
What is electromeric effect?
Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint: The electromeric effect is related to the movement of electrons in multiple bonds towards a particular atom which is in the multiple bonds when an electron attacking reagent is present.
Complete answer:
Electromeric effect refers to the occurrence of intramolecular electron displacement that results in molecular polarizability. Polarizability is the property by the virtue of which a matter can form instantaneous dipoles. Let us understand this effect in a detailed manner.
1. Electromeric effect is observed only in the unsaturated organic compound. The unsaturated organic compounds have double or triple bonds in them.
2. Due to the electromeric effect, the molecule instantaneously forms dipoles due to the transfer of electrons when an attacking reagent is introduced. The pi electrons of the multiple bonds are transferred to one of the atoms participating in the multiple bonds and that creates a dipole.
3. The electromeric effect is a temporary effect that takes place only in the presence of an attacking reagent. This effect remains as long as the attacking reagent is exposed to the molecule. On the removal of the attacking reagent, the polarized molecule goes back into its original state.
4. There are two types of electromeric effect: the +E effect and the –E effect.
+E effect: The +E effect occurs when the pi-electron pair shifts toward the attacking reagent. The +E effect generally takes place when the attacking reagent is electrophile i.e. electron loving or positively charged. It attaches itself to the negatively charged atom of the molecule. The +E effect can be observed in the case of the addition of acid to an alkene.
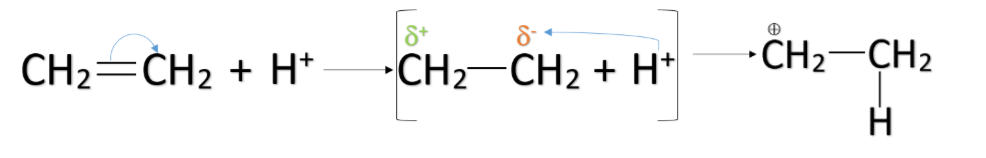
–E effect: The –E effect occurs when the pi-electron pair shifts away from the attacking reagent. The –E effect generally takes place when the attacking reagent is a nucleophile i.e. nucleus loving or negatively charged. It attaches itself to the positively charged atom of the molecule. The –E effect can be observed in the case of the addition of nucleophiles like cyanide ions to the carbonyl compounds.
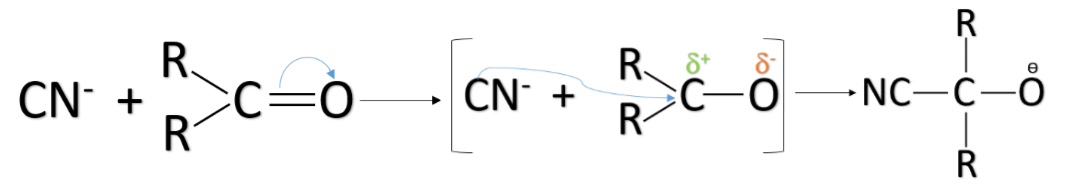
Note: Don’t confuse the inductive effect with the electromeric effect. The inductive effect refers to the formation of dipoles due to the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Unlike the electromeric effect, it does not require multiple bonds and it is a permanent effect.
Complete answer:
Electromeric effect refers to the occurrence of intramolecular electron displacement that results in molecular polarizability. Polarizability is the property by the virtue of which a matter can form instantaneous dipoles. Let us understand this effect in a detailed manner.
1. Electromeric effect is observed only in the unsaturated organic compound. The unsaturated organic compounds have double or triple bonds in them.
2. Due to the electromeric effect, the molecule instantaneously forms dipoles due to the transfer of electrons when an attacking reagent is introduced. The pi electrons of the multiple bonds are transferred to one of the atoms participating in the multiple bonds and that creates a dipole.
3. The electromeric effect is a temporary effect that takes place only in the presence of an attacking reagent. This effect remains as long as the attacking reagent is exposed to the molecule. On the removal of the attacking reagent, the polarized molecule goes back into its original state.
4. There are two types of electromeric effect: the +E effect and the –E effect.
+E effect: The +E effect occurs when the pi-electron pair shifts toward the attacking reagent. The +E effect generally takes place when the attacking reagent is electrophile i.e. electron loving or positively charged. It attaches itself to the negatively charged atom of the molecule. The +E effect can be observed in the case of the addition of acid to an alkene.
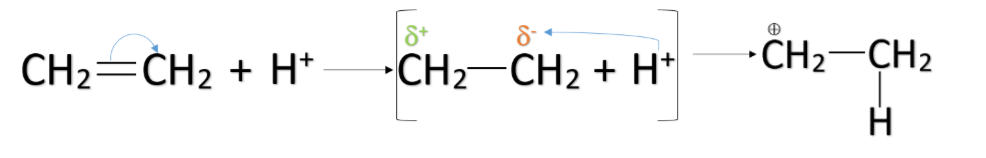
–E effect: The –E effect occurs when the pi-electron pair shifts away from the attacking reagent. The –E effect generally takes place when the attacking reagent is a nucleophile i.e. nucleus loving or negatively charged. It attaches itself to the positively charged atom of the molecule. The –E effect can be observed in the case of the addition of nucleophiles like cyanide ions to the carbonyl compounds.

Note: Don’t confuse the inductive effect with the electromeric effect. The inductive effect refers to the formation of dipoles due to the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Unlike the electromeric effect, it does not require multiple bonds and it is a permanent effect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




