
What is Curtius Rearrangement?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Curtius Rearrangement reaction is the preparation reaction of Amines from Acid Chloride as starting material. Hydrazine is used as the reagent in this particular rearrangement.
Complete step by step answer:
The curtius rearrangement is a reaction where acid chloride is converted to lower homologous amine.
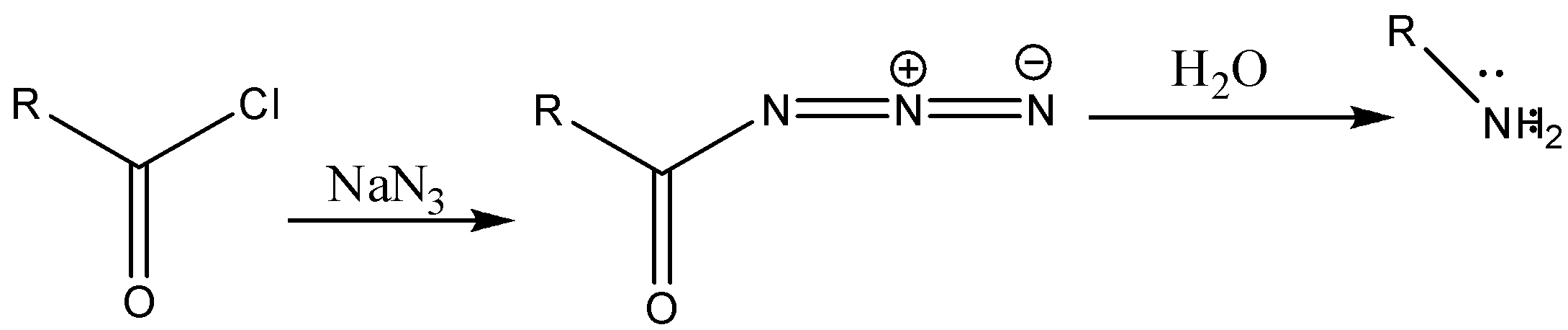
Reaction with mechanism is as follows:
Step 1-The starting material in the reaction is the acid chloride. The acid chloride on reaction with sodium azide will produce acid azide. The reaction will be as follows:
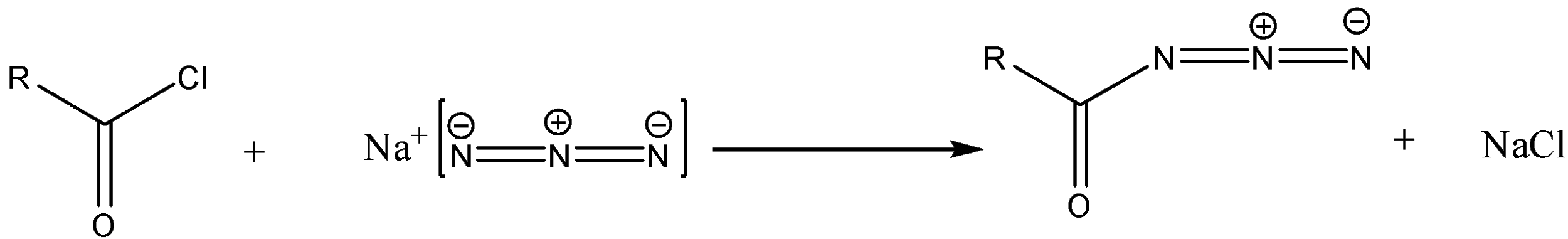
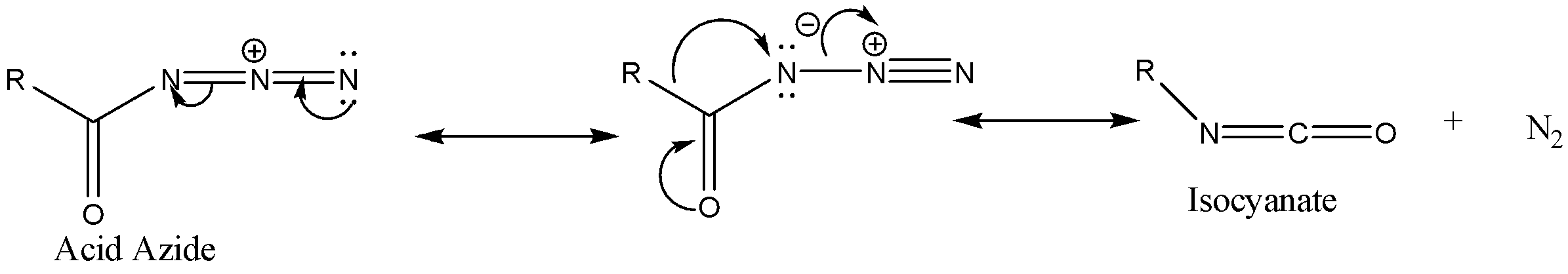
Step 2: The acid azide formed due to thermal decomposition then undergoes rearrangement thus releasing nitrogen gas and Isocyanate is formed.
