
Step by step answer:
A spermatogonium is mainly an undifferentiated male germ cell which is diploid. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. Spermatogonium produces mature sperm cells which are haploid through successive mitotic and meiotic division which fertilise an egg to produce a zygote.
The testis is the primary sex organ of the male that produces large numbers of sperm and it is found in nearly all animal species. Spermatogonia are a group of proliferative cells in the testis that further divide to produce mature sperm cells. Like stem cells, spermatogonium cells are also capable of replicating and hence male are continuously producing sperm . All the process of maturation and formation of sperm takes place in the scrotal sac which is situated outside the body. As the formation and maturation of sperm cells require lower temperature than our body.
Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell development. Immature sperm cells undergo successive mitotic and meiotic division to produce mature sperm cells.
At puberty, hormones stimulate these cells to begin dividing by mitosis. Some of the daughter cells produced by mitosis remain at the periphery as spermatogonia.
Spermatogenesis occurs within the seminiferous tubules of the testes. Male germ cell differentiation occurs continuously in the seminiferous tubules of the testes throughout the life of a normal animal.
The spermatogonium cells (2n) undergo first mitotic division to produce primary spermatocytes which further undergo first meiotic division to produce primary spermatids and undergoes second meiotic division to produce spermatids which upon further maturation to form mature spermatozoa or sperm cells (1n).

Note:
Mature sperm cells ejaculate from the seminiferous tubules to epididymis and from there it excretes out through the urethra. Millions of sperm enter the vagina during copulation. In the vaginal environment the sperm cells become active and only one cell reaches an egg and is capable of fertilising an egg.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




