
What are free radicals?
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: A molecular species which contains an unpaired electron in its atomic orbitals is called the free radical. These are highly reactive as unstable species. Radicals are represented as $\text{ }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$.free radicals are rare species and can be synthesized in specific conditions.one of the common pathway for the generation of free radicals is a treatment of photo irradiation. For example, chlorine molecules generate chlorine radical as,$\text{ Cl}-\text{Cl }\xrightarrow{\text{h }\!\!\nu\!\!\text{ }}\text{ C}{{\text{l}}^{\bullet }}\text{ + C}{{\text{l}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$
Complete answer:
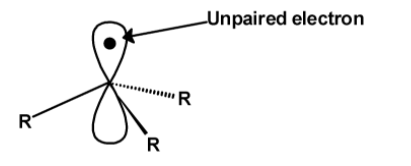
Free radical is defined as the neutral or the uncharged molecules which have high reactivity and have an unpaired electron in their orbitals. Free radicals are short-lived species. Free radical is generally represented as $\text{ }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$. All free radicals contain an unpaired electron.
Some of the properties of free radicals are as follows,
1. Free radicals are obtained in certain special conditions. Some of the free radicals are well familiar to us.
2. Most of the free radicals are unstable and reactive in nature.
3. Free radicals can either donate their unpaired electrons or accept an electron from other molecules thus they behave as oxidant or reductant.
4. Radicals are synthesized by the homolytic fission of bonds. In this bond fission, each atom forming a bond acquires single electrons and generates radicals.
$\text{ A}-\text{A }\to \text{ }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ + }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$
Radicals can be synthesized through various pathways. Some of the methods are redox reaction, ionization radiation (photochemical pathway $\text{ h}\nu \text{ }$ ), heat, electrical charge, electrolysis, etc.
-There are two types of radicals as sigma radicals and pi radicals.in sigma radical unpaired electron is in sigma orbitals for example phenyl radical, vinyl radical, etc. for pi radical unpaired electrons is in pi orbital for example t-butyl radical, etc. Pi radicals are stabilized by the resonance effect or hyperconjugation effect .However, sigma radicals do not have a stabilization effect hence they are more reactive.
Free radicals are used in the manufacturing of various polymers. Polyvinyl chloride is prepared by the polymerization reaction following a free radical mechanism that initiates the chain reaction. Alkoxy free radical initiates the polymerization reaction.
$\text{ R}-\text{O}-\text{O}-\text{R }\to \text{ 2 R}{{\text{O}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$
Note: Note that, free radicals are unstable thus to attain stability free radical attacks on the biomolecules and start a cascade of chain reaction. Free radicals are produced by the oxidation reaction. This damages the living cell. Thus we are advised to consume antioxidants which inhibit the oxidation. Some of the examples of antioxidants are vitamin C (ascorbic acid), vitamin E, etc.
Complete answer:
Free radical is defined as the neutral or the uncharged molecules which have high reactivity and have an unpaired electron in their orbitals. Free radicals are short-lived species. Free radical is generally represented as $\text{ }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$. All free radicals contain an unpaired electron.

Some of the properties of free radicals are as follows,
1. Free radicals are obtained in certain special conditions. Some of the free radicals are well familiar to us.
2. Most of the free radicals are unstable and reactive in nature.
3. Free radicals can either donate their unpaired electrons or accept an electron from other molecules thus they behave as oxidant or reductant.
4. Radicals are synthesized by the homolytic fission of bonds. In this bond fission, each atom forming a bond acquires single electrons and generates radicals.
$\text{ A}-\text{A }\to \text{ }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ + }{{\text{A}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$
Radicals can be synthesized through various pathways. Some of the methods are redox reaction, ionization radiation (photochemical pathway $\text{ h}\nu \text{ }$ ), heat, electrical charge, electrolysis, etc.
-There are two types of radicals as sigma radicals and pi radicals.in sigma radical unpaired electron is in sigma orbitals for example phenyl radical, vinyl radical, etc. for pi radical unpaired electrons is in pi orbital for example t-butyl radical, etc. Pi radicals are stabilized by the resonance effect or hyperconjugation effect .However, sigma radicals do not have a stabilization effect hence they are more reactive.
Free radicals are used in the manufacturing of various polymers. Polyvinyl chloride is prepared by the polymerization reaction following a free radical mechanism that initiates the chain reaction. Alkoxy free radical initiates the polymerization reaction.
$\text{ R}-\text{O}-\text{O}-\text{R }\to \text{ 2 R}{{\text{O}}^{\bullet }}\text{ }$
Note: Note that, free radicals are unstable thus to attain stability free radical attacks on the biomolecules and start a cascade of chain reaction. Free radicals are produced by the oxidation reaction. This damages the living cell. Thus we are advised to consume antioxidants which inhibit the oxidation. Some of the examples of antioxidants are vitamin C (ascorbic acid), vitamin E, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