Step 3: Isocyanate formed reacts in a different manner when different solvent is used. The reaction is carried out in aqueous or alcohol solution. Isocyanate gets converted to primary amine or urethane respectively.
Case 1: Reaction in Aqueous medium.
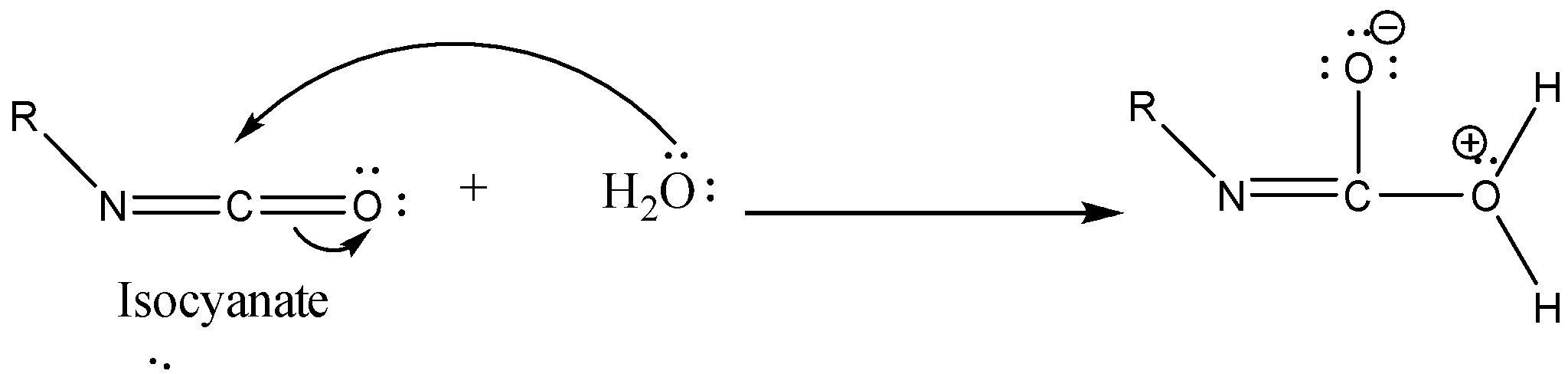
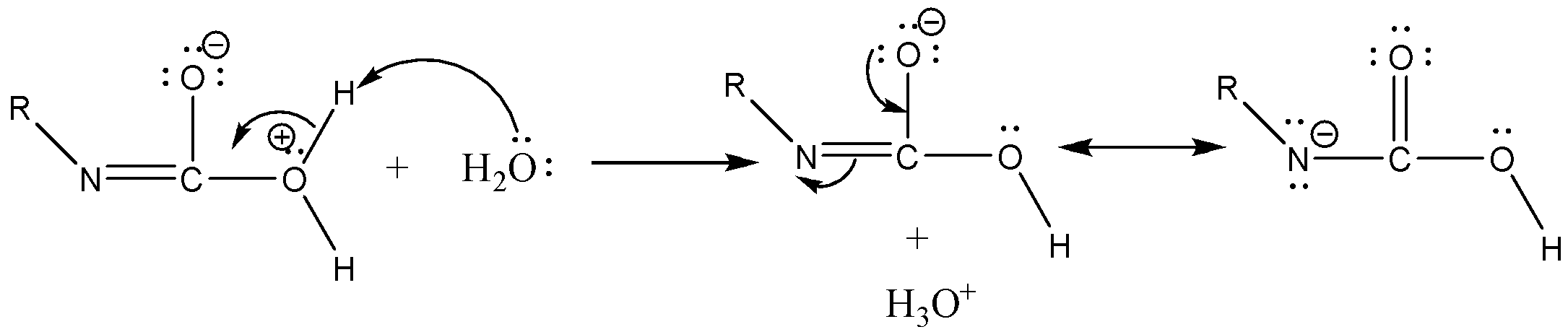
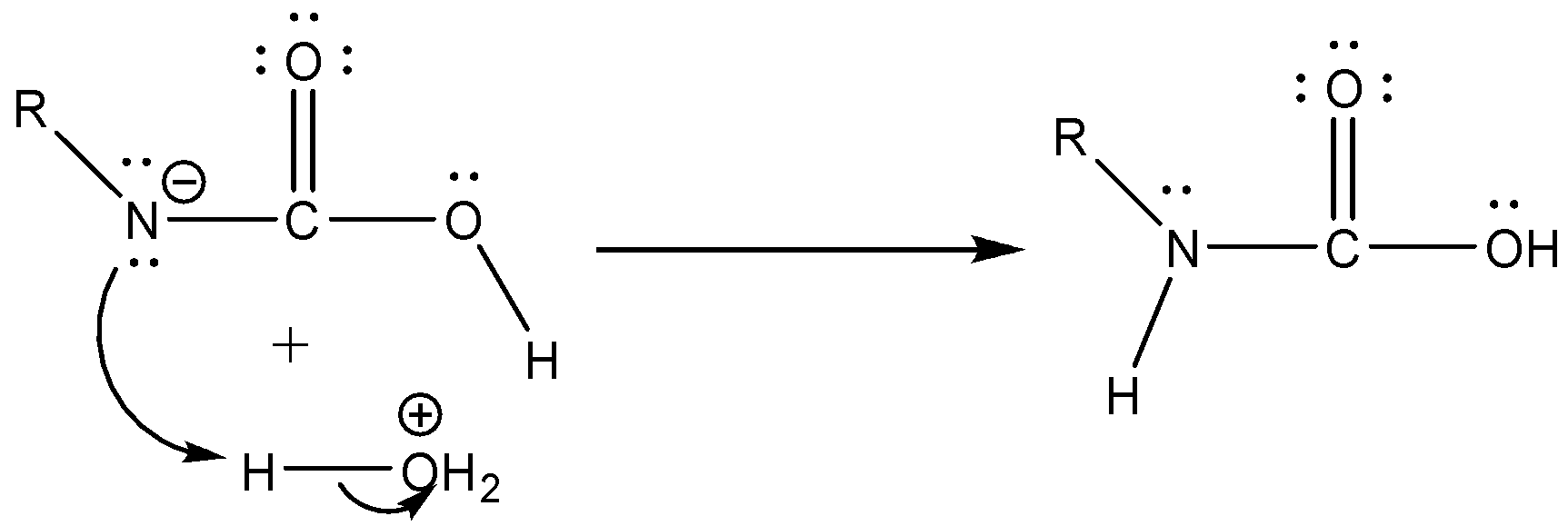
