
What is impedance?
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: In an electrical circuit, resistance is a measure of the resistance to current flow. The Greek letter omega (\[\Omega \]) is used to represent resistance in ohms. Georg Simon Ohm (1784-1854), a German physicist who investigated the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, is the name given to Ohms.
Complete answer:
Impedance (symbol Z) is a measurement of a circuit's total resistance to current, or how much it obstructs the flow of charge. It's similar to resistance, but it also takes capacitance and inductance into account. Ohms are the unit of measurement for impedance (ohm).
Since the consequences of capacitance and inductance correlate with the frequency of the current flowing through the device, impedance differs with frequency, it is more complicated than resistance. Resistance has the same influence regardless of frequency.
Impedance is divided into two categories:
R is for resistance (the part which is constant regardless of frequency).
Reactance X (the part which varies with frequency due to capacitance and inductance).
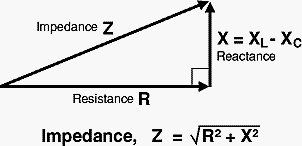
Resistance (R), capacitance (C), inductance (L), and frequency (f)are the four electrical quantities that specify a circuit's impedance (Z).
Electrical impedance is the measurement of a circuit's resistance to current when a voltage is applied in electrical engineering.
The ratio of the complex representation of the sinusoidal voltage between its terminals to the complex representation of the current flowing through it is the impedance of a two-terminal circuit part. In general, it is determined by the sinusoidal voltage's frequency.
In contrast to resistance, which only has magnitude, impedance applies the principle of resistance to alternating current (AC) circuits and has both magnitude and phase.
Note:
Since it requires a basic linear law to relate sinusoidal voltages and currents, the concept of impedance is useful for conducting AC analysis of electrical networks. The two-terminal concept of impedance is insufficient in multiple port networks, but the impedance matrix also linearly relates the dynamic voltages at the ports and the currents flowing through them. Admittance is the inverse of impedance, and its SI unit is the Siemens, formerly known as the mho.
Complete answer:
Impedance (symbol Z) is a measurement of a circuit's total resistance to current, or how much it obstructs the flow of charge. It's similar to resistance, but it also takes capacitance and inductance into account. Ohms are the unit of measurement for impedance (ohm).
Since the consequences of capacitance and inductance correlate with the frequency of the current flowing through the device, impedance differs with frequency, it is more complicated than resistance. Resistance has the same influence regardless of frequency.
Impedance is divided into two categories:
R is for resistance (the part which is constant regardless of frequency).
Reactance X (the part which varies with frequency due to capacitance and inductance).

Resistance (R), capacitance (C), inductance (L), and frequency (f)are the four electrical quantities that specify a circuit's impedance (Z).
Electrical impedance is the measurement of a circuit's resistance to current when a voltage is applied in electrical engineering.
The ratio of the complex representation of the sinusoidal voltage between its terminals to the complex representation of the current flowing through it is the impedance of a two-terminal circuit part. In general, it is determined by the sinusoidal voltage's frequency.
In contrast to resistance, which only has magnitude, impedance applies the principle of resistance to alternating current (AC) circuits and has both magnitude and phase.
Note:
Since it requires a basic linear law to relate sinusoidal voltages and currents, the concept of impedance is useful for conducting AC analysis of electrical networks. The two-terminal concept of impedance is insufficient in multiple port networks, but the impedance matrix also linearly relates the dynamic voltages at the ports and the currents flowing through them. Admittance is the inverse of impedance, and its SI unit is the Siemens, formerly known as the mho.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




