
What is an example of random mating?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: Random mating is a phenomenon in population genetics in which mating is possible between any individuals belonging to the same species. It means that all members of one sex are possible matches for all members of the opposite sex. It is not influenced by any factors like genotype, physical structures or environmental conditions.
Complete answer:
Mating is an important concept in reproduction. For internal fertilization of male and female gametes, physical contact is necessary. Mating is the term used for this type of physical contact. Mating is also known as copulation or breeding.
Random mating is also known as Panmixia. The term ‘Panmixia’ is derived from the Latin word ‘pan-’ meaning all and the Greek root ‘-mixis’ meaning mixing/an act of mating. Random mating ensures that any male gamete of a species can fertilize any female gamete.
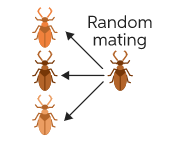
Let us consider the following example. In a population of beetles, the beetle chooses to mate with any member of the population irrespective of the external and internal conditions. This is known as random mating. Random mating is the opposite of assortative mating.
In nature, random mating is seen in populations of a green algae Monostroma latissimum, a burrowing bee Amegilla dawsoni, the American eel Anguilla rostrata etc.
Note:
Random mating is considered as an important concept in Hardy-Weinberg principle. Random mating can reinstate genetic equilibrium, when other evolutionary forces fail to operate. There are no mating limitations in random mating within a population. Random mating permits species to achieve genetic variation more readily through gene flow than monogamous species.
Complete answer:
Mating is an important concept in reproduction. For internal fertilization of male and female gametes, physical contact is necessary. Mating is the term used for this type of physical contact. Mating is also known as copulation or breeding.
Random mating is also known as Panmixia. The term ‘Panmixia’ is derived from the Latin word ‘pan-’ meaning all and the Greek root ‘-mixis’ meaning mixing/an act of mating. Random mating ensures that any male gamete of a species can fertilize any female gamete.
Let us consider the following example. In a population of beetles, the beetle chooses to mate with any member of the population irrespective of the external and internal conditions. This is known as random mating. Random mating is the opposite of assortative mating.

In nature, random mating is seen in populations of a green algae Monostroma latissimum, a burrowing bee Amegilla dawsoni, the American eel Anguilla rostrata etc.
Note:
Random mating is considered as an important concept in Hardy-Weinberg principle. Random mating can reinstate genetic equilibrium, when other evolutionary forces fail to operate. There are no mating limitations in random mating within a population. Random mating permits species to achieve genetic variation more readily through gene flow than monogamous species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