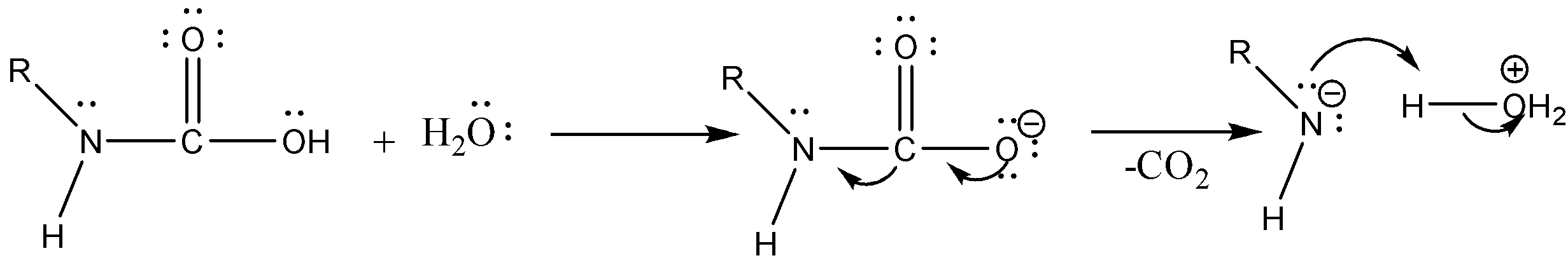
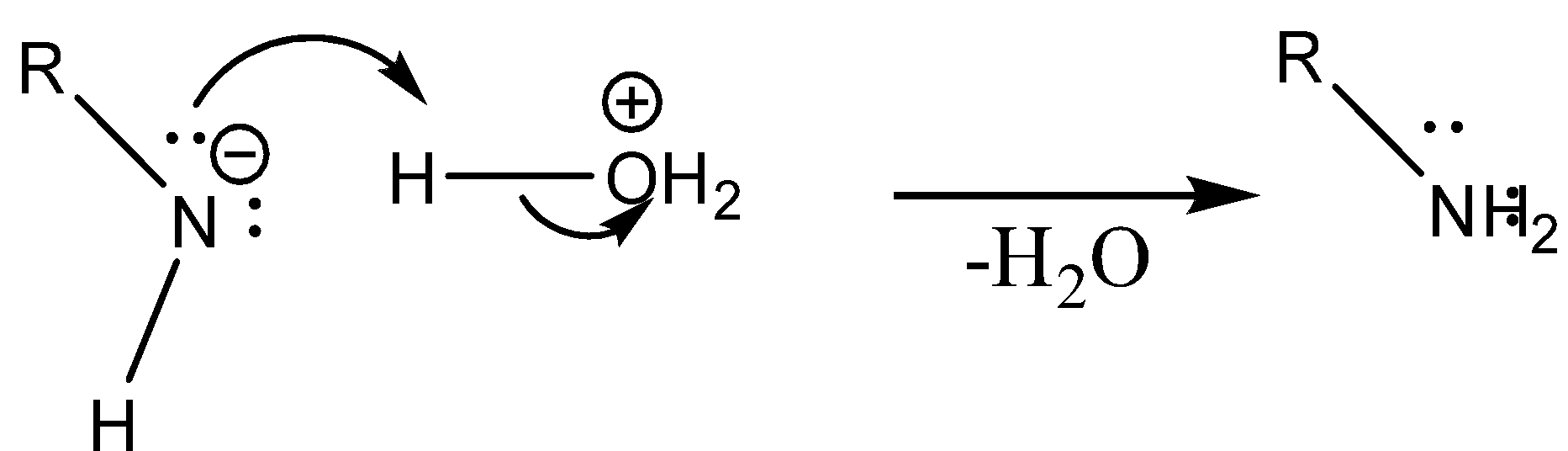
In this reaction the carbonyl group is removed due to which the number of carbon atoms in the product reduces by one. The amine group is then attached to the terminal carbon atom.
Case 2: Reaction in alcoholic solvent.
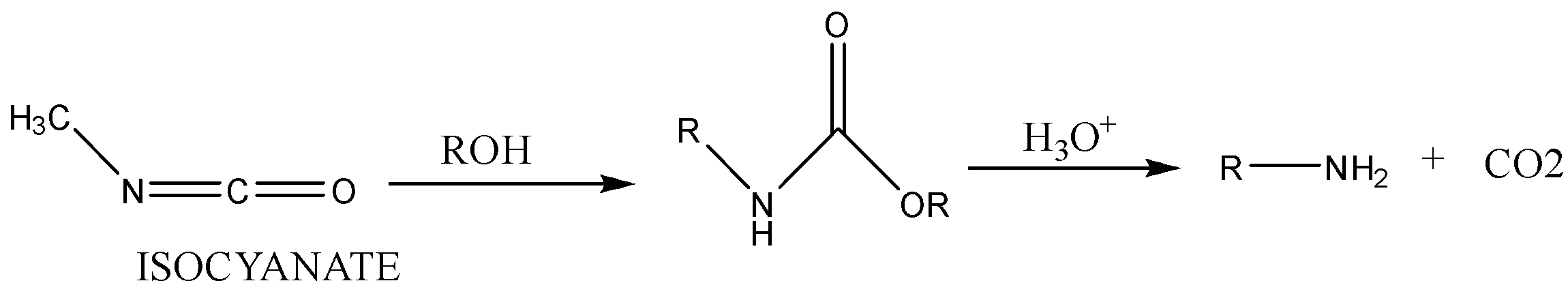
Note: This reaction involves a migration of alkyl or aryl groups from adjacent atom carbon atom to electron deficient nitrogen atom.
In this reaction the carbonyl group is removed due to which the number of carbon atoms in the product reduces by one. The amine group is then attached to the terminal carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
The curtius rearrangement is a reaction where acid chloride is converted to lower homologous amine.

