
What is Perfect Modulation?
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint:To avoid distortion in the modulated signal, the message signal's maximum amplitude must be smaller than (or equal to) the carrier signal's maximum amplitude. If the carrier signal has an amplitude of \[5\] volts, the message signal must have an amplitude of less than (or equal to) \[5\] volts. As a result, when \[Am{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}Ac\], the modulation index's maximum value will be less than or equal to one (\[Mi < = 1\]). The modulation index will have a minimum value of zero.
Based on this, there are \[3\] types of modulation:
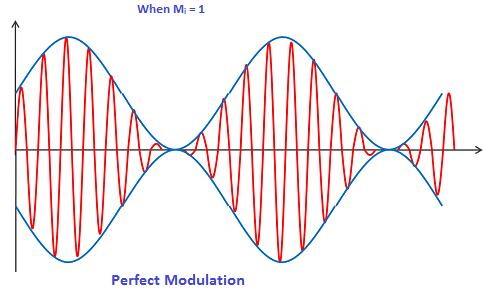
Perfect-Modulation
Under-Modulation
Over-Modulation
Complete step-by-step solution:
Perfect modulation:
When the message signal or modulating signal, maximum amplitude is approximately equal to the carrier signal's maximum amplitude (\[Am{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}Ac\]), perfect-modulation occurs.
The modulation index is the ratio of the message signal's maximum amplitude to the carrier signal's maximum amplitude. For example, if the maximum amplitude of the message signal is \[4\] volts and the maximum amplitude of the carrier signal is also \[4\] volts, the modulating signal amplitude (\[4\] volts) to the carrier signal amplitude (\[4\] volts) ratio is\[1\]. As a result, with perfect-modulation, the modulation index is one (\[Mi{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1\]).
The modulation depth is another name for the modulation index. The modulation depth of the perfect-modulation is\[100\% \]. The carrier level in perfect-modulation drops to $0$. There is no distortion with perfect modulation.
Note:Modulation benefits:
The size of the antenna was reduced.
There is no signal mixing.
The range of communication expands.
The transmissions multiplexed.
It is possible to change the bandwidth.
The quality of the reception improves.
Based on this, there are \[3\] types of modulation:
Perfect-Modulation
Under-Modulation
Over-Modulation
Complete step-by-step solution:
Perfect modulation:
When the message signal or modulating signal, maximum amplitude is approximately equal to the carrier signal's maximum amplitude (\[Am{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}Ac\]), perfect-modulation occurs.
The modulation index is the ratio of the message signal's maximum amplitude to the carrier signal's maximum amplitude. For example, if the maximum amplitude of the message signal is \[4\] volts and the maximum amplitude of the carrier signal is also \[4\] volts, the modulating signal amplitude (\[4\] volts) to the carrier signal amplitude (\[4\] volts) ratio is\[1\]. As a result, with perfect-modulation, the modulation index is one (\[Mi{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1\]).
The modulation depth is another name for the modulation index. The modulation depth of the perfect-modulation is\[100\% \]. The carrier level in perfect-modulation drops to $0$. There is no distortion with perfect modulation.

Note:Modulation benefits:
The size of the antenna was reduced.
There is no signal mixing.
The range of communication expands.
The transmissions multiplexed.
It is possible to change the bandwidth.
The quality of the reception improves.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




