
What is a homocyclic compound?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint: Organic compounds can be classified on the bases of structure and function. Based on their structure they can be classified as acyclic and cyclic compounds. Cyclic compounds are further divided as heterocyclic and homocyclic compounds.
Complete answer:
Homocyclic compounds are those compounds that are ring structures and contain only carbon atoms within the ring.
An example of a homocyclic compound is benzene. Benzene is said to be a homocyclic compound because it contains six carbon atoms that are bonded together in a hexagonal ring, with a single hydrogen atom bonded to each of the six carbon atoms.
The structure of benzene is as follows:
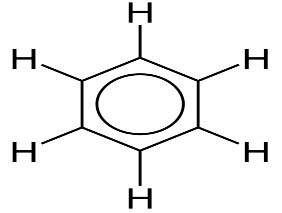
Benzene is a highly volatile and toxic compound. It is used in cleaning solutions.
Other examples are cyclohexane, toluene, cyclohexanol.
Homocyclic compounds are also known as carbocyclic compounds or carbocycles. The ring of the homocyclic compounds contains atoms of the same element.
Additional information: Homocyclic compounds are divided into two compounds. Alicyclic compounds and aromatic compounds.
Note:
Homocyclic and Heterocyclic compounds are composed of ring structures in which the atoms are bonded to each other forming an enclosed cyclic structure. The main difference between homocyclic and heterocyclic compounds is that homocyclic compounds are composed of rings made of atoms of the same element whereas heterocyclic compounds are composed of rings made of atoms of different elements. The different elements can be nitrogen, oxygen and Sulphur. Examples of heterocyclic compounds are pyrrole, furan and thiophene.Each has a single heteroatom.
Complete answer:
Homocyclic compounds are those compounds that are ring structures and contain only carbon atoms within the ring.
An example of a homocyclic compound is benzene. Benzene is said to be a homocyclic compound because it contains six carbon atoms that are bonded together in a hexagonal ring, with a single hydrogen atom bonded to each of the six carbon atoms.
The structure of benzene is as follows:

Benzene is a highly volatile and toxic compound. It is used in cleaning solutions.
Other examples are cyclohexane, toluene, cyclohexanol.
Homocyclic compounds are also known as carbocyclic compounds or carbocycles. The ring of the homocyclic compounds contains atoms of the same element.
Additional information: Homocyclic compounds are divided into two compounds. Alicyclic compounds and aromatic compounds.
Note:
Homocyclic and Heterocyclic compounds are composed of ring structures in which the atoms are bonded to each other forming an enclosed cyclic structure. The main difference between homocyclic and heterocyclic compounds is that homocyclic compounds are composed of rings made of atoms of the same element whereas heterocyclic compounds are composed of rings made of atoms of different elements. The different elements can be nitrogen, oxygen and Sulphur. Examples of heterocyclic compounds are pyrrole, furan and thiophene.Each has a single heteroatom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




