
What is a Silver Nitrate Test?
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint: Before moving on with the description of the Silver Nitrate Test, we should know the aim of the Silver Nitrate Test. The main of the test is to find out which halogen is present in a suspected halogenoalkane. Once we know the aim of the Silver Nitrate Test, we can move to the detail of the process.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The most effective way to find the suspected halogenoalkane is to do a substitution reaction which turns the halogen into a halide ion, and then to test for that ion with silver nitrate solution.
The basic structure of silver nitrate is given below.
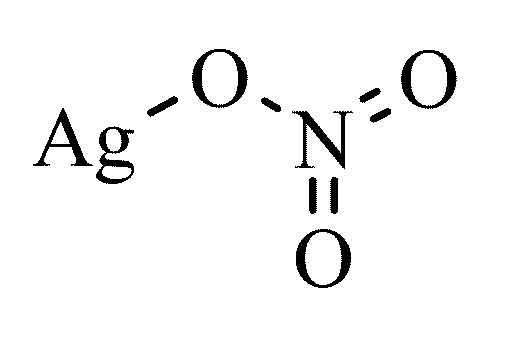
The solution is first acidified by adding dilute \[\text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] followed by silver nitrate solution.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]${{\text{F}}^{-}}\text{,C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}\text{,B}{{\text{r}}^{-}}\text{ }\!\!\And\!\!\text{ }{{\text{I}}^{-}}$ react as given below:
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+}{{\text{F}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgF}$ (No precipitate as it is soluble)
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgCl(s)}$ (white precipitate)
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+B}{{\text{r}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgBr(s)}$ (pale cream precipitate)
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+}{{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgI(s)}$ (pale yellow precipitate)
The precipitate is treated with \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] solution to confirm the halide. The following observation is done.
\[\text{AgCl }\to \] dissolves to give a colourless solution.
\[\text{AgBr}\to \] dissolves in conc. \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] to give a colourless solution.
\[\text{AgI}\to \] insoluble in \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] of any concentration.
The purpose of adding the dilute nitric acid is the removal of other ions that might also give a confusing precipitate with silver nitrate.
The purpose for the addition of ammonia is to form a complex ion with silver (I) ions which then allows the precipitate to redissolve.
Note: We should know that silver nitrate in as a compound is a prescription topical solution which is used for treating wounds and burns on the skin as an anti - infective agent.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The most effective way to find the suspected halogenoalkane is to do a substitution reaction which turns the halogen into a halide ion, and then to test for that ion with silver nitrate solution.
The basic structure of silver nitrate is given below.
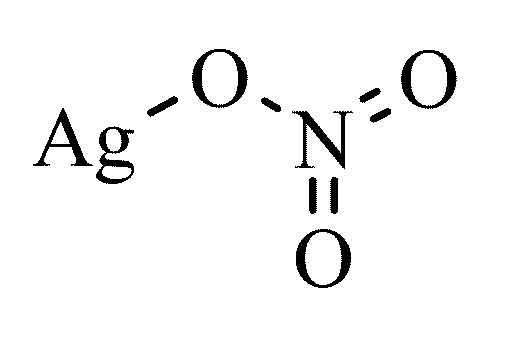
The solution is first acidified by adding dilute \[\text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] followed by silver nitrate solution.
\[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\]${{\text{F}}^{-}}\text{,C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}\text{,B}{{\text{r}}^{-}}\text{ }\!\!\And\!\!\text{ }{{\text{I}}^{-}}$ react as given below:
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+}{{\text{F}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgF}$ (No precipitate as it is soluble)
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+C}{{\text{l}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgCl(s)}$ (white precipitate)
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+B}{{\text{r}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgBr(s)}$ (pale cream precipitate)
$\text{A}{{\text{g}}^{+}}\text{(aq)+}{{\text{I}}^{-}}\text{(aq)}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{AgI(s)}$ (pale yellow precipitate)
The precipitate is treated with \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] solution to confirm the halide. The following observation is done.
\[\text{AgCl }\to \] dissolves to give a colourless solution.
\[\text{AgBr}\to \] dissolves in conc. \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] to give a colourless solution.
\[\text{AgI}\to \] insoluble in \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] of any concentration.
The purpose of adding the dilute nitric acid is the removal of other ions that might also give a confusing precipitate with silver nitrate.
The purpose for the addition of ammonia is to form a complex ion with silver (I) ions which then allows the precipitate to redissolve.
Note: We should know that silver nitrate in as a compound is a prescription topical solution which is used for treating wounds and burns on the skin as an anti - infective agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




