
What is resonance effect?
Answer
533.5k+ views
Hint: Molecules which shows the resonance effect are considered to be more stable than the ones which do not experience the resonance effect. The molecules experiencing the resonance effect are resonance stabilized.
Complete step by step answer:
> Resonance effect is the polarity produced in a molecule due to interaction between a lone pair of electrons and a pi bond or it is produced due to interaction of two pi bonds between two adjacent atoms.
> Resonance effects can be seen in molecules having conjugated double bonds or in molecules having at least one lone pair of electrons and one double bond.
> There are two types of resonance effect:
1) Positive Resonance Effect: Positive resonance effect occurs when the groups release electrons to the other molecules by the process of the delocalization. The groups are usually denoted by +R or +M. In this process the molecular electron density increases.
2) Negative Resonance Effect: Negative resonance effect occurs when the groups withdraw the electrons from other molecules by the process of the delocalization. The groups are usually denoted by -R or -M. In this process the molecular electron density decreases.
Here is a diagram which will give us a better understanding of the resonance effect:
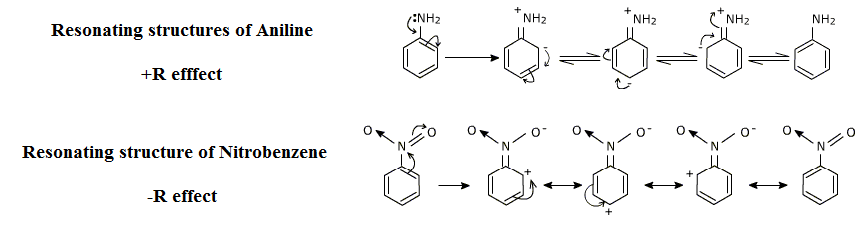
Note:Resonance effect allows for the delocalization in which the overall energy of a molecule is lowered. Since its electrons occupy a greater volume, molecules that experience a resonance are more stable than those that do not.
>Resonance structures are diagrammatic representations used predominantly in organic chemistry to symbolize resonant bonds between atoms in molecules. Because Lewis dot diagrams often cannot represent the true electronic structure of a molecule, resonance structures are often employed to approximate the true electronic structure.
The order of +M effect is:
${{\text{-O}}^{-}}>\text{-N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}>\text{-NHR }>\text{-OR }>\text{-NHCOR }>\text{-OCOR }>\text{-Ph }>\text{-F }>\text{-Cl }>\text{-Br }>\text{-I}$
The order of -M effect is:
$\text{-N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}>\text{-CN}>\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{H} >\text{-CHO } > \text{>C=O }> \text{-COOCOR }>\text{-COOR }> \text{-COOH }> \text{-CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ }> \text{-CO}{{\text{O}}^{-}}\text{ }$
Complete step by step answer:
> Resonance effect is the polarity produced in a molecule due to interaction between a lone pair of electrons and a pi bond or it is produced due to interaction of two pi bonds between two adjacent atoms.
> Resonance effects can be seen in molecules having conjugated double bonds or in molecules having at least one lone pair of electrons and one double bond.
> There are two types of resonance effect:
1) Positive Resonance Effect: Positive resonance effect occurs when the groups release electrons to the other molecules by the process of the delocalization. The groups are usually denoted by +R or +M. In this process the molecular electron density increases.
2) Negative Resonance Effect: Negative resonance effect occurs when the groups withdraw the electrons from other molecules by the process of the delocalization. The groups are usually denoted by -R or -M. In this process the molecular electron density decreases.
Here is a diagram which will give us a better understanding of the resonance effect:

Note:Resonance effect allows for the delocalization in which the overall energy of a molecule is lowered. Since its electrons occupy a greater volume, molecules that experience a resonance are more stable than those that do not.
>Resonance structures are diagrammatic representations used predominantly in organic chemistry to symbolize resonant bonds between atoms in molecules. Because Lewis dot diagrams often cannot represent the true electronic structure of a molecule, resonance structures are often employed to approximate the true electronic structure.
The order of +M effect is:
${{\text{-O}}^{-}}>\text{-N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}>\text{-NHR }>\text{-OR }>\text{-NHCOR }>\text{-OCOR }>\text{-Ph }>\text{-F }>\text{-Cl }>\text{-Br }>\text{-I}$
The order of -M effect is:
$\text{-N}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}>\text{-CN}>\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{3}}\text{H} >\text{-CHO } > \text{>C=O }> \text{-COOCOR }>\text{-COOR }> \text{-COOH }> \text{-CON}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ }> \text{-CO}{{\text{O}}^{-}}\text{ }$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




