
______ was the first scientist who produced electromagnetic waves in a laboratory.
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint – You can start the solution by defining, who was the first scientist who produced electromagnetic waves in a laboratory. Then move on to briefly introduce the scientist and then move on to briefly explain the experiment he used with a simplified but well labelled diagram.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Michael Faraday was the first scientist who produced electromagnetic waves in a laboratory.
Michael Faraday, a name you might be already familiar with was an English scientist who was born in September, 1971. He is famously known for his contributions in the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Some of his important achievements include the discovery of the fundamental principle of electrolysis, electromagnetic induction and diamagnetism. The unit of capacitance i.e. Farad is named as such to honor Michael Faraday for his achievements.
Faraday in an experiment dated Aug 29, 1831 he created the first electromagnetic wave made in a lab.
For his experiment he wrapped two wires around the opposite sides of an iron ring. A simplified version of the apparatus that he used is shown below
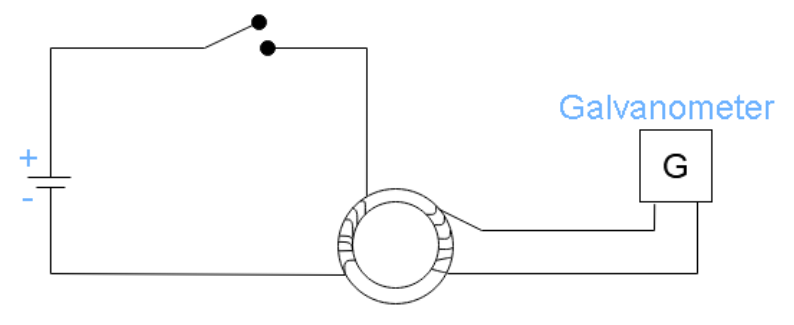
He observed the properties of electromagnets and based on his observation, he believed that as soon as the current starts to flow in the wire on one end, it will produce a sort of wave that carries energy as it travel to the wire on the opposite side and this would lead to an electrical effect (flow of electron or current) on the opposite side.
Note – Michael faraday further explained electromagnetic induction using a concept he liked to call the “lines of force”. This idea was mostly rejected back then because it had no mathematical calculations backing it. However this concept was accepted when it was brought to light by the work of James Clerk Maxwell, who used this idea as the foundation of his electromagnetic theory.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Michael Faraday was the first scientist who produced electromagnetic waves in a laboratory.
Michael Faraday, a name you might be already familiar with was an English scientist who was born in September, 1971. He is famously known for his contributions in the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Some of his important achievements include the discovery of the fundamental principle of electrolysis, electromagnetic induction and diamagnetism. The unit of capacitance i.e. Farad is named as such to honor Michael Faraday for his achievements.
Faraday in an experiment dated Aug 29, 1831 he created the first electromagnetic wave made in a lab.
For his experiment he wrapped two wires around the opposite sides of an iron ring. A simplified version of the apparatus that he used is shown below

He observed the properties of electromagnets and based on his observation, he believed that as soon as the current starts to flow in the wire on one end, it will produce a sort of wave that carries energy as it travel to the wire on the opposite side and this would lead to an electrical effect (flow of electron or current) on the opposite side.
Note – Michael faraday further explained electromagnetic induction using a concept he liked to call the “lines of force”. This idea was mostly rejected back then because it had no mathematical calculations backing it. However this concept was accepted when it was brought to light by the work of James Clerk Maxwell, who used this idea as the foundation of his electromagnetic theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