Reaction with mechanism is as follows:
Step 1-The starting material in the reaction is the acid chloride. The acid chloride on reaction with sodium azide will produce acid azide. The reaction will be as follows:
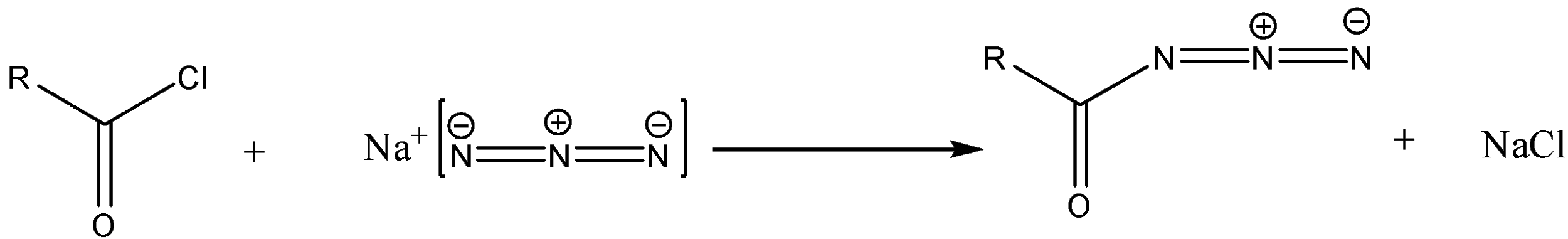
Step 2: The acid azide formed due to thermal decomposition then undergoes rearrangement thus releasing nitrogen gas and Isocyanate is formed.

Step 3: Isocyanate formed reacts in a different manner when different solvent is used. The reaction is carried out in aqueous or alcohol solution. Isocyanate gets converted to primary amine or urethane respectively.
Case 1: Reaction in Aqueous medium.
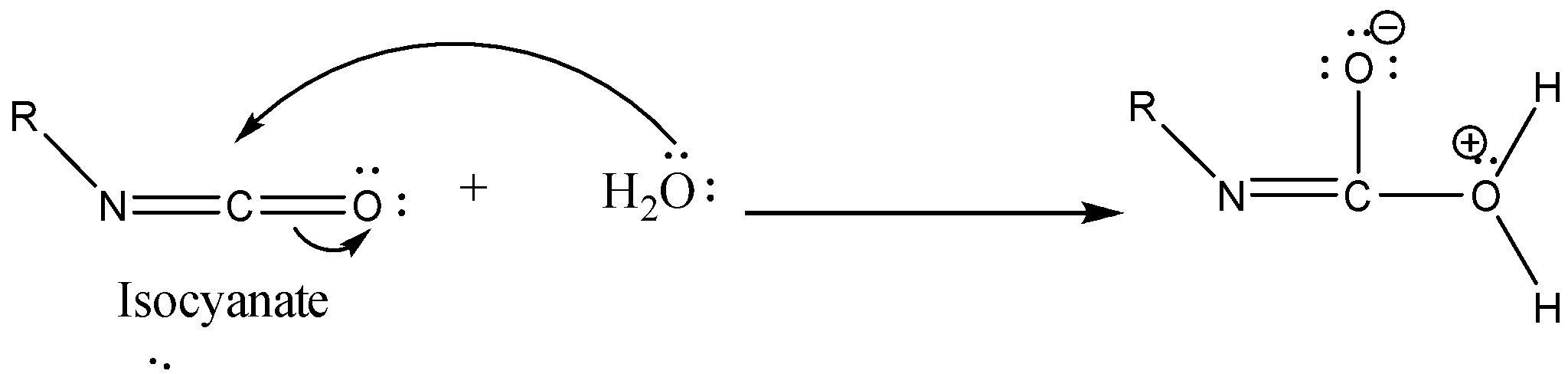




In this reaction the carbonyl group is removed due to which the number of carbon atoms in the product reduces by one. The amine group is then attached to the terminal carbon atom.
Case 2: Reaction in alcoholic solvent.

Note: This reaction involves a migration of alkyl or aryl groups from adjacent atom carbon atom to electron deficient nitrogen atom.
In this reaction the carbonyl group is removed due to which the number of carbon atoms in the product reduces by one. The amine group is then attached to the terminal carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




