
Very short answer type question: How you can define a food web?
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: The term food web refers to the interconnected food chains operating in an ecosystem that establishes a relationship between various species. A community that consists of living organisms and non-living things that interact as a system is called an ecosystem. Various processes such as primary production, energy flow, decomposition, and nutrient cycling is important for maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Complete answer:
The energy and nutrients in the ecosystem move through a chain called the food chain. The food chain is also referred to as the food web. Plants are at the basic stage which produces the energy. Plants are autotrophs that can produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. They make use of sunlight and carbon dioxide as a source of carbon to form an energy molecule called ATP.
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. Then this energy is moved to higher-level organisms called the herbivores. Herbivores can be referred to as an organism which feeds on plants only. The higher organisms after herbivores are carnivores which consume herbivores animals. Carnivores are called meat-eaters. Herbivores and carnivores are heterotrophs that feed on living organisms or dead material. The two categories of consumers are macro-consumers and micro-consumers.
Herbivores animals, carnivores animals, and detritivores belong to the group of macroconsumers. Omnivores also belong to the macro-consumer as they feed on both plants and animal matter. Mainly bacteria and fungi are included in micro-consumer which feed on dead protoplasm.
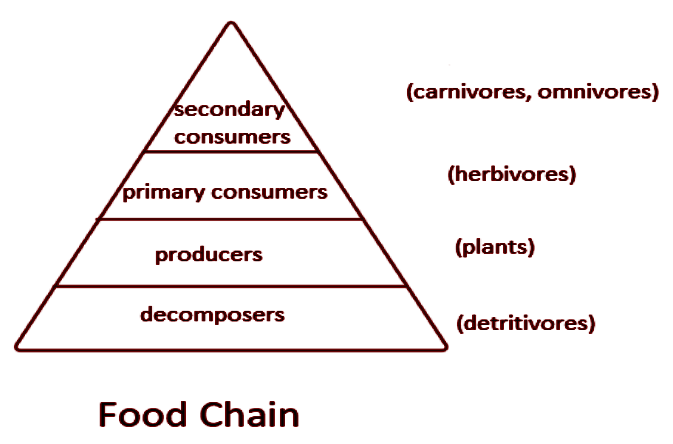
Note: The primary producers are placed at the base in the ecological pyramid. The detritivores are the invertebrate heterotrophic organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus. They play an important role in maintaining the fertility and moisture of soil in which the primary producers of plants grow.
Complete answer:
The energy and nutrients in the ecosystem move through a chain called the food chain. The food chain is also referred to as the food web. Plants are at the basic stage which produces the energy. Plants are autotrophs that can produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. They make use of sunlight and carbon dioxide as a source of carbon to form an energy molecule called ATP.
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate. Then this energy is moved to higher-level organisms called the herbivores. Herbivores can be referred to as an organism which feeds on plants only. The higher organisms after herbivores are carnivores which consume herbivores animals. Carnivores are called meat-eaters. Herbivores and carnivores are heterotrophs that feed on living organisms or dead material. The two categories of consumers are macro-consumers and micro-consumers.
Herbivores animals, carnivores animals, and detritivores belong to the group of macroconsumers. Omnivores also belong to the macro-consumer as they feed on both plants and animal matter. Mainly bacteria and fungi are included in micro-consumer which feed on dead protoplasm.

Note: The primary producers are placed at the base in the ecological pyramid. The detritivores are the invertebrate heterotrophic organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus. They play an important role in maintaining the fertility and moisture of soil in which the primary producers of plants grow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




